АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК
Учебное пособие
Йошкар-Ола
2019 год
УДК 811:61
ББК 5
К 92
Печатается по решению педагогического совета
ПОО ЧУ «Столичный бизнес колледж»
Ответственный редактор – Н.С. Бастракова
Рецензенты:
Лапочкина Е.В. – кандидат педагогических наук, доцент ФГБОУ ВО «ИвГМА Минздрава России».
Серебрякова М.А. – кандидат педагогических наук, доцент ФГБОУ ВО «Марийский государственный университет».
Купцова О.Г.
К 92 Английский язык: учебное пособие / О.Г. Купцова. – Йошкар-Ола, 2018. – 209 с.
Учебное пособие по дисциплине «Иностранный язык (английский)» предназначено для студентов средних профессиональных образовательных организаций медицинского профиля очной и очно-заочной форм обучения. Парамедицинское содержание материалов пособия позволяет использовать его для аудиторной и самостоятельной работы студентов, обучающихся по специальностям «Сестринское дело», «Лечебное дело», «Акушерское дело». Специфика специальностей может быть учтена в дополнительных дидактических материалах преподавателя. Основная цель пособия – формирование коммуникативной компетенции: создание прочной языковой подготовки, на основе которой возможно дальнейшее совершенствование навыков и умений чтения и перевода англоязычной литературы, развитие диалогической и монологической речи по вопросам специальности. Пособие построено по тематическому принципу и включает в себя широкий спектр разделов профессионально-ориентированной направленности. Все тексты и работа над ними являются подготовкой студентов к самостоятельному чтению и пониманию оригинальной медицинской литературы и к устному общению на английском языке в пределах изучаемой тематики. Пособие так же может быть рекомендовано для обучающихся 10-11 классов профильной направленности общеобразовательных организаций, студентов высших образовательных организаций медицинского профиля для самостоятельного изучения или подготовки к конкурсам и олимиадам.
Оглавление
Unit 1. Тело человека
Unit 2 . Скелет
Unit 3 . Системы организма
Unit 4 . Внутренние органы
Unit 5 . Режим питания. Витамины
Unit 6 . Всемирная организация здравоохранения
Unit 7 . Система здравоохранения в Великобритании
Unit 8 . Гиппократ.
Unit 9 . История сестринского дела и медицины
Unit 1 0 . Профессия медицинской сестры
Unit 1. Human body
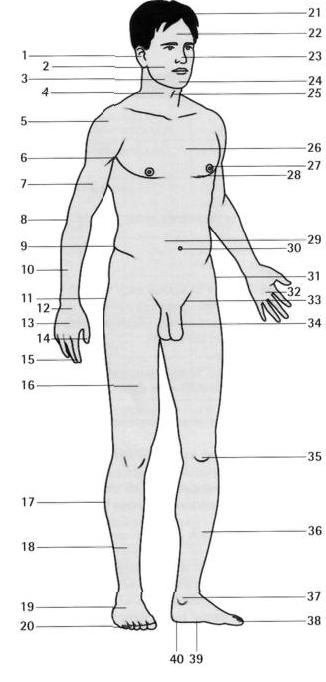
Ознакомьтесь с таблицей, прочитайте и переведите основные части тела человек. (P, p.12)
Most external parts of the body have ordinary English names as well as anatomical names. Doctors normally use the English names, even when talking to each other.
|
| |
| 1 eаr 2 check 3 jaw (mandible) 4 neck 5 shoulder 6 armpit (axilla) 7 upper arm 8 elbow 9 loin 10 forearm 11 buttock 12 wrist 13 hand 14 thumb 15 finger 16 thigh 17 calf 18 leg 19 foot 20 toe 21 hair 22 forehead 23 nose 24 chin 25 Adam’s apple (laryngeal prominence) 26 chest (thorax) | ||
| 27 nipple 28 breast 29 stomach, tummy, belly (abdomen) 30 navel, belly button (umbilicus) 31 hip 32 palm 33 groin (inguinal region) | 34 genitals (penis and testicles) 35 knee (patella = kneecap) 36 shin 37 ankle 38 big toe 39 sole 40 heel | |
NB: Limb means arm (upper limb) or leg (lower limb). The trunk is the body excluding the head and limbs
In the practical anatomy class we study the human body. The principal parts of the human body are the head, the trunk and limbs (extremities). We speak of the upper extremities (arms) and of the lower extremities (legs).
The head consists of two parts: the skull, which contains the brain and the face, which consists of the forehead, the eyes; the nose, the lips, the cheeks, the ears and the chin. The ear includes three principal parts: the external ear, the middle ear and the internal ear.
The mouth has two lips: an upper lip and a lower lip. In the mouth there are gums with teeth, a tongue and a palate. The head is connected with the trunk by the neck. The upper part of the trunk is the chest and the lower part is the abdomen. 'The principal organs in the chest are: the lungs, the heart and the gullet (esophagus) .We breathe with the lungs. The heart contracts and makes about 60-80 beats per minute.
The heart regulates the rate at which the blood circulates and also gives direction to the blood flow. You can strengthen your heart, protect it from disease by exercises and regular regimen. Take your pulse and in such a way you can control the work of your heart.
About 5 litres of blood fill our arteries, veins, capillaries. Due to the oxygen content it is of a bright red colour when it flows from the arteries and due to the waste products it is of a dark red colour when it flows from the veins. Arteries carry blood from the heart, veins carry blood to the heart.
The blood corpuscles are erythrocytes, leucocytes and blood-platelets. The function of erythrocytes is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and aid in the transport of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. Leucocytes play a very important part in the protection of the body against disease. The function of the blood-platelets is to start the coagulation of blood and to stop bleeding.
The principal organs in the abdominal cavity are the stomach, the liver, the spleen, the intestines, the kidneys, the gall-bladder and the bladder. The framework of bones called the skeleton supports the soft parts and protects the organs from injury.
The upper extremity is connected with the chest by the shoulder. Each arm consists of the upper arm, the forearm, the elbow, the wrist and the hand. We have four fingers and a thumb on each hand.
The lower extremity (the leg) consists of the hip , the knee, the calf, the ankle and the foot. The body is covered with the skin.
Word-box
1. human body - человеческое тело
2. trunk - туловище
3. limb - конечность, член (тела)
4. extremity - конечность
5. upper - верх
6. lower - низ
7. to consist of- состоять из
8. skull-череп
9. to contain - содержать
10. brain - мозг
11. forehead - лоб
12. mouth - рот
13. lip - губа
14. cheek - щека
15. chin - подбородок
16. external - внешний, наружный
17. internal - внутренний
18. gum - десна
19. tooth (teeth) - зуб (зубы)
20. tongue - язык
21. palate -нёбо
22. to connect – соединять
23. neck - шея
24. chest - грудная клетка
25. abdomen - брюшная полость
26. lung - лёгкое
27. heart - сердце
28. gullet - пищевод
29. to breathe - дышать
30. beat - биение
31. abdominal - брюшной
32. cavity - полость
33. stomach - желудок
34. liver - печень
35. bone - кость
36. skeleton - скелет
37. to support - поддерживать
38. soft - мягкий
39. to protect - предохранять
40. injury - рана, ушиб, ранение
41. muscle - мускул
42. shoulder - плечо
43. forearm - предплечье
44. elbow - локоть
45. wrist - запястье
46. thumb - большой палец (руки)
47. hip = thigh - бедро
48. knee - колено calf - икра (ноги)
49. ankle – лодыжка
50. skin - кожа
51. spleen - селезёнка
52. intestine - кишечник
53. kidney - почка
54. gall-bladder - желчный пузырь
55. bladder ~ мочевой пузырь
56. framework –каркас
57. to circulate – циркулироватьregular regimen – правильный режим
58. to take somebody’s pulse – щупать пульс
59. to strengthen the heart – укреплять сердце
60. to control the work of somebody’s heart – контролировать работу сердца
61. beats per minute – ударов в минуту
62. to protect from disease – защитить от болезни
63. to fill – заполнять
64. arteries, veins, capillaries – артерии, вены, капилляры
65. corpuscles – тельца
66. erythrocytes – эритроциты
67. leucocytes - лейкоциты
68. blood-platelets – тромбоциты
69. tissue – ткань
70. bleeding – кровотечение
71. rate – скорость
72. content - содержание
73. due to – благодаря
74. to flow – течь
75. to aid - помогать, способствовать
Упр. 1 . Скажите по-английски:
укрепить сердце, защитить сердце от болезни, щупать пульс, 70 ударов в минуту, контролировать работу сердца, правильный режим, сердце сокращается, сердце регулирует скорость, кровь циркулирует, поток крови, содержание кислорода, течь, нести, кровяные тельца, ткани, свертывание крови, остановить кровотечение.
Упр 2. Ответьте на вопросы по содержанию текста.
1. What are the principal parts of the human body? 2. What parts does the head consist of? 3. What parts does the ear include? 4. What are the upper part and the lower part of the trunk? 5. What do you know about the upper extremity? 6. What does the lower extremity consist of? 7. What is the body covered with?
А) Посмотрите на картинки, назовите части тела по порядку.
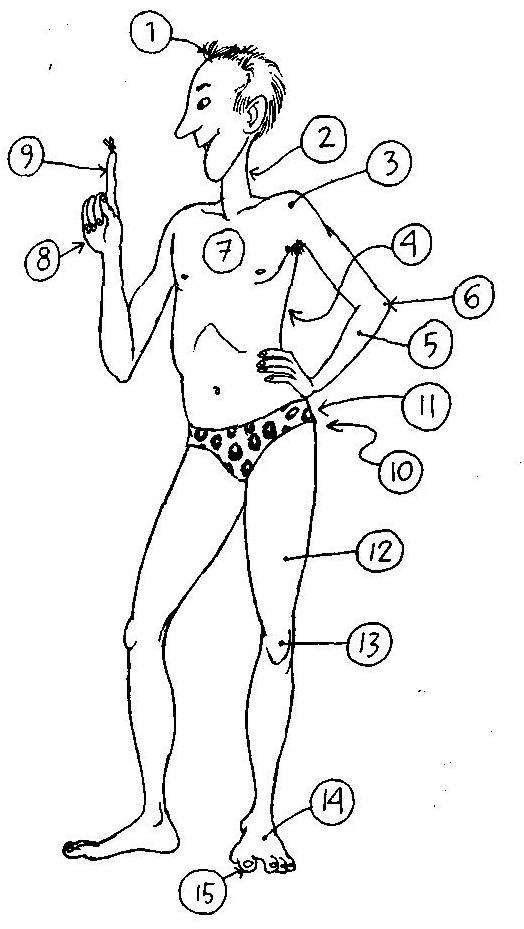
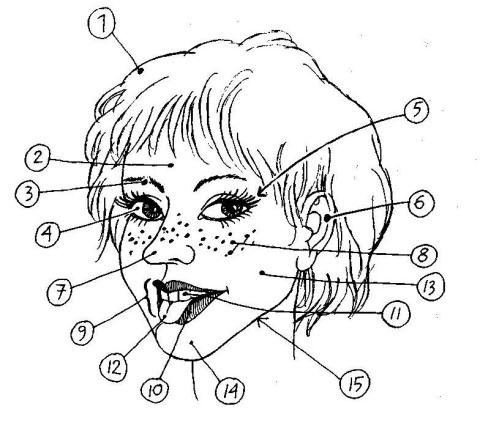
В) Заполните таблицу. Подберите эквиваленты к анатомическим терминам.
| Anatomical term | Common word |
| abdomen | |
| axilla | |
| carpus | |
| coxa | |
| cubitus | |
| mamma | |
| nates | |
| patella |
Unit 2 . S keleton
The bones form the skeleton of the body. The most important part of the skeleton is the backbone, or vertebral column. The bones which form the skeleton or bony framework of the body are divided into the bones of the head, the bones of the trunk, the bones of the lower and upper limbs.
At the upper end of the backbone there is the skull. Inside the skull is the brain which is in many ways the most important organ of the body. The bones of the head include the bones which make up the box-like structure we call the skull, and also that freely movable bone which forms our lower jaw.
There is another box of bones in front of the backbone. The ribs, which are joined to the backbone behind and bend round towards the breastbone in front, form a strong cage – the chest, inside of which are placed the heart and the lungs. The bones of the trunk include the spinal column, the ribs and the breastbone.
The arms join the body at the shoulder, and the shoulder itself is formed of two bones – the collar-bone in front, and the shoulder-blade behind. Between the shoulder and the elbow there is only one bone in the arm, but between the elbow and the wrist there are two. In the wrist there are eight small bones. They are very firmly bound together, but their large number allows the wrist to bend much more freely than if there were only one or two. Next come the bones of the hand itself. In the body or palm of the hand there are five long bones – one for each finger and one for the thumb. Each of the fingers has three bones, and the thumb has two. Thus we have twenty-seven bones in the framework of the hand and wrist alone.
The trunk is divided into the chest or thorax, and the abdomen. Of the limbs there are two pairs – the upper, or arms, and the lower, or legs; and the legs and arms again are subdivided into several parts – the thigh, the leg, the foot and the toes in the lower limb and the upper arm, the forearm, the wrist and the fingers in the upper limb.
The abdominal cavity contains two kidneys, connected by a tube, the ureter, to a muscular bag, the bladder; the liver, the pancreas and the spleen. The thorax encloses the heart and two lungs.
Cavity of the skull opens into the spinal canal. It contains the brain, which is continuous with the spinal cord. The brain and the spinal cord together constitute the cerebrospinal system. And cavity of the face is occupied by mouth and pharynx, into which the upper end of the alimentary canal (called gullet or esophagus) opens.
Word-box
| 1. backbone – позвоночник 2. vertebral column позвоночный столб, спинной хребет 3. spinal column – позвоночный столб 4. bony framework – костный остов, каркас 5. trunk – туловище 6. lower limbs – нижние конечности 7. upper limbs – верхние конечности 8. pancreas – поджелудочная железа 9. to include – включать, содержать в себе 10. lower jaw – нижняя челюсть 11. rib – ребро 12. to join – соединять(ся), присоединять(ся), связывать 13. to bend (bent, bent) – сгибаться 14. breastbone – грудина 15. chest – грудная клетка, грудь 16. thorax (pl тж. thoraces) – грудная клетка 17. arm – рука 18. shoulder – плечевой сустав | 19. collar-bone – ключица 20. shoulder-blade – лопатка 21. pharynx – глотка 22. esophagus – пищевод 23. to bind (bound, bound) – связывать 24. firmly – плотно, крепко, твердо 25. hand – кисть руки 26. palm – ладонь 27. finger – палец руки 28. spinal cord – спинной мозг 29. to constitute – составлять, представлять 30. leg – нога, голень 31. thigh – бедро 32. foot (pl feet) – нога, стопа, ступня 33. toe – палец на ноге 34. upper arm – плечо 35. cerebrospinal system –спинномозговая система 36. to contain – содержать в себе, вмещать 37. muscular bag – мышечная сумка 38. ureter – мочеточник |
Word-box
| 1. skeletal - скелетный 2. muscular - мышечный 3. digestive - пищеварительный 4. respiratory - дыхательный 5. urinary - мочевой 6. endocrine - эндокринный 7. reproductive - репродуктивный, половой 8. bone - кость 9. ligament - связка 10. cartilage - хрящ 11. join - соединять 12. structural - структурный 13. spinal - спинной, позвоночный 14. cord - столб 15. vessel - сосуд 16. pump – насос 17. stream - ток, поток | 18. alimentary - пищеварительный 19. gland - железа 20. convey - передавать, переносить 21. carbon dioxide - двуокись углерода 22. kidney - почка 23. urine - моча 24. ureter – мочеточник 25. urethra - уретра 26. urinary bladder - мочевой пузырь 27. be stored - сохраняться, храниться, скапливаться 28. discharge - удалять, выводить из организма 29. hormone - гормон |
Notes
1. to move us about — осуществлять наше движение
2. for receiving, processing and communicating information - для получения, обработки и передачи информации
3. which are required by cells — которые необходимы клеткам
4. by removing nitrogenous and other wastes — путем выведения азотосодержащих и других продуктов отхода
5. where urine is stored — где накапливается моча
Упр. 1. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих слов и словосочетаний:
несколько основных систем, которые их соединяют, основная функция, со всеми необходимыми средствами, переноситься кровотоком, ведущих к ним воздухоносных путей, где он поступает в кровоток, выводить мочу из почек, до тех пор, пока она не выведена, вырабатывают вещества-регуляторы
Unit 4 . Internal organs
Word-box
| bladder – мочевой пузырь brain – мозг esophagus – пищевод gallbladder – желчный пузырь heart – сердце intestines – кишечник kidneys – почки liver – печень lungs – лёгкие ovaries – яичники pancreas – поджелудочная железа spleen – селезенка stomach – желудок thyroid gland – щитовидная железа uterus – матка alimentary – пищеварительный cecum – слепая кишка junction – соединение urine – моча | pelvic floor – диафрагма таза pharynx – глотка digestion – пищеварение concave portion – вогнутая часть fossa – впадина to pump – качать blood vessels – кровеносные сосуды rhythmic contractions- ритмичные сокращения urinary system – мочеполовая система electrolytes – электролиты acid-base balance – кислотный баланс detoxification – детоксикация bloodstream – кровоток ovum – яйцеклетка lateral wall of the pelvis – боковая стенка таза to recycle iron – перерабатывать железо fallopian tubes – маточные трубы gestational period – гестационный период (период беременности) |
Examination of the abdomen
To examine the patient for enlarged abdominal (1).......................... first feel for the {2).......................... and the (3)............................. on the right side. To do this, ask the patient to take a deep breath, while pressing with the fingers upwards and inwards. Next feel for the right (4)..............................
and then cross over to the other side for the left (5)......................... Still on the left side, palpate for an enlarged (6) ................... Finally, moving to the lower abdomen, feel for the (7)....................... which is only felt if it is full.
Unit 5. The Diet
We are built from the food we eat. The food we eat consists of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals, water and vitamins.
Meat, fish, eggs, milk and cheese contain proteins. Protein is necessary for cell growth and repair. Sweet and starchy foods such as sugar, flour and potatoes contain carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide body cells with the energy required to perform their functions. Fats are found in meat, fish, dairy products and vegetable oils. They are used to produce heat and energy. Fats are necessary for the continued health of the cells. Minerals, such as calcium, phosphorus, iron, iodine come from our food and water. Calcium and phosphorus are needed for bone and teeth and to help cells to work. Dairy products are good sources of both calcium and phosphorus. Iron is needed for forming hemoglobin and iodine for thyroid hormones. Liver, meat, cereals are rich in iron. The body requires water for the production of blood, digestive juices, urine and sweat. More than 70% of the body consists of water. It is necessary to drink more than a litre of fluid daily.
Vitamins are special organic substances which are necessary for the organism. About 20 vitamins are known today. Vitamin A is present in carrots, green vegetables, fruit, butter, fish-liver oil, eggs. It is necessary for healthy eyes and the proper growth of bones. Vitamin B is present in cereals, milk, eggs, liver. It is needed to strengthen our nervous system and to form red blood cells. Vitamin C is present in lemons, oranges, black currant and vegetables. It is needed to increase resistance to infection and recover after illness. Vitamin D is present in eggs, butter, fish, dairy products. We get most of our vitamin D from the sun. It is necessary for bone and tooth formation and the prevention of the rickets.
Prolonged deficiency of any vitamin leads to avitaminosis. The food we eat is called our diet. The diet in health and disease is very important. If a person wants to be in good health he must eat a balanced diet. It means eating foods from all of the four basic food groups: the milk group, the meat group, the fruit and vegetable group and the grain group. Daily calorie requirements depend on the age, build and occupation. Doctors can treat many diseases by diet.
Word-box
| 1. protein – белок 2. carbohydrate – углевод 3. fat – жир 4. mineral – минеральная соль 5. necessary – необходимо 6. cell – клетка 7. growth – рост 8. repair – восстановление 9. sweet – сладкий 10. starchy – крахмалистый 11. flour – мука 12. to provide - обеспечивать 13. required – необходимый 14. to perform – выполнять 15. continued – длительный 16. iron – железо 17. iodine – йод 18. forming – образование 19. source – источник 20. thyroid-щитовидная железа 21. hormone-гормон 22. production – производство 23. digestive juice – пищеварительный сок | 24. urine – моча 25. sweat – пот 26. fluid – жидкость 27. to be present – присутствовать 28. proper – надлежащий 29. cereals – каши 30. nervous system – нервная система 31. black currant – черная смородина 32. to increase – повысить 33. resistance – сопротивляемость 34. to recover – выздороветь 35. prevention – предотвращение 36. rickets – рахит 37. prolonged – длительный 38. deficiency – недостаток 39. avitaminosis – авитаминоз 40. to be in good health – быть здоровым 41. to treat – лечить 42. grain-зерно |
Упр. 1. Найдите словосочетания, эквивалентные следующим:
состоит из белков, жиров, углеводов, минеральных солей; необходим; рост и восстановление клеток; сладкие и крахмалистые продукты; обеспечивать клетки организма энергией; выполнять функции; образование костей и зубов; источник кальция; пищеварительный сок; богат железом; особые органические вещества; участвовать в обмене веществ; присутствует; надлежащий рост костей; укреплять нервную систему; создавать красные кровяные тельца; повысить сопротивляемость инфекции; выздороветь; предотвращение рахита; длительный недостаток; иметь хорошее здоровье; лечить болезни диетой.
Упр. 2. Ответьте на вопросы :
1. What does the food we eat consist of? 2. What food contains proteins? 3. What is protein necessary for? 4. What food contains carbohydrates? 5. What do they provide body cells with? 6. Where are fats found? 7. What are they necessary for? 8. Where do minerals come from? 9. What are calcium and phosphorus necessary for? 10. What is iron necessary for? 11. What products are rich in iron? 12. What does the body require water for? 13. What are vitamins? 14. Where is vitamin A present? 15. What is it necessary for? 16. Where is vitamin B present? 17. What is it needed for? 18. Where is vitamin C present? 19.What is it needed for? 20. Where is vitamin D present? 21. What is it necessary for? 22 What does prolonged deficiency of any vitamin lead to? 23. Must a person be careful about his diet? 24. Can doctors treat many diseases by diet?
Упр. 3. Дополните предложения :
1. The food we eat consists of… 2. Carbohydrates provide body cells… 3. Minerals come… 4. The body requires… 5. Prolonged deficiency of… 6. If a person wants… 7. Doctors can treat…
Упр. 4. Практическое задание. Вычислите свой индекс массы тела . Обсудите в группе, что нужно сделать, что снизить ИМТ.
BMI(n)BMI means Body Mass Index. It is used to assess whether a person's weight is healthy or not. To calculate a patient's BMI you use the formula:
| weight in kilograms height in metres2 |
BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 is the right weight
BMI of below 18.5 is underweight
BMI of 25 to 29.9 is overweight
BMI of over 30 is obese
Упр. 6. Прочитайте текст.
Vitamins
Vitamins are classified as fat-soluble or water-soluble based on how they are absorbed by the body. Vitamins A,D,E and K are fat soluble. Vitamin C and the B-complex vitamins (thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), vitamin B6, vitamin B12, biotin, and folic acid are water- soluble.
Until the 1900s, vitamins could only be obtained by eating food. Now they are commercially available. There are a few vitamins that we obtain by other means than directly from the diet: for example, microorganisms in the intestine- commonly known as guta flora – produce vitamin K and biotin. One form of vitamin D is synthesized in the skin with the help of natural ultraviolet sunlight. Some vitamins can also be obtained from precursors that can be obtained in the diet. Examples include vitamin A, which can be produced from beta carotene and niacin from the amino acid tryptophan.
Vitamins enable the body to use the calories provided by the food that we eat and to help process proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
Vitamins have diverse biochemical functions. Some have hormone-like functions as regulators of mineral metabolism(e.g., vitamin D), or regulators of cell and tissue growth and differentiation (e.g., vitamin A). Others function as antioxidants (e.g., vitamin E and sometimes vitamin C).The B-complex vitamins function as precursors for enzyme cofactors, that help enzymes in their work as catalysts in metabolism.
Word – box
1. obtain - получать
2. available - доступный
3. means – способ, средство
4. gut flora – кишечная флора
5. sunlight – солнечный свет
6. precursor – прекурсор, предшественник
7. diverse – различный
8. enable – давать возможность
Упр. 7. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих слов и словосочетаний:
основываясь на том, как они всасываются; водорастворимые, никотиновая кислота; другим способом, естественный солнечный свет, функции, похожие на функции гормонов, регуляторы минерального метаболизма; регуляторы роста и дифференциации клеток и тканей, действуют как прекурсоры, фермент
Упр.8. Ответьте на вопросы
1. How are vitamins classified?
2. What are fat-soluble (water-soluble) vitamins?
3. Can vitamins be obtained only by eating food?
4. Can we obtain vitamins by other means?
5. Do vitamins enable the body to use the calories provided by the food?
6. Vitamins have diverse biochemical functions, don’t they?
7. Do vitamins help process proteins, fats, carbohydrates?
Упр . 9 Найдите соответствие
Vitamins have diverse biochemical functions. What are these vitamins? What are their functions?
| Vitamin D | antioxidant |
| Vitamin A | regulator of mineral metabolism |
| Vitamin B | regulator of cell and tissue growth and differentiation |
| Vitamin C,E | helping enzymes in their work as catalysts in metabolism |
Упр. 10.Дополните текст данными ниже словами:
| teeth | organs | enzymes | nervous system | cells |
| brain | eyes | skin | immune system | |
| blood | muscles | bones | cardiovascular system |
Vitamin C is needed to help the 1 repair itself when it is cut or damaged. It is found in fruit, especially citrus fruit like oranges and grapefruit.
The B-vitamins keep the 2 healthy and help reduce stress. They are found in foods like wholegrain bread and cereals.
Vitamin A keeps the 3 healthy and is important for good vision. It is found in fatty foods like butter, cheese, whole milk, and yoghurt.
Vitamin D is needed for healthy bones and__________ 4 because it helps the body absorb calcium. Our body makes Vitamin D when our 5 is exposed to sunlight.
Calcium is needed for children's 6 and teeth to grow. It is found in foods like milk, cheese, and yoghurt.
Iron helps your 7 carry oxygen. If you do not get enough iron, you will be pale and tired and you may get anaemia. Iron is found in red meats, especially liver.
Zinc makes your 8 stronger so that you can fight colds and infections. It is found in shellfish, nuts, and seeds.
Omega-3 is an essential fatty acid which helps your 9 function well. It is found in oily fish like mackerel, sardines, salmon, and tuna.
Protein builds up, maintains, and replaces the tissues in your body. Your
10, your 11, your immune system are made up mostly of protein.
Carbohydrates are sugars which are broken down by 12, then stored in the 13 as a source of energy. Grain products such as rice, bread, and pasta are sources of carbohydrate.
Fats fuel the body and help absorb some vitamins. They are also the building blocks of hormones, and they insulate nervous system tissue in the body. Unsaturated fats, found in oils and nuts, for example, are believed to protect the 14.
Упр . 11 Соотнесите слова с их определением.
| 1. balance | a. taking regular exercise |
| 2. childhood | b. small amounts of food that you eat between meals |
| 3. diet | c. sugar that the body uses for energy |
| 4. glucose | d. the time of your life when you are a child |
| 5. active | e. the correct amount of different things |
| 6. obesity | f. the type of foods that you usually eat |
| 7. overweight | g. the condition of being very fat, in a way that is not healthy |
| 8. snacks | h. too heavy and fat |
Упр . 12 . Заполните пропуски словами из упражнения 1 1 .
Diabetes occurs when your body does not produce enough insulin, a hormone that controls the level of ___ (1) in the blood. One type of diabetes appears in ___ (2) and the other type appears the age of eighteen.
It is very common for very ___ (3) people to get diabetes, so the illness is linked to ___ (4).
For this reason, it is important to get the right __ (5) between food and exercise. It is important to be ___ (6), and to eat a healthy ___ (7), containing plenty of fruit and vegetables. Nutritionists say ____ (8) are better than big meals.
Overweight and obesity
Overweight and obesity have become world-wide concerns, reaching epidemic proportions. Obesity is caused by an energy imbalance where energy intake exceeds energy expended over time. This imbalance has been linked to lifestyle factors such as increased consumption of foods with high levels of sugar and saturated fats, as well as a reduction in physical activity.
Overweight and obesity pose a major risk to long-term health by increasing the risk of chronic illnesses such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and some cancers. It has been estimated that obesity and its associated illnesses cost Australian society and governments a total of $21 billion in 2005. In July 2006, the Australian Government implemented a five-year, $500 million program, the Australian Better Health initiative, aimed at reducing the impacts of chronic disease which includes a focus on promoting healthy weight.
This article discusses adults who were classified as overweight or obese according to their body mass index (BMI), based on self-reported height and weight.
Perceptions of own weight
For many people, particularly men and older women, self perception of ‘acceptable weight’ differs from the standard BMI definitions.
This may have implications for the management of healthy body weight in adults. In 2004-05. more than hall of adults (63% of males and 59 % of females) considered themselves to he of acceptable weight. The proportion of males (32%) and females (38%) who considered themselves to be overweight was considerably lower than those who were classified и overweight / obese according to their BMI (62% and45% respectively).
Between 1995 and 2004-05, after adjusting for differences in the age structure of the population, the proportion of people in the overweight and obese BMI categories, who considered themselves to be of acceptable weight increased. In 2004-05, almost half (47%) males and around one-fifth (21%) of females who were overweigh or obese considered themselves to be of acceptable weight. This compares with age-standardized rates of around one-third (35%) for males and 12% for females in 1995.
Unit 6. WHO.
WHO (World Health Organization) is one of the largest specialized agencies of the United Nations. It was founded in 1948. WHO acts as the central authority directing and coordinating international cooperation for improved health conditions.
The major function of WHO is to establish measures for the control of epidemic diseases. This consists of mass campaigns promoted by WHO against communicable diseases.
Another major function of WHO is working in specific fields of particular need such as maternal and child health and welfare, mental health, nutrition and improvement of water supplies. It also assists educational programs for nurses and assistants. WHO is coordinating an international effort against Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
Word-box
1. found – основывать
2. authority – орган, власть
3. improve – улучшать
4. major – главный, основной
5. establish – устанавливать, определять
6. measure – мера
7. promote – содействовать, поддерживать
8. communicable – инфекционный, заразный
9. particular – особый
10. welfare – благополучие
11. nutrition – питание
12. supply – запасы
Word-box
1. the National Health Service – Государственная служба здравоохранения
2. population – население
3. completely – полностью
4. free – бесплатный, свободный
5. majority – большинство
6. the general practitioner services – служба врачей общей практики
7. general practitioner – врач общей практики
8. the hospital and specialist services – больничная и специализированная службы
9. the local health authority services – местные органы здравоохранения
10. partnership – партнерство
11. refer – направлять
12. choose – выбирать
13. accept – принимать
14. refuse – отказывать
15. government – правительство
16. minor – малый, мелкий, незначительный
Упр. 1. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих слов и словосочетаний:
была создана; полностью бесплатное медицинское обслуживание (лечение); государственная служба здравоохранения; подавляющее большинство специалистов; врач общей практики; служба врачей общей практики; местные органы здравоохранения; оплачиваются правительством; иметь частную практику; медицинские центры; направлять людей в больницы; свободен в выборе.
Упр . 2. Ответьте на вопросы.
1. When was the National Health Service established?
2. What can you say about the number of people in Great Britain using the Service?
3. What parts does the Service consist of?
4. Who are Health Service doctors paid by?
5. May these doctors have private practice?
6. Is the patient free to choose his doctor?
7. Is the doctor free to accept or refuse patients as he wishes?
Word-box
1. plague – чума
2. the art of medicine – искусство врачевания
3. by lighting fires – разжигая костры
4. drive (drove) out – изгонять
5. attentively – внимательно
6. set fractures – лечить переломы
7. oath – клятва
8. code of honour – кодекс чести
Упр.1. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих слов и словосочетаний:
изучал медицину; практиковался в искусстве медицины; изгнал чуму; основывал медицинские школы; обследовать пациентов; очень внимательно; оказывать пациентам быструю помощь; на основе опыта; создавал медицину; естественный процесс; естественные причины; соленые морские ванны; массаж; лечил переломы; использовать лекарства; письменные труды; знаменитая клятва; кодекс чести; основные мысли и принципы.
Упр . 2. Ответьте на вопросы.
1. When and where was Hippocrates born? 2. What was his father? 3. Where did he practise the art of medicine? 4. How did he drive out plague from Athens? 5. Was Hippocrates an excellent doctor and a teacher of medicine? 6. Did he establish medical schools? 7. What did he teach his pupils? 8. What was the medicine based on? 9. How did he treat diseases? 10. Was he a good surgeon? 11. How is Hippocrates often called? 12. How many books does the Collection consist of? 13. What does the Collection begin with? 14. What does the Oath form?
Упр. 3. Вспомните предложения из текста со следующими словами и словосочетаниями:
was born; studied medicine; drove out; established medical schools; taught his pupils; created medicine; treated diseases by; consists of; basic thoughts.
Упр . 4. Продолжите предложения.
1. Hippocrates was the son …
2.He practised …
3. He taught that …
4. He set …
5. He knew how …
6. His writings …
7. The famous oath contains …
Упр. 5. Вставьте предлоги или наречия:
In an attempt to explain states ... the disease and health, Hippocrates defined the existence of four principal fluids ... the body. They were blood, phlegm, black bile and yellow bile. He also suggested that there were four elemental conditions — cold, hot, dry and moist — and that a state ... health existed when these four fluids and qualities were in balance. Disruption ... the natural balance would result in disease: for example, too much phlegm made the body too cold and too wet.
Word-box
| 1. surgeon – хирург 2. outstanding – выдающийся 3. personality – личность 4. wounded – раненый 5. to make wide use of – широко использовать 6. effect – действие 7. associate – коллега 8. ether – эфир 9. to convince – убеждаться 10. harmless – безвредный 11. discovery – открытия 12. to define – определять 13. cause – причина 14. inflammation – воспаление 15. to prevent – предотвращать 16. wound – рана 17. substance – вещество 18. to introduce – вводить 19. to search – искать | 20. limb – конечность 21. to arrive – приходить, приезжать 22. rigid plaster cast – жесткая гипсовая повязка 23. to employ – применять 24. resection of joints – резекция суставов 25. pride – гордость 26. besieged – осажденный 27. medical assistance – медицинская помощь 28. to care for – ухаживать 29. to appreciate – ценить 30. modest – скромный 31. noble – благородный 32. to proclaim – заявлять 33. disease prevention – предотвращение болезни 34. task – задача to belong – принадлежать |
Упр . 7. Ответьте на вопросы .
1. What was Nikolai Pirogov?
2. When was he born?
3. Was he the first surgeon to make wide use of anesthesia at field hospitals?
4. What anesthetic did he use?
5. What did he introduce?
6. Did he employ rigid plaster casts?
7. Is the rigid plaster cast the pride of Russian surgery?
8. Did he work out principles for giving medical assistance at the front?
9. Was he the first medical man in Russia to use nurses to care for the sick and wounded in the fields?
10. Did he proclaim disease prevention a very important task of medicine?
Some good rules for nurses
1. Do not reveal your personal reaction to any symptoms or complains of the patient, because it can alarm him.
2. Be patient with old people.
3. Don’t be rude when you speak with patients.
4. Don’t gossip about your patients.
5. Never say the word “incurable”.
6. If you made a mistake in your work tell the doctor about it at once.
7. When you give medicines:
· Wash your hands
· Read carefully the doctor’s instructions
· Don’t substitute one drug for another
· Address patients by name not to be mistaken
· Be sure of the drug, dose, time, method of giving
1Word-box
1. rude – грубый
2. patient – терпеливый
3.to reveal – раскрывать, показывать
4.complaint – жалоба
5. to gossip – сплетничать
6. incurable – неизлечимый
7. drug – лекарство
8. to substitute – заменять
& A Nurse
Every nurse must have enough knowledge of her work. She must know anatomy and physiology, pharmacology, social psychology, ethics, data analysis, management and administrative science. She must read medical journals. She must learn much of the nurse’s work by practice.
The fundamental responsibility of the nurse is fourfold: to promote and restore health, to prevent illness and to alleviate suffering.
A nurse must give good care to sick people. She must be very attentive and try to observe any changes in a patient’s condition. She must know what is a normal and what is an abnormal condition and be able to recognize significant symptoms. Careful observation and charting by the nurse are very important. They help the doctor to diagnose and treat the patient.
1Word-box
1. enough – достаточно
2. knowledge – знания
3. ethics – этика
4. management – управление
5. fundamental – основной
6. fourfold – четырехкратный
7. to promote – содействовать, поддерживать
8. to prevent –предотвращать
9. to restore – восстанавливать
10. to alleviate – облегчать
11. suffering – страдания
12. to give good care to – осуществлять хороший уход за
13. sick – больной
14. to diagnose – ставить диагноз
15. to treat – лечить
16. abnormal – ненормальный
17. to recognize – распознать
18.significant –значимый
Упр . 5 . Ответьте на вопрос What must a nurse have (know, read, give, be, be able)? используя следующие слова :
good care, anatomy, physiology, journals, attentive, a normal and an abnormal condition, pharmacology, ethics, medical journals, enough knowledge, to recognize, significant symptoms.
Упр . 6 . Ответьте на вопросы :
1. What is the fundamental responsibility of a nurse?
2. Why are careful observation and charting by the nurse very important?
& Nurse’s duties
A nurse takes the patients’ temperature and writes it down in temperature charts. She gives the patients medicines and carries out other prescriptions of the doctors. She airs the wards. Each ward nurse tells the doctor in charge about the condition of the patients. She must do everything in the ward quickly and quietly. If there is a bed-patient in the ward she must come up to him, brush his sheets or change them if it is necessary, shake his pillow. Then she must wash the patient’s face and hands and feed him.
Nurses 1) give intravenous (intradermal, intramuscular, subcutaneous) injections; cleansing (medicinal) enemas; 2) put cups (mustard plasters, sticking plasters, ice-bags, hot water bags, cold (hot) compresses) etc.
1Word-box
1. to take the patient’s temperature – измерить температуру пациента
2. a temperature chart – температурный лист
3. to carry out – выполнять
4. prescription – назначение
5. to air – проветривать
6. doctor in charge – лечащий врач
7. a bed-patient – лежачий больной
8. pillow – подушка
9. to feed – кормить
10. intravenous – внутривенный
11. intramuscular – внутримышечный
12. intradermal - внутрикожный
13. subcutaneous – подкожный
14. to give injections – делать инъекции
15. a ward -палата
Word - box
1. potentially – потенциально
2. tending – уход, забота, присмотр
3. entire – весь, целый
4. to happen – случаться, происходить
5. in charge – ответственный
6. nature – природа
7. statement – высказывание
8. object – цель
9. to consider – считать
10. elsewhere – в другом месте
11. to identify – устанавливать, определять
12. recording – регистрация, запись
13. inference – вывод
14. to define – определять, характеризовать
15. to cure – вылечивать
16. to heal – излечивать, заживлять
17. wounded – раненый
18. to preserve – сохранить
19. independent – независимый
20. step – шаг, ход, мера, ступень, действие
21. scientific – научный
Упр . 1 1 . Ответьте на вопросы :
1. What is nursing?
2. What did Florence Nightingale use the word “nursing” for?
3. What does a nurse mean?
4. What is the object of nursing?
5. Was Florence Nightingale’s book the first writing in nursing theory?
6. What need did she identify in this monograph?
7. How did Harmer define the object of nursing?
8. How did Virginia Henderson identify basic nursing actions?
9. What did she state?
& Nursing process
The term nursing process was first introduced by Lydia Hall in 1955. Nursing process is a problem-solving method for providing individualized care for clients in all states of health. The nursing process has five interrelated steps: assessment, nursing problem, planning, implementation and evaluation.
During the assessment the nurse collects data about the client to identify his problems. The collected information is analyzed and specific client health problems are stated during the nursing problem step.
During the planning step a care plan is formulated. It is based on the assessment and nursing problem. The care plan contains client goals with expected client outcomes and appropriate nursing interventions.
Implementation is the action step of the nursing process. During this step individualized client care is delivered according to the care plan. The evaluation step allows the nurse and client to evaluate the success of nursing care through the achievement of client goals and expected outcomes.
When a nursing process is used to organize and deliver nursing care the client becomes an active participant in an individualized health care process.
The nurse benefits from the structured approach, with economy of time and energies, professional growth, a sense of profession and increased job satisfaction.
The nursing process is the means by which nurses increase their autonomy and fulfill their professional and legal responsibilities.
Word - box
1. to provide – обеспечивать, предоставлять
2. state of health – состояние здоровья
3. interrelated – взаимосвязанный
4. assessment – оценка
5. implementation – выполнение, осуществление
6. evaluation – анализ, оценка
7. to identify – устанавливать, определять
8. to state – устанавливать, определять
9. step – шаг, ход, ступень, мера, действие
10. goal – цель
11. to expect – ожидать
12. outcome – результат, исход
13. appropriate – соответствующий, подходящий
14. intervention – вмешательство
15. to deliver – доставлять, передавать, осуществлять
16. success – успех
17. achievement – достижение
18. nursing care – сестринский уход
19. to benefit – получать пользу, извлекать выгоду
20. structured approach – структурный подход
21. sense – чувство
22. satisfaction – удовлетворение
23. legal – юридический, правовой, законный
24. responsibility – ответственность
25. fulfill – выполнять
26. according – согласно, в соответствии
27. to allow – позволять
28. autonomy - автономия
Упр. 12. Ответьте на вопросы:
1. When was the term nursing process first introduced?
2. What is nursing process?
3. What are the steps of the nursing process?
Упр. 13. Прочитайте статью. Определите, какие из высказываний соответствуют содержанию текста ( T) , а какие нет (F).
1) The more responsibility you have, the higher your grade.
2) Nursing officers are the same as auxiliary nurses.
3) Students are paid less then auxiliary nurses.
4) A charge nurse is a man.
5) There are not many opportunities for British nurses to specialize.
6) Many nurses say that the job is rewarding, but the pay is low.
One hundred and fifty years ago, nurses were unpaid, untrained, and unpopular, but then Florence Nightingale made nursing into a profession. The methods she introduced in the 1850s were copied all over the world, and now nursing is a career with a three- or four-year training, qualifications, grades, unions and pensions.
In Britain, every nurse is on a grade. The grade depends on experience and skills, and each grade has different responsibilities and pay. On the bottom grades are unqualified auxiliary nurses who do the routine work on hospital wards. On the top grades are nursing officers, who are usually administrators.
Auxiliary nurses are on the bottom grades, but student nurses get the lowest pay. However, students don’t stay at the bottom of the pay scale forever. When they qualify, they start working on a middle grade. As they get experience, they can get promotion and move up the ranks to become staff nurse, then sister and perhaps eventually nursing officer.
Many nurses work shifts, and often they work overtime earn more money. After basic training, many nurses choose to do further study and become specialists. Nurses can specialize in many different fields – there are triage nurses working in Casualty, and psychiatric nurses who treat the mentally ill. There are health visitors who visit patients in their own homes, practice nurses working in GPs’ surgeries, and midwives who deliver babies.
Many of them say they do not get enough pay and respect for the work they do. They say that the work is physically and mentally hard, that they work long hours and get very tired. But they also say that there are many great rewards which have nothing to do with money.
Упр. 14. Найдите в тексте выражения со схожим значением.
1) exams and courses that you have taken q______
2) money that you will receive when you are old p______
3) similar work that you have done before e______
4) special abilities s______
5) levels of pay p____ s_____
6) extra hours you can work to earn more money o______
7) study and practice to learn how to do a job b____ t_____
8) more advanced learning f____ s_____
Упр. 15. Найдите в тексте следующие словосочетания и выражения.
Клиника врача общей практики, главная медсестра, патронажные медсестры, практикующие медсестры, (фельдшера-) акушерки, должностной разряд, зависеть от опыта и мастерства, иметь различные функциональные обязанности, на низшем уровне, неквалифицированные медицинские сестры, на высшем уровне, студенты медицинских училищ, на среднем уровне, получить повышение и продвинуться по службе, медицинская сестра, старшая медицинская сестра, работать по сменам, медсестры приемного отделения, отделение реаниматологии.
Упр. 16 . А) Миссис Берсон (Mrs Benson) поступила в больницу. Прослушайте пять коротких сообщений. Определите последовательность, кто из медицинского персонала с ней разговаривает.
An admission.
___ a a receptionist ____ d a sister
___ b a consultant ____ e a radiologist
___ c a paramedic
Б) Прослушайте запись еще раз и определите, какие из высказываний соответствуют содержанию текста (T) , а какие нет (F).
1) Mrs. Benson has had a fall. _______
2) This is not Mrs. Benson’s x-ray. _______
3) Mrs. Benson cannot find the toilet. _______
4) She has a heart problem. _______
5) The consultant sends her home. _______
6) Mrs. Benson’s appointment is next week. _______
Список использованной литературы
1. Английский язык для медицинских специальностей (для СПО). Учебник : учебник / Т.В. Шадская, Л.В. Шаманская. — Москва : КноРус, 2019. — 285 с.
2. Большой англо – русский словарь: в 2-х т. Ок. 160000 слов. Авт. Н.Н.Амосова, Ю.Д. Апресян и др. Под общ. рук. И.Р. Гальперина. – 4-е изд., испр., с Дополнением – М:. Рус. яз., 1988.
3. Новейший англо – русский, русско - английский словарь/состав. Крысенко С.М.- К: Издательство Арий; Екатеринбург: У – Фактория., 2007. – 960 с.
4. Перфильева, Г.М. Английский язык для медицинских сестёр: Учебник для студентов медицинских вузов, обучающихся по специальности 060109 (040600)-Сестринское дело / Г.М. Перфильева, И.Ю. Марковина.-М.: «Эксмо», 2008.-448 с.
5. Сухоцкая Л.А. Английский язык: учебное пособие для медицинских образовательных оранизаций / составитель Л.А.Сухоцкая, Н.М.Смоленцева, Н.А. Смирнова -Й-Ола, 2017.-83 с.
6. Сухоцкая Л.Н. Английский язык: учебное пособие для студентов медицинского колледжа / Л.Н. Сухоцкая – Й-Ола, 2011.-114 с.
7. Eric H. Glendinning, Ron Howard. Professional English in Use. Medicine. – Cambridge University Press, 2007.– 167 p.
8. Sam McCarter. Medicine 1: Student’s book – Oxford University Press, 2010. – 143 p.
9. Sam McCarter. Medicine 2: Student’s book – Oxford University Press, 2010. – 143 p.
10. Tony Grice, James Greenan. Nursing 2: Student’s book – Oxford University Press, 2010. – 136 p.
11. Tony Grice. Nursing 1: Student’s book – Oxford University Press, 2009. – 139 p.
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК
Учебное пособие
Йошкар-Ола
2019 год
УДК 811:61
ББК 5
К 92
Печатается по решению педагогического совета
ПОО ЧУ «Столичный бизнес колледж»
Ответственный редактор – Н.С. Бастракова
Рецензенты:
Лапочкина Е.В. – кандидат педагогических наук, доцент ФГБОУ ВО «ИвГМА Минздрава России».
Серебрякова М.А. – кандидат педагогических наук, доцент ФГБОУ ВО «Марийский государственный университет».
Купцова О.Г.
К 92 Английский язык: учебное пособие / О.Г. Купцова. – Йошкар-Ола, 2018. – 209 с.
Учебное пособие по дисциплине «Иностранный язык (английский)» предназначено для студентов средних профессиональных образовательных организаций медицинского профиля очной и очно-заочной форм обучения. Парамедицинское содержание материалов пособия позволяет использовать его для аудиторной и самостоятельной работы студентов, обучающихся по специальностям «Сестринское дело», «Лечебное дело», «Акушерское дело». Специфика специальностей может быть учтена в дополнительных дидактических материалах преподавателя. Основная цель пособия – формирование коммуникативной компетенции: создание прочной языковой подготовки, на основе которой возможно дальнейшее совершенствование навыков и умений чтения и перевода англоязычной литературы, развитие диалогической и монологической речи по вопросам специальности. Пособие построено по тематическому принципу и включает в себя широкий спектр разделов профессионально-ориентированной направленности. Все тексты и работа над ними являются подготовкой студентов к самостоятельному чтению и пониманию оригинальной медицинской литературы и к устному общению на английском языке в пределах изучаемой тематики. Пособие так же может быть рекомендовано для обучающихся 10-11 классов профильной направленности общеобразовательных организаций, студентов высших образовательных организаций медицинского профиля для самостоятельного изучения или подготовки к конкурсам и олимиадам.
Оглавление
Unit 1. Тело человека
Unit 2 . Скелет
Unit 3 . Системы организма
Unit 4 . Внутренние органы
Unit 5 . Режим питания. Витамины
Дата: 2019-02-25, просмотров: 1017.