Purulent processes of hand fingers are called panaritiums. Sup-purative processes usually spread into deep tissues and affects tendons, bones and interphalageal joints. The most severe type of panaritium which is life threatening and affects the function of the hand is the purulent lesion of synovial vagina membranes of flexor tendons of fingers. Panaritiums are divided into: dermal, hypodermic, tendonous (tendovaginalis), articular, osteal, paronychial, pandactylitis etc.
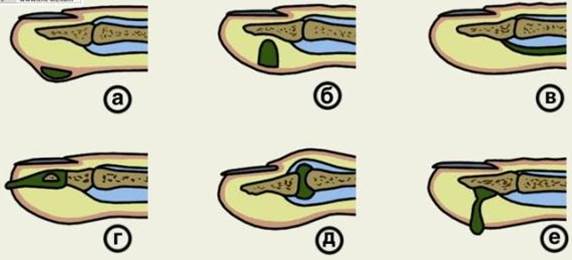
Fig 23. Types and localization of the panaritiums.
а - dermal, б - hypodermic, в - tendinous, г - paronychial, д - articular, е - osteal
Purulent diseases of the hand: intermuscular phlegmon of the thenar, intermuscular phlegmon of the hypo thenar, comissural phlegmon (a corn abscess), phlegmon of the medial Palm space (supra- and subtendinous), U-shaped phlegmon, supra- and Subaponeurotical phlegmon of the back of the hand, furuncles of the dorsal surface of the hand.
In hypodermic panaritium of the nail and medial phalanges, hyponychial panaritium and paronychia the operation is performed under block anaesthetic of Oberst-Lykachevich. The preliminary application of tourniquet at the base of the finger prevents bleeding, careful treatment of the wound and careful removal of necrotizing tissues.
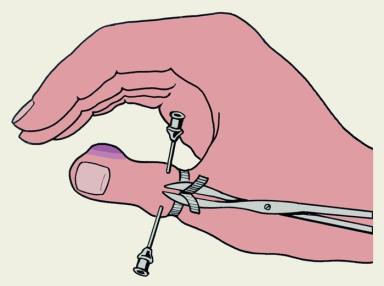
Fig 24. Oberst-Luckashevich`s Block anesthesia.
In severe forms of panaritiums (tendonous, pandactylitis), phlegmons of the hand and the phlegmon of Pirogov space the operation is performed under intravenous anaesthetic.
Depending on the spread of the purulent process linear, uni- and bilateral incisions are made.
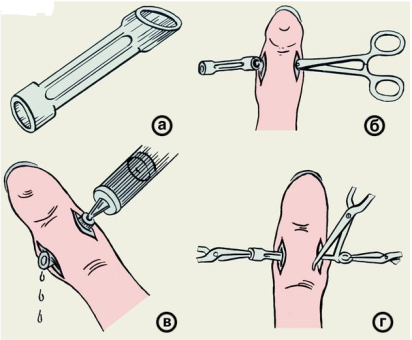
Fig 25. Panaritium drainage.
In most cases, except for for derma, hyponychial panaritium and dermal Palm abscess, the operation is completed with the drainage of the wound. For this purpose the rubber fenestrated tube is used, which allows treatment of the Purulent site with solutions of antiseptic agents or proteolytic enzymes leading to fast discharge of pus, decreased pain, rejection of necrotic tissue and fast wound healing.
In dermal and hyponychial panaritium only the detached part of the epidermis or the nail plate is excised, the wound is treated with 3% Hydrogen peroxide solution; the skin around the wound is treated with alcohol.
To open the tendon sheath, the intermittent unilateral and double linear-side incisions are made in the middle and proximal phalanges. The drainage of the tendon sheath is performed with fenestrated tubes in transversal direction above the tendon to avoid injuring its mesentery. In U-shaped phlegmons the drainage of vaginal synovial membranes of I, II fingers and Pirogov- Paron space is performed.
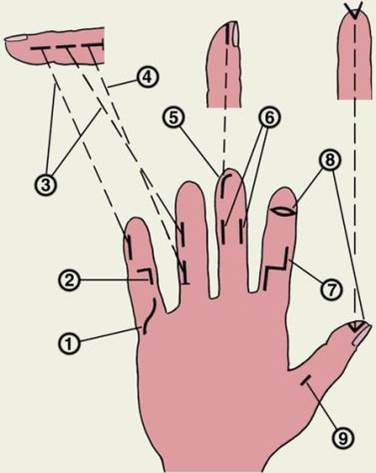
Fig 26. 1, 2, 7 - a surgical incision is made on the palmar surface of the hand
3, 4, 6, 9 – mid-lateral incision
5 – hockey stick-shaped incision
8 – ellipsoidal incision
In bone-articular panaritiums the double linear-side incisions are made, the purulent-necrotic cavity is opened and treated. Necrotic tissues and sequesters are removed, the affected bone is resected; the fenestrated-tube drainage is applied. In pandactylitis of II-V fingers the exarticulation of the finger is usually performed to prevent the generalization of the infection and to eliminate the purulent process when other kinds of therapy prove to be ineffective. In pandactylitis of the 1st finger such intervention should not be rushed upon, as even having lost its flexion-extension movement, the thumb keeps its antagonist function, without it the practical activity of a person is considerably reduced.
In deep phlegmons of the hand the incision is made according to anatomic features, and flow-rising drainage is performed through additional incisions.
PUNTURE OF JOINTS
Puncture of joints are performed in order to see the state of the contents of the joint cavity (blood, pus), to remove the pathological fluid, to apply antibiotics.
To anasthetize the zone of puncture, 0, 5% Novocaine solution is injected with a fine needle. Before the punture of the joint the tools are prepared, the surgeon’s arms and the operation room is treated like in most common types of operations. It is necessary to remember that joints are susceptible to infections as the articular fluid can serve as a medium for growth of microflora, therefore the inflammation of joint is often associated with septic effects.
Skin on the place of puncture is shifted aside to get the curve of the wound canal when the skin returns to its place after the puncture. A thick needle (sometimes even a thin trocar) is introduced into the joint cavity. When the needle reach the joint the resistance noted during passage of the needle through soft tissues diminishes. After the removal of the needle the place of puncture is covered with collodium or plaster.
Дата: 2019-03-05, просмотров: 898.