Telecommunications - is the transmission and reception of any information (sound, image, data) over long distances through various systems (cable channels, radio channels and other communication channels).
Telecommunication technologies - is a set of algorithms, methods and tools of information transmission and reception.
New technical means and methods of data transmission, storage and processing appeared at different stages of society development.
At different times widespread: telegraph, telephone, fax, teletype, radio and TV.
Traditional telecommunication networks include:
• Computer networks (data transmission).
• Telephone networks (voice transmission).
• Radio networks (transmission of sound information).
• Television networks (audio and image transmission).
Computer Network is a collection of computers connected by communication channels and switching equipment into a single system for exchanging messages and access of users to software, technical and information resources of the network.
Two very important problems were solved with the advent of computer networks:
• Access to hardware, software and information resources regardless of their location;
• The possibility of rapid movement of large amounts of information to any distance.
In 1969, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) developed the first computer network by order of the US Department of Defense.
The network consisted of two computers. The first was at the University of California, and the second at a distance of 600 km from him - at Stanford University.
The first operator entered the word "LOGON", and the second had to confirm that he sees it on his screen.
As a result, the ARPANET network was created in 1969.
The Internet was introduced on January 1, 1983. On this day, the ARPANET switched to TCP/IP protocol (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), which has been successfully used till now for interconnection networks.
Classification of computer networks
Local area network (LAN) - a network that connects several computers in an area that is limited to one room or building.
Regional network (MAN - Metropolitan Area Network) - a network connecting computers located at a considerable distance from each other within the region.
Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers the territory of several countries and regions.
A local area network (LAN) is the connection of several computers in the same room or building.
To connect a computer to a local network, you need:
• Network cable;
• Network Card.
Separation of local networks
1. Peer-to-peer networks.
2. Client-server networks.
Client-server technology
A server is a computer that provides its resources to the general user.
A client is a computer using a server.
The client sends a request to the server, displays the response received from the server. The server receives requests from clients, executes queries and sends a response with results.
Equipment for building networks
1. Network cards.
2. Network cables.
3. Concentrators (hubs) - duplicate the received data on all ports.
4. Switches (switches) - transmit the received data only to the address-tu.
Network Cables
Coaxial cable. This is one of the first conductors used to create networks (fig. 12.1).
The maximum data transfer rate is 10 Mb / s.
The cable is strongly susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
Coaxial cable assembly
1- inner conductor;
2- insulation;
3- screen in aluminum braid;
4-shell.
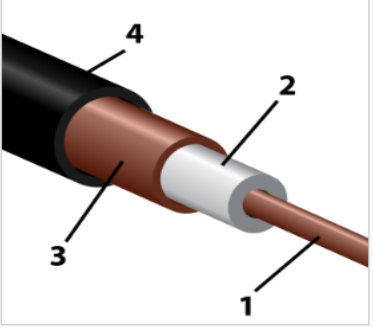
Figure 12.1 – Coaxial cable
Twisted Pair. Currently, this is the most common network cable (fig. 12.2).
There are several categories of cable, which are numbered from 1 to 8 and determine the effective transmitted frequency range. The larger the category, the higher the data transfer rate.
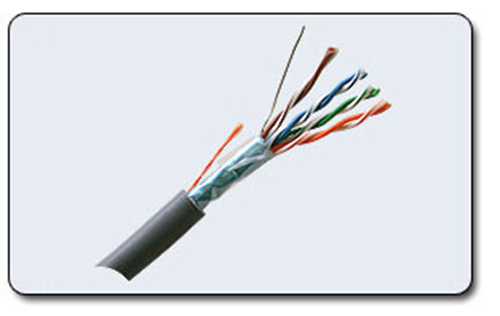
Figure 12.2 – Twisted pair
When building local networks, a cable of the 5th category is used. The cable supports up to 100 Mbps data rate when using 2 pairs and up to 1 Gb / s when using 4 pairs.
Fiber optic cable. The cable contains optical fibers protected by plastic insulation (fig.12.3). The data transfer rate is from 1 to 10 Gbit / s. Absolutely not subject to interference.
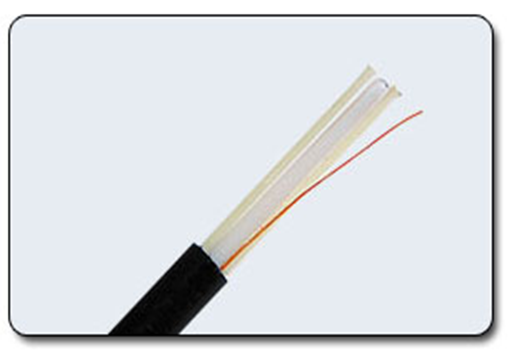
Figure 12.3 – Optic cable
A network card is a peripheral device that allows a computer to communicate with other computers on the network.
According to the constructive implementation, the network cards are divided into:
• Built-in motherboard;
• Internal boards inserted into the slots of the motherboard;
• External boards that connect via USB interface.
The network card contains a microprocessor that encodes-decodes network packets. Each card has its own Mac address.
The MAC address (Media Access Control) is a unique number for network equipment.
The MAC address allows you to identify each computer on the network in which the network card is inserted.
Hubs have several ports to which computers are connected. Concentrators are active and passive. Active hubs amplify and restore signals. Passive concentrators do not require power connection.
Switch is an intelligent device, where there is a processor and a buffer memory. The switch analyzes the Mac address, where and where the packet of information is sent and connects only these computers. This allows you to greatly increase network performance.
Дата: 2019-02-02, просмотров: 925.