The purpose of these operations is removing sharp pains, decreasing or completely stopping muscle tone.
Neurotomies, neurotripsy, neuroectomy, neuroexeresis, resection of a nerve are referred to as those operations.
The neurotomy is crossing of a nerve.
The neurotripsy is crushing of a nerve (hemostatic clamps may be used for compression of a nerve).
The neuroectomy is removal of a nerve.
The neuroexeresis is extraction of a nerve.
The resection of a nerve is removal of a part of a nerve.
OPERATIONS DURING BIG DIASTASES (DEFECTS)
OF PERIPHERAL NERVES
Surgical treatment of nervous trunk injury is difficult during big defects. Nerve diastases of up to 4 cm are liquidated by suturing nerve pieces together without application of additional complex actions. Replacement of nerve defects of 12-20 cm without using special receptions is impossible. Two methods are applied here: rapprochement of nerve ends and plastic replacement.
1. Rapprochement of nerve ends is reached by mobilization of the nervous trunk to a long extent and changing of extremity position (flexion – extension in a joint or in combination with extension of nerves).
2. Rapprochement of nerve ends may be carried out by changing the topography-anatomic position of the nerve (during big diastases). This allows the nerve suturing of defects of 10-11 cm.
3. Rapprochement of nerve ends is reached with the help of bone resection if bone trauma and nerve defect have occurred at the same time (on upper extremity).
PLASTIC METHODS OF NERVE DEFECTS REPLACEMENT
1. Peripheral part of the nerve is split and the formed flap sutured to the central part during flap plasty. This flap serves as prosthesis for the growth of the central part on the periphery.
2. Plasty of nerve defect and its branches that don't have a great value and departing above the defect.
3. Nerve tubulisation is the connection of nerve ends by various tubes (gelatinous, agaric, pieces of veins).
4. Method of transplantation of a free nerve (autoplasty). The method is not widely spread and is not used now.
5. Method of dermal nerves transplantation and their suturing to the central end of the injured nerve.
OPERATIONS ON TENDONS
Damage of tendons leads to functional disorders of extremities which are eliminated only by surgical operations.
The most common type of operation on tendons is tendon suturing.
Suturing of a tendon, J.J. Dzhanelidze, especially during operations of the hand and forearm are carried out as follows:
1. To grasp the minimal amount of tendon fascicles.
2. To provide a smooth, slippery surface on the tendon.
3. Don't suppose garneting of tendon.
4. Don't compress the vessels supplying the tendon.
Primary and secondary sutures of tendons are distinguished in dependence on the operation time after trauma. Initial suturing is made – during the first 6-8 hours after trauma on clean surfaces and a small zone of soft tissues that are damaged.
Secondary suture is imposed after wound repair with first intentions of within 2-3 weeks. If the wounds were purulent, the operation is postponed to the 3-4th months.
Tendons sutures are classified into 4 groups according to the location of the strings and knots.
1. Strings and knots outside (on the tendon surface).
2. Strings inside, knots outside.
3. Strings and knots inside.
4. Other.
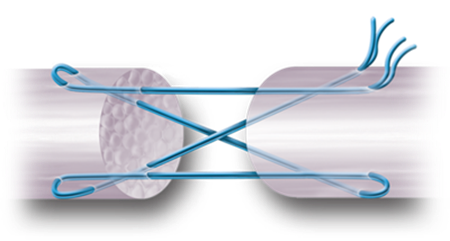
Fig. 18. Strings inside, knots outside.
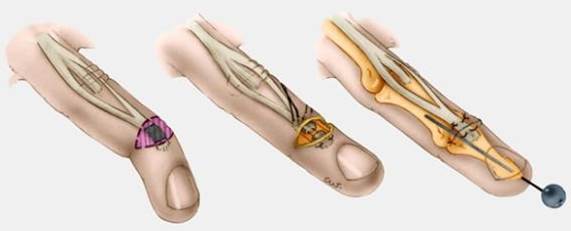
Fig. 19. Other group.
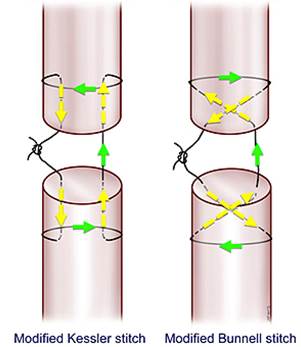
Fig. 20. Strings and knots inside
STAGES OF THE OPERATION
1. Access. Extra projective access is usually at 1-2 cm from the tendon projective line.
2. Mobilization or tenolysis which involves a tendon in cicatrical tissue.
3. Tenosuture. The ends of the damaged tendon are excised. Special tendon suture is imposed.
4. Level-by-level suturing of wounds and immobilization of extremity.
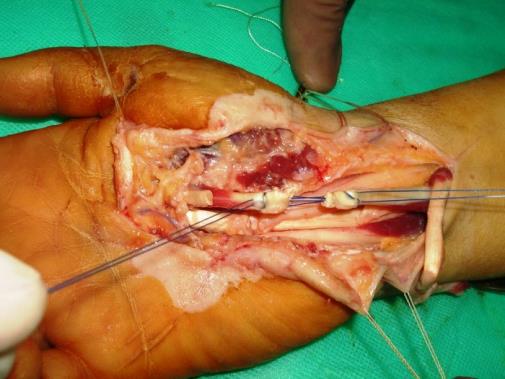
Fig. 21. Operations on tendons
PLASTIC OPERATIONS
Plastic operations are the most common types of operations on tendons which consist of elongation or shortening of tendons, transplantations and moving of a tendon.
Elongation or shortening of tendons without infringement of its continuity is made with the purpose of improvement of muscle function.
Elongation of tendons is carried out with the help of a Z-shaped dissection of the tendon in the sagittal or frontal plane with the subsequent suturing of tendon ends. Other sections are rarely applied to elongation of tendons, such as slanting, three and four-stage, transversal and their various combinations.
Shortening of tendons is made by its resection on extent or formation of dublication.
TENDON TRANSPLANTATION
Tendon transplantation serves mainly for the correction of unsuccessful tendon sutures and for replacement of large defects. Pieces of tendons taken in the operation are material for autoplastic replacement of tendon defects.
MOVING OF A TENDON
It is applied for replacement of muscles that have lost their function because of neighboring healthy muscles. So tendons of functioning muscles are cut entirely from the place of attachment and moves in a new bed.
Tenotomy – is an operation of tendon section. This operation is made for elimination of the excessive draft of muscles.
Tenolysis – is an operation consisting of tendon mobilization from cicatrical solderings with surrounding tissues.
Tenodesis – is fixation of one or several tendons of paralysed muscles subperiostalis (tenoperiosteodesis) or in specially prepared osteal canal (tenoosteodesis).



Fig. 22. Operations on tendons
|
|
|
Дата: 2019-03-05, просмотров: 753.