OPERATIONS ON NERVES
Neororrhaphy, neurolysis (allocation of nerves from the cicatrical tissue) and plasty refer to regenerative operations on peripheral nerves of extremities. The basic indication of these operations is damage. Soft tissues, blood vessels are injured usually during damaging of nerves, there is fracturing of bones.
Nerves of the upper extremities are damaged 1,5 times more often than nerves of the lower extremities.
Damage of nerves is divided into open and closed depending on the condition of the external environment (epineurium). Concussion, injury, compression, dislocation, stretching of nerves refers to closed damages.
Open wounds are accompanied not only by the damage of the epineurium, but also infringement of continuity of axons.
Thus, in injured nerves two processes develop at the same time: degeneration in the peripheral department; and neogenesis in the central department. The central neuroma thickening is formed on the central end of the damaged nerve as a result of inexpedient neogenesis if during neogenesis axons cannot find appropriate empty Shwann’s environments of the distal part of the nerve.
The rate of axon growth in the central part of a nerve into the peripheral end is 1-1,5 mm in a day.
Demands of a neurorrhaphy:
1. Exact compression of nervous fibres fascicles;
2. Nonprojective access (access at 1-2 cm from the nerve projective line);
3. Distance between the ends of the nerve (diastases) up to 1 mm;
4. Suture should pass only if the epineurium is captured
NEURORRHAPHY
It is a nerve stitching operation. Indications are a complete break of a nervous trunk and absence of muscle contraction during examination of electro excitability in a place above a cicatrix. There are primary and delayed neurorrhaphy (early and late). Primary neurorrhaphy is made at the same time with a primary surgical treatment of a wound.
STAGES OF THE OPERATION
- Access. Consists of level-by-level dissection of tissues. Usually access is carried out at a distance of 1-2 cm from the projective line of a nerve.
- Mobilization. Consists of allocation of a nerve from vessels, nerves, muscles near it. This stage of the operation can be called neurolysis if the nerve is involved in the cicatrical tissue.
- Neurorrhaphy. The ends of a damaged nerve excise till there is bleeding from the nerve vessel. Nerve ends are matched to the exact. 3-4 epineuria sutures are imposed. Sutures are tightened till there is easy contact of ends or until there is a distance of up to 1 mm between ends.
- Level-by-level wound suturing and immobilization of the extremity for 2-3 weeks.
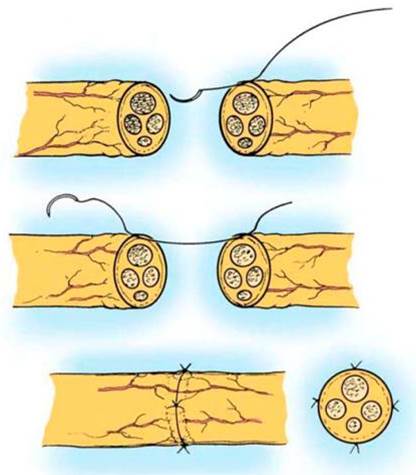
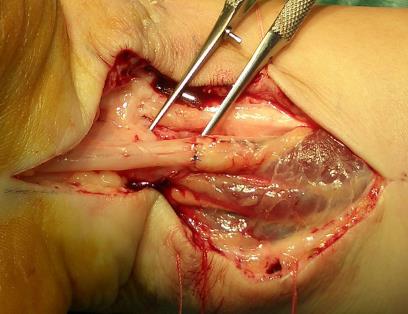
Fig. 17. Transepineurium of the nerves sutures.
NEUROLYSIS
Neurolysis is an operation of mobilization from cicatrical tissues. This operation is carried out better by using an operative microscope. Neurorrhaphy is made during damage of a nerve.
There are internal and external neurolysis.
External neurolysis – is mobilization of a nerve from the cicatrical tissue, placing it over a nerve trunk and causing its compression to be crushed and connected with its functional disorders.
Internal neurolysis – is excision of scars that penetrate into the trunk between its fascicles.
Дата: 2019-03-05, просмотров: 440.