FEMORAL TRIANGLE, FEMORAL CANAL, ADDUCTOR CANAL
GLUTEAL REGION
The gluteal region is limited: superiorly by crista iliaca, inferiorly by sulcus gluteus, medially by the middle area od the sacral bone, laterally by the line that joins the spina iliaca anterior superior to the trochanter major of the femur.
The layer-by-layer composition of the region: skin, subcutaneous fatty layer, superficial and proper fascias (fascia glutea).
The muscles of the gluteal region are located in three layers:
1 layer- m. Gluteus maximus, 1/3 of m. Gluteus medius
2 layer- 2/3 of m. Gluteus medius, m. Piriformis, m. Gemilli, m. Obturatorius internus, m. Quadratus femoris,
3 layer- m. Gluteus minimus, m. Obturatorius externus.
M. piriformis divides the major ischiadic foramen into 2: foramen suprapiriformis and foramen infrapiriformis. Foramen suprapiriformis is limited superiorly by m. Gluteus medius and inferiorly by m. Piriformis. Through the foramen suprapiriformis passes the superior neuro-vascular bundle a.v.n. gluteus superior. Foramen infrapiriformis is limited superiorly by m. Piriformis and inferiorly by m. Gemelli. Through the foramen infrapiriformis passes three neuro-vascular bundles. Inferiorly - a.v.n. gluteus inferior; inferio-medially - a.v. pudenda interna, n. pudendus; inferio-laterally- n. ischiadicus, a.v. comitans n. ischaidicus, n. cutaneous femoris posterior.
ARTICULATIO COXAE
The hip joint is formed by the facies lunata os the acetabulum of the pelvic bone and the femoral head.
The articulation consists of two intra- articular ligaments: lig. Transversum acetabuli and lig. Capitis femoris.
The external ligaments of the joint, which corresponds to the three axes of rotation are: 3 longitudinal (lig. Iliofemorale, pubofemorale and lig. Ischiofemorale) and circular (orbicular zone).
FEMORAL REGION
The femoral region is limited superiorly in the front by inguinal ligament, posteriorly above by the gluteal fold: iferiorly by the circular line which passes at the level two transverse fingers above the patella.
The layer-by layer structure of this region: skin, subcutaneous fatty layer, superficial fascia, the proper fascia (lata fascia). In the subcutaneous fatty layer arre located: v. Saphena magna, n. cutaneous femoris anterior (n. femoralis), n. cutaneous femoralis medialis (n. obturatorius ), n. cutaneous femoris lateralis (plexus lumbalis), ramus femoralis (n. genitofemoralis), n. cutaneous femoris posterior (plexus sacralis).
ANTERIOR FEMORAL REGION:
The main neuro-vascular bundle of the region in the upper thirds of the femur is a.v. femoralis et n. femoralis. In between the inguinal ligament and the bones of the pelvis is located the lacuno musculorum and lacuna vasorum. Lacuna musculorum is limited superiorly by the inguinal ligament, inferiorly by the ileal bone, medially by the iloiopectineal arch. Lacuno vasorum is limited superiorly by the inguinal ligament, laterally by the iliopectineal arch, inferiorly by lig. Pectineale, medially by lig. Lacunare. Through the lacuna vasorum passes a.v. femoralis.
FEMORAL CANAL:
In the medial corner of the lacuna vasorum is located the cellulose, through which protrudes the femoral hernia. In this case, a femoral canal of length 1-2 cms is formed. The femoral canal has an internal ring, external ring and a wall.
The internal ring is limited: superiorly by inguinal ligament, laterally by v. Femoralis, inferiorly by lig. Pectineale, medially by lig. Lacunare.
The external ring- this is the hiatus saphenus on the superficial lamina of the fascia lata, through which normally passes v. Saphena magna
The walls of the canal are formed laterally by v. Femoralis, anteriorly and posteriorly by superficial lamina and deep lamia of the fascia lata.
FEMORAL TRIANGLE:
The femoral triangle is limited superiorly by lig. Inguinale, laterally by m. Saratorius, medially by m.adductor longus. The fundus of the triangle is covered by two muscles: m. Pectineus and m. Iliopsoas.
In the triangle, below the inguinal ligament in the upper third of the femur passes: v. Femoralis medially, a. Femoralis laterally, and n. femoralis more laterally.
In the lower thirds of the femur is located medially n. saphenus, laterally- a. Femoralis and more laterally and deeply- v. Femoralis.
ADDUCTOR CANAL (GUNTER’S):
In the lower third of the femur, n. saphenus, a. Femoralis and v. Femoralis enter the adductor canal through its upper foramen. The canal is limited laterally by vastus medialis of m. Quadriceps femoralis, medially by m. Adductor magnus, anteriorly by lamina vasoadductoria, on which lies m. Sartorius. Through the anterior foramen of the canal passes n. saphenus and a.v. genus descendens (a.v. femoralis). Through the inferior foramen of the canal in the popliteal fossa passes the a.v. poplitea (a.v. femoralis).
A. FEMORALIS is the continuation of a.iliaca externa. On the femur it passes through the sulcus ileopectineus, and then through the sulcus femoris anterior and then through the adductor canal enters into the popliteal fossa, where the a. Poplitea is located. To stop the bleeding from a. Femoralis, we can apply pressure under lig. Inguinale to the pubic bone.
The branches of a. Femoralis:
A) Superficial (subcutaneous):
1. a. Epigastrica superficialis
2. a. Circumflexa ileum superficialis.
3. a. Pudenda externae
B) Deep (primary):
4. a. Profunda femoris
Branches of a. Profunda femoris:
a) a. Circumflexa femoris medialis
b) a. Circumflexa femoris lateralis , divides into ramus ascendens and ramus descendens.
c) aa. Perforantes
5. r. Musculares
6. a. Genus descendens.
POSTERIOR FEMORAL REGION
The primary neuro vascular bundles of the region are n. ischiadicus and a.v. comitans n. ischiadici. N. ischiadicus is located between m. Semitendinosus, m. Semi membranosus and m. Biceps femoris. N. ischiadicus in the lower third of the femur divides into n.tibalis and n. peroneus communis.
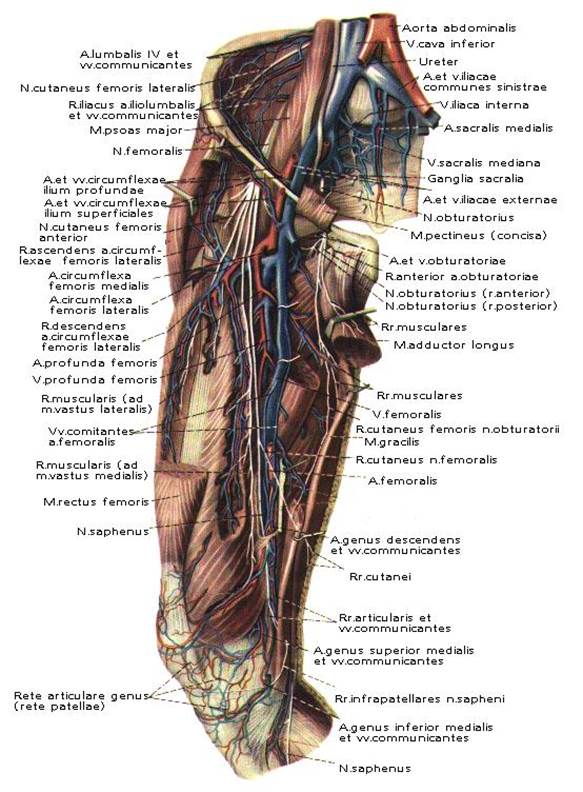
Fig. 10. Topography of regio femoris anterior.
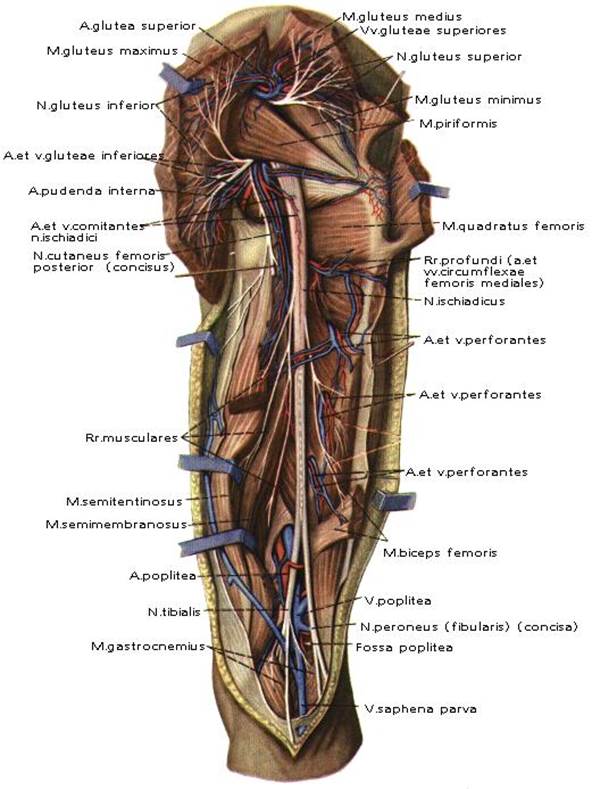
Fig.11. Topography of regio femoris posterior.
ЗАНЯТИЕ № 4.
Дата: 2019-03-05, просмотров: 842.