Blood Suckers/Leeches/Vampires - those who take blood samples, such as laboratory technicians and phlebotomists. Tough Stick - a patient whose veins are hard to find when drawing blood. Very Close Veins - varicose veins. Blue pipe –vein. Red pipe - artery (as opposed to 'blue pipe' or vein).
THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
Phonetic exercise: alimentary canal [,æli’mentəri k  ’næl], gut [gΛt], digest [di’d3est], extract [iks’trækt], expel [iks’pel], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d
’næl], gut [gΛt], digest [di’d3est], extract [iks’trækt], expel [iks’pel], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d  minl], gastrointestinal tract [,gæstrəuin’testinl ‘trækt], lower gastrointestinal tract [‘louə ,gæstrəuin’testinl ‘trækt], mouth [mauθ], cavity [‘kæviti], salivary [‘sælivəri], mucosa [mju’kousə], tongue [tΛŋ], pharynx [‘færiŋks], esophagus [i:’s
minl], gastrointestinal tract [,gæstrəuin’testinl ‘trækt], lower gastrointestinal tract [‘louə ,gæstrəuin’testinl ‘trækt], mouth [mauθ], cavity [‘kæviti], salivary [‘sælivəri], mucosa [mju’kousə], tongue [tΛŋ], pharynx [‘færiŋks], esophagus [i:’s  :fəgəs], stomach [‘stΛmək], digestion [di’d3est∫ən], environment [in’vaiərənmənt], secrete [si’kri:t], intestine [in’testin], duodenum [,djuo’di:nəm], jejunum [d3i’d3u:nəm], ileum [‘iliəm], caecum [‘si:kəm], colon [‘koulən], ascending colon [ə’sendiŋ ‘koulən], transverse colon [‘trænzv
:fəgəs], stomach [‘stΛmək], digestion [di’d3est∫ən], environment [in’vaiərənmənt], secrete [si’kri:t], intestine [in’testin], duodenum [,djuo’di:nəm], jejunum [d3i’d3u:nəm], ileum [‘iliəm], caecum [‘si:kəm], colon [‘koulən], ascending colon [ə’sendiŋ ‘koulən], transverse colon [‘trænzv  :s ‘koulən], descending colon [di’sendiŋ ‘koulən], sigmoid flexure [‘sigmoid ‘flek∫ə], rectum [‘rektəm], anus [‘einəs], approximately [ə’proksimitli], pharyngitis [,færin’d3aitis], esophagitis [i,s
:s ‘koulən], descending colon [di’sendiŋ ‘koulən], sigmoid flexure [‘sigmoid ‘flek∫ə], rectum [‘rektəm], anus [‘einəs], approximately [ə’proksimitli], pharyngitis [,færin’d3aitis], esophagitis [i,s  fə’d3aitis], cancer [‘kænsə], gastritis [gæs’traitis], ulcer disease [‘Λlsə ‘di’zi:z], proctitis [pr
fə’d3aitis], cancer [‘kænsə], gastritis [gæs’traitis], ulcer disease [‘Λlsə ‘di’zi:z], proctitis [pr  k’taitis]
k’taitis]
Make a report on the gastrointestinal tract according to the plan below:
Definition: the GI tract, the alimentary canal or the gut.
Functions: first(ly) to take in food; second((ly), to digest food; third(ly), to extract energy and nutrients; fourth(ly), to expel the remaining waste.
Location: in the upper and lower chest, and the abdomen.
Structure: the upper gastrointestinal tract and the lower gastrointestinal tract.
The upper gastrointestinal tract:
the mouth (the cavity; the salivary glands, mucosa, the teeth and the tongue), the pharynx, the esophagus, and the stomach.
The stomach: a bean-shaped hollow muscular organ; is involved in the second phase of digestion; has a highly acidic environment; produces and secretes about 2 to 3 liters of gastric acid per day.
The lower gastrointestinal tract: first(ly), the small intestine and second(ly), the large intestine.
The small intestine: the duodenum, the jejunum, the ileum
The large intestine: the caecum, the colon (ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and sigmoid colon), the rectum, and the anus.
Length: approximately 7.5 meters (25 feet).
The most common diseases: esophagitis, esophagus cancer, gastritis, peptic ulcer disease (PUD), stomach perforation, stomach cancer, gastroenteritis, enteritis, duodenitis, colitis, colon cancer, proctitis, rectum cancer.
GASTRITIS
Phonetic exercise: stomach [stΛmək], digestion [di’d3est∫ən], gastritis [gæs’traitis], ulcer disease [‘Λlsə ‘di’zi:z], proctitis [pr  k’taitis], Helicobacter pylori [,hɛlɨkə’bæktər pɪˈlɔraɪ], consumption [kən’sΛmp∫n], steroid [‘ster
k’taitis], Helicobacter pylori [,hɛlɨkə’bæktər pɪˈlɔraɪ], consumption [kən’sΛmp∫n], steroid [‘ster  id], severe [si‘viə], traumatic [tr
id], severe [si‘viə], traumatic [tr  :’mætik], bacteria [bæk’tiəriə], autoimmune [,
:’mætik], bacteria [bæk’tiəriə], autoimmune [,  :t
:t 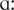 im’ju:n], appetite [‘æpitait], nausea [‘n
im’ju:n], appetite [‘æpitait], nausea [‘n  :siə], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d
:siə], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d  minl], pancreas [‘pæŋkriəs; ‘pæŋkriæs; ‘pænkriəs], bile [bail], reflux [‘ri:flΛks], antacids [,æn’tæsid], antibiotic [,æntibai’
minl], pancreas [‘pæŋkriəs; ‘pæŋkriæs; ‘pænkriəs], bile [bail], reflux [‘ri:flΛks], antacids [,æn’tæsid], antibiotic [,æntibai’  tik]
tik]
Make a report on gastritis according to the plan below:
Definition: an inflammation of the lining of the stomach.
Causes: excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen, major surgery, traumatic injury, burns, severe infections, weight loss surgery resulting in infection with bacteria, primarily Helicobacter pylori, certain diseases, such as chronic bile reflux, stress and certain autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms, signs, clinical manifestations, clinical features: upper central abdominal pain, dull pain, vague pain, burning pain, sharp pain; other signs and symptoms: nausea, clear, green or yellow, blood-streaked, or completely bloody vomiting, bloating, feeling full after only a few bites of food, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, etc.
Evaluation:
History: a personal medical history or a previous history, a history of the present illness, a history of presenting complaint, a childhood illness history, a past medical history, a family history, a pregnancy history, a medication or drug history, an occupational history, a social history, a surgical history, an environmental history, a diet history, etc.
Physical evaluation: observation, percussion, palpation, and auscultation.
Instrumental examination: blood tests: blood cell count, tests for presence of H. pylori, pregnancy, liver, kidney, gallbladder, or pancreas functions; urinalysis, stool sample to look for blood in the stool; X-rays, ECGs, endoscopy to check for stomach lining inflammation and mucous erosion, stomach biopsy to test for gastritis and other conditions.
Treatment: over-the-counter antacids in liquid or tablet for mild gastritis; antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, cytoprotective agents, bismuth subsalicylate, etc.
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
Phonetic exercise: ulcer disease [‘Λlsə ‘di’zi:z], gastrointestinal tract [,gæstrəuin’testinl ‘trækt], stomach [stΛmək], prevalence [‘prevələns], occurrence [ə’kΛrəns; ə’k  :rəns], Helicobacter pylori [ˌhɛlɨkəˈbæktər pɪˈlɔraɪ], esophagus [i:’s
:rəns], Helicobacter pylori [ˌhɛlɨkəˈbæktər pɪˈlɔraɪ], esophagus [i:’s  :fəgəs], duodenum [,djuo’di:nəm], gnawing [‘n
:fəgəs], duodenum [,djuo’di:nəm], gnawing [‘n  :iŋ], erosions [i’rəu3ənz], peritonitis [,peritəu’naitis], antacids [,æn’tæsid], antibiotic [,æntibai’
:iŋ], erosions [i’rəu3ənz], peritonitis [,peritəu’naitis], antacids [,æn’tæsid], antibiotic [,æntibai’  tik], pancreas [‘pæŋkriəs; ‘pæŋkriæs; ‘pænkriəs], hemorrhage [‘hemərid3], biopsy [‘baiəpsi], reflux [‘ri:flΛks], species [‘spi:∫iz], tarry [‘tæri], feces [‘fi:si:z], perforation [,pə:fə’rei∫n], penetration [,peni’trei∫n]
tik], pancreas [‘pæŋkriəs; ‘pæŋkriæs; ‘pænkriəs], hemorrhage [‘hemərid3], biopsy [‘baiəpsi], reflux [‘ri:flΛks], species [‘spi:∫iz], tarry [‘tæri], feces [‘fi:si:z], perforation [,pə:fə’rei∫n], penetration [,peni’trei∫n]
Make a report on peptic ulcer disease according to the plan below:
Definition: an ulcer (defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm) of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful.
Epidemiology: the lifetime risk for developing a peptic ulcer: approximately 10%.
In the United States about 4 million people have active peptic ulcers and about 350,000 new cases are diagnosed each year. Approximately 3,000 deaths per year in the United States are due to duodenal ulcer and 3,000 to gastric ulcer.
Causes: 70-90% of ulcers are associated with Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that lives in the acidic environment of the stomach: ulcers can also be caused or worsened by drugs such as aspirin and other non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs); about 4% of stomach ulcers are caused by a malignant tumor.
Classification: stomach ulcer (called gastric ulcer), duodenum ulcer (called duodenal ulcer), oesophagus ulcer (called oesophageal ulcer).
Symptoms, signs, clinical manifestations, clinical features: abdominal pain, classically epigastric pain with severity relating to mealtimes, bloating and abdominal fullness, nausea, vomiting, burning or gnawing feeling, loss of appetite, weight loss, vomiting of blood, tarry feces, rarely a gastric or duodenal perforation, which leads to acute peritonitis. This is extremely painful and requires immediate surgery.
Evaluation:
History: a personal medical history: a history of heartburn, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a medication history, a history of use of certain forms of medications such as NSAID (non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs).
Physical examination: observation, percussion, and palpation.
Instrumental evaluation: urea breath test, biopsy, measurement of antibody levels in blood, stool antigen tests, histological examination of biopsy, etc.
Complications: gastrointestinal bleeding, perforation that leads to acute peritonitis, penetration into adjacent organs such as the liver and pancreas, scarring and swelling, duodenal and gastric obstruction, etc.
Treatment: antacids, antibiotics, bismuth compounds, surgical repair of the perforation, endoscopy urgently to stop bleeding, etc.
THE LIVER
Phonetic exercise: liver [‘livə], largest [‘l  d3ist], [‘l
d3ist], [‘l  d3əst], glandular [‘glændjulə], detoxification [,di:t
d3əst], glandular [‘glændjulə], detoxification [,di:t  ksifi’kei∫n], glycogen storage [‘glaikəud3ən ‘sto:rid3], glycogen [‘glikəud3en], plasma protein synthesis [‘plæmə ‘proutiin ‘sinθəsis], bile production [bail prə’dΛk∫n], diaphragm [‘daiəfræm], upper abdomen [‘Λpə ‘æbdəmen], triangular [,trai’æŋgjulə], lobes [loubz], visceral peritoneum [‘visərəl ,peritəu’ni:əm], membrane [‘membrein], hepatocytes [‘hepətəsaits], hepatitis [,hepə‘taitis], cirrhosis [si’rousis]
ksifi’kei∫n], glycogen storage [‘glaikəud3ən ‘sto:rid3], glycogen [‘glikəud3en], plasma protein synthesis [‘plæmə ‘proutiin ‘sinθəsis], bile production [bail prə’dΛk∫n], diaphragm [‘daiəfræm], upper abdomen [‘Λpə ‘æbdəmen], triangular [,trai’æŋgjulə], lobes [loubz], visceral peritoneum [‘visərəl ,peritəu’ni:əm], membrane [‘membrein], hepatocytes [‘hepətəsaits], hepatitis [,hepə‘taitis], cirrhosis [si’rousis]
Make a report on the liver according to the plan below:
Definition: the largest glandular organ, a soft reddish brown triangular organ.
Functions: first(ly), drug detoxification, second(ly), glycogen storage, third(ly), plasma protein synthesis, fourth(ly), bile production.
Location: under the diaphragm on the right side of the upper abdomen.
Structure: 4 lobes; 8 segments; covered by visceral peritoneum;
the peritoneum: a thin, double-layered membrane that reduces friction against other organs; major cells: hepatocytes
Size and weight: the second largest organ; the largest gland in the human body; 1.4 and 1.6 kilograms; the abnormal liver: 16-20 kg
The most common diseases: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, cirrhosis, liver cancer, etc.
LIVER CIRRHOSIS
Phonetic exercise: cirrhosis [sɪˈroʊsɪs], liver [‘livə], consequence [‘k  nsikwəns], chronic [‘kr
nsikwəns], chronic [‘kr  nik], fibrosis [fai’broʊsis], process [‘proʊsəs], hepatitis [,hepə‘taitis], damage [‘dæmid3], toxins [‘t
nik], fibrosis [fai’broʊsis], process [‘proʊsəs], hepatitis [,hepə‘taitis], damage [‘dæmid3], toxins [‘t  :ksinz], acute [ə‘kju:t], cyanosis [,saiə’n
:ksinz], acute [ə‘kju:t], cyanosis [,saiə’n 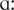 usis], pressure [‘pre∫ə], hypertension [,haipə’ten∫n], inflammation [,inflə’mei∫n], characterized [‘kæktəraizd], ascites [ə’saiti:z], tissue [’tisju:, ’ti∫ju:], virus [‘vaiərəs], viral [‘vaiərəl], asymptomatic [ə,simptə‚mætik], scar [‘sk
usis], pressure [‘pre∫ə], hypertension [,haipə’ten∫n], inflammation [,inflə’mei∫n], characterized [‘kæktəraizd], ascites [ə’saiti:z], tissue [’tisju:, ’ti∫ju:], virus [‘vaiərəs], viral [‘vaiərəl], asymptomatic [ə,simptə‚mætik], scar [‘sk  ], alcohol [‘ælkə‘h
], alcohol [‘ælkə‘h  l], alcoholic [,ælkə‘h
l], alcoholic [,ælkə‘h  lik], malaise [mə‘leiz, mæ‘leiz], nausea [‘n
lik], malaise [mə‘leiz, mæ‘leiz], nausea [‘n  :siə], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d
:siə], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d  minl], diarrhea [‚daiə‘riə, ‚daiə‘ri:ə], jaundice [‘d3
minl], diarrhea [‚daiə‘riə, ‚daiə‘ri:ə], jaundice [‘d3  :ndis], discomfort [dis‘kΛfət], diet [daiət], ultrasound [‘Λltrəsaund]
:ndis], discomfort [dis‘kΛfət], diet [daiət], ultrasound [‘Λltrəsaund]
Make a report on liver cirrhosis according to the plan below:
Definition: consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules.
Causes: alcoholism, hepatitis B and C, fatty liver disease, hepatotoxic drugs or toxins etc.
Epidemiology: the 10th leading cause of death for men and the 12th for women in the United States.
Complications: ascites (fluid retention in the abdominal cavity), hepatic encephalopathy (confusion and coma), hepatocellular carcinoma, portal hypertension, immune system dysfunction, leading to infection.
Symptoms, signs, clinical manifestations, clinical features: enlarged or shrunken liver, splenomegaly (increase in size of the spleen), ascites (accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity), jaundice (yellow discoloring of the skin and eyes); other symptoms: weakness, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, bruising and bleeding, itching, etc.
Evaluation:
History: a personal medical history, a medication history, a family history, an alcohol consumption history, an infectious disease history, a social history, an occupational history, etc.
Physical examination: observation, percussion, and palpation.
Instrumental evaluation: liver biopsy, laboratory blood tests, ultrasound, etc.
Treatment: cannot be reversed; a healthy diet, antibiotics, laxatives; avoidance of alcohol and paracetomol; vaccination of susceptible patients for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B; diuretics to suppress ascites; propranolol to lower blood pressure over the portal system; liver transplantation, etc.
LIVER CANCER
Phonetic exercise: cirrhosis [sɪˈroʊsɪs], liver [‘livə], cancer [‘kænsə], carcinoma [,k  si‘noumə], consequence [‘k
si‘noumə], consequence [‘k  nsikwəns], chronic [‘kr
nsikwəns], chronic [‘kr  nik], fibrosis [fai’broʊsis], process [‘proʊsəs], hepatitis [,hepə‘taitis], damage [‘dæmid3], metastases [mi‘tæstəesi:z], nausea [‘n
nik], fibrosis [fai’broʊsis], process [‘proʊsəs], hepatitis [,hepə‘taitis], damage [‘dæmid3], metastases [mi‘tæstəesi:z], nausea [‘n  :siə], cyanosis [,saiə’n
:siə], cyanosis [,saiə’n 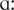 usis], pressure [‘pre∫ə], hypertension [,haipə’ten∫n], inflammatimon [,inflə’mei∫n], characterized [‘kæktəraizd], ascites [ə’saiti:z], tissue [’tisju:, ’ti∫ju:], virus [‘vaiərəs], viral [‘vaiərəl], asymptomatic [ə,simptə‚mætik], scar [‘sk
usis], pressure [‘pre∫ə], hypertension [,haipə’ten∫n], inflammatimon [,inflə’mei∫n], characterized [‘kæktəraizd], ascites [ə’saiti:z], tissue [’tisju:, ’ti∫ju:], virus [‘vaiərəs], viral [‘vaiərəl], asymptomatic [ə,simptə‚mætik], scar [‘sk  ], alcohol [‘ælkə‘h
], alcohol [‘ælkə‘h  l], alcoholic [,ælkə‘h
l], alcoholic [,ælkə‘h  lik], malaise [mə‘leiz, mæ‘leiz], nausea [‘n
lik], malaise [mə‘leiz, mæ‘leiz], nausea [‘n  :siə], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d
:siə], abdomen [‘æbdəmen], abdominal [æb’d  minl], diarrhea [‚daiə‘riə, ‚daiə‘ri:ə], jaundice [‘d3
minl], diarrhea [‚daiə‘riə, ‚daiə‘ri:ə], jaundice [‘d3  :ndis], discomfort [dis‘kΛfət], diet [daiət], ultrasound [‘Λltrəsaund], cadaveric [kə‘dævərik], infectious [in‘fek∫əs], methods [‘meθədz], prostate [‘pr
:ndis], discomfort [dis‘kΛfət], diet [daiət], ultrasound [‘Λltrəsaund], cadaveric [kə‘dævərik], infectious [in‘fek∫əs], methods [‘meθədz], prostate [‘pr  steit], techniques [tek’ni:ks], modality [məu’dæləti], auscultation [,
steit], techniques [tek’ni:ks], modality [məu’dæləti], auscultation [,  :skəl’tei∫n], percussion [pə’kΛ∫n; pə:’kΛ∫n], palpation [pæl’pei∫n]
:skəl’tei∫n], percussion [pə’kΛ∫n; pə:’kΛ∫n], palpation [pæl’pei∫n]
Make a report on liver cancer according to the plan below:
Definition: a cancer which starts in the liver, as opposed to a cancer which originates in another organ and migrates to the liver, known as a liver metastasis.
The most frequent forms: hepatocellular carcinoma; metastases from other tumors, frequently from tumors of the GI tract (like colon cancer) but also from breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, renal cancer, prostate cancer, etc.
The main risk factors, risk situations, risk groups for hepatocellular carcinoma: alcoholism, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Aflatoxins (naturally occurring mycotoxins), cirrhosis of the liver, Wilsons disease (a genetic disorder in which copper accumulates in tissues), anabolic steroids,
Symptoms, signs, clinical manifestations, clinical features: abdominal mass, abdominal pain, nausea,vomiting, anemia, back pain, jaundice, itching, weight loss, fever, an enlarged liver, some other liver dysfunction, etc.
Evaluation: History: a personal medical history, a medication history, a family history, an alcohol consumption history, an infectious disease history, a social history, an occupational history, a history of toxins, etc.
Physical examination: observation, percussion, and palpation.
Instrumental evaluation: CT scanning of the abdomen, MRI studies, etc.
Treatment: surgical resection to remove a tumor together with surrounding liver tissue; liver transplantation to replace the diseased liver with a cadaveric liver or a living donor graft; selective internal radiation therapy; hormonal therapy; cryosurgery: a new technique that can destroy tumors in a variety of sites (brain, breast, kidney, prostate, liver), etc.
Дата: 2018-09-13, просмотров: 522.