1) Fourteen elements a) during maturation from other plant parts to the grain, seed or tuber
2) The primary and secondary nutrients b) are called plant nutrients
3) Plant growth c) are secondary nutrients
4) Nutrient uptake d) in small or trace quantities
5) Calcium, magnesium, sulphur e) starts slowly and accelerates
6) Nutrients are relocated f) are required in the largest amounts
7) The micronutrients are required g) differs between development stages
Исправьте предложения, не соответствующие содержанию текста.
1) Plant nutrients are fourteen elements derived from the soil.
2) The micronutrients are required in the largest amounts.
3) The plant growth doesn’t depend on plant nutrients.
4) Plants form their complex organic matter from carbon dioxide taken from the air.
5) Nitrogen and phosphorus are trace elements.
6) Plant nutrients are divided into four subgroups
7) The crop passes through a series of development stages during the period of growth.
14. Задайте вопросы к утверждениям из упражнения №13, используя разные типы вопросов.
15. Ответьте на вопросы .
1) What originates from plants?
2) What are plant nutrients?
3) What do plants form?
4) How many groups are plant nutrients divided into?
5) What primary nutrients do you know?
6) What secondary nutrients do you know?
7) What trace elements do you know?
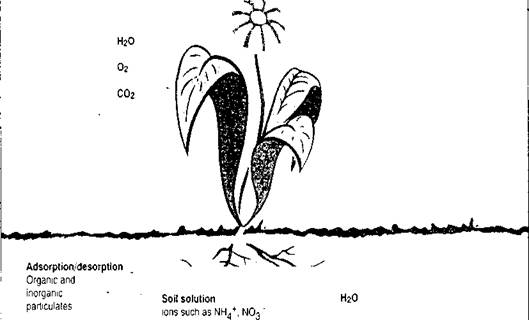
16. Рассмотрите схему поступления питательных веществ из почвы в растение и ответьте на вопросы.
1) What soil factors affect the availability of nutrients for plants?
2) What processes govern plant uptake from soil?
3) What substances take part in these processes?
Используя информацию из таблицы, расскажите подробно о любой группе элементов, необходимых в тех или иных количествах для правильного роста растения.
Table 2.1. Plant nutrients, their form of uptake and function
| Nutrient | Taken up as | Some important functions |
| Nitrogen | NO3-, NH4+ | Component of important cell compounds, ranging from proteins to chlorophyll and plant |
| Phosphorus | H2PO4-, HPO42- | Constituent of genes, has a central role in plant energy transfer and protein metabolism |
| Potassium | K+ | Helps in osmotic and ionic regulation. Important for many enzyme functions in carbohydrate and protein metabolism |
| Calcium | Ca2+ | Involved in cell division and plays a major role in the maintenance of membrane integrity |
| Magnesium | Mg2+ | Component of chlorophyll, and a factor in many enzymatic reactions |
| Sulphur | SO42- | Constituent of proteins, amino acids and vitamins. Necessary for production of plant oils |
| Iron | Fe2+ | Component of many enzymes, including cytochromes[3] (respiratory enzymes) and the ferredoxins[4] involved in functions such as N fixation and photosynthesis |
| Zinc | Zn2+ | Necessary for the correct functioning of a range of important enzyme systems, for the synthesis of nucleic acids, and the metabolism of an iron-containing protein found in plants that is active in photosynthesis auxin[5](a plant hormone) |
| Manganese | Mn2+ | Component of several enzymes including those involved in photosynthesis |
| Copper | Cu2+ | Component of a range of important enzymes. Necessary for proper photosynthesis. Involved in grain production |
| Boron | H3BO3 | Specific function unknown |
.
| Molybdenum | MoO42- | Required for normal assimilation of N in plants, for the reduction of NO3- to NH4+ Also required for N fixation and for chlorophyll |
| Chlorine | Cl- | Essential for photosynthesis, and for osmoregulation[6] of plants growing on saline soils |
| Nickel* | Ni2+ | Constituent of the enzyme urease[7] in legumes |
* Plants cannot complete their life cycle without nickel, thus it is now included in the list of
micronutrients.
Дата: 2018-11-18, просмотров: 805.