Протезирование коленного сустава или эндопротезирование, это хирургическая операция, при которой суставные поверхности коленного сустава замещаются протезами из металла. Показанием к операции является остеоартрит, а также другие заболевания, такие как ревматоидный артрит и псориатический артрит.
LECTURE 9
Amputations.
Amputation of an extremity dissecting along the length of the bone. The indications for amputation are non-vital extremity (complete abruption of an extremity, extensive crushing damage of tissues, damage of vessels and nerves), progressing infection (mainly anaerobic), gangrene of an extremity, burns, frost bites etc. Reamputations are performed in defects of an amputated stump, interfering its function and prosthetic treatment.
The degree of amputation is done according to line of vital tissues and by the degree of the destruction of the bone. The amputation of upper extremities should be performed in best economic way. Amputations are performed using tourniquet, except for amputations in patients with atherosclerosis or oblitering endarteritis.
When making an incision bear in mind of the future prosthetic treatment. The end of the stump shouldn't have scar. To prevent defective stump, the muscles are dissected 4-5cm distally from the bone being cut since muscles contract after dissection. Arteries and veins are lighted, large arteries are sutured. Hemostasis is done carefully. Nerves are cut using a razor 4-5cm above the end of the stump. The soft tissues are sutured in layers forming the scar mobile and away from the place of future contact with prosthesis. For the upper extremity such place is the palmar surface, for the lower extremity- the front surface of a stump. Depending on the type of incision on soft tissues the amputations are divided into: circular (guillotine, one staged, two staged, three staged), flapped (one flapped, two-flapped) and osteoplastic.
Guillotine amputation
All soft tissues and bones are dissected on the same level. Such amputations are performed quickly, enabling the control of infections especially anaerobic, allows saving the maximum length of an extremity. A disadvantage of operation is formation of defective stump due to contraction of soft tissues and exposure of the bone, the process of healing takes a long, terminal osteomyelitis may develop. Therefore this amputation is performed seldom to prevent the development of an infection.
One--staged amputation
One-staged amputation involves circular dissection of skin, subcutaneous fat and fascia and subsequent dissection of muscles and bone above the incision.
Reamputation is always indicated after one-staged amputation to form full functioning stump.
Two-staged amputation
The skin, subcutaneous fat and fascia are dissected, then the muscles are dissected at the level of the skin, drawn off in a proximal direction and the bone is sawn at the level of where muscles were drawn off. Another technique of this operation is the amputation of the forearm in its lower third using the cuff. The circular dissected skin, subcutaneous fat and fascia are separated simultaneously in a cuff and turned back in proximal direction.
Three-staged cone-circular Pirogov amputation of a hip
The skin, subcutaneous fat and are dissected with a circuit the lower third of hip. The muscles are dissected to the bone along the contracted skin. The repeated incision of deep muscles to bone is done along the edge of soft whia re then drawn in proximal direction, and then the bone is sawn.
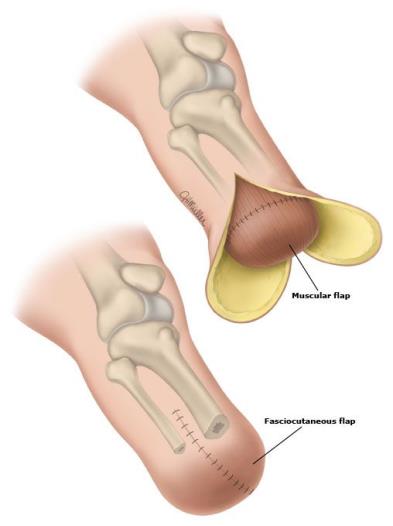
Fig 35. Technique of below-knee amputation with skew flap
Flapped amputation
For this kind amputation one or two flaps maybe performed. For one-flapped method the length of the skin flap should be equal to the diameter of an extremity on the level of amputation that is 1/3 of the circle. For two-flapped method one of the flaps is made longer than the other. Their total length should be equal to the diameter. It is necessary to add several cm to allow skin contraction. Skin contraction on the flexor surface of an extremity is more on the extensor surface. The flap may consist of skin with subcutaneous fat (dermal flap) or may include skin with muscles (myosplastic flap), skin with tendons (tendoplastic flap), and skin with muscles, periosteum and bone (osteoplastic).
The technique of any amputation includes four stages:
1 stage - of soft tissue dissection. To one of the methods mentioned before
2 stage - dissection of periosteum and bone sawing
a) Periosteal-on the periosteum level
b) Aperiosteal- 2-5mm below periosteal level (in osteoplastic operations)
c) Subperiosteal-sawing the bone with subsequent closing of bone-saw line with periosteum ( in children)
3 stage- ligation of all the vessels and truncation of nerves 4-5cm above the level of amputation
4 stage- formation of stump acc to of the methods mention

Fig 36. Flapped amputation
Дата: 2019-03-05, просмотров: 405.