Definition: degenerative joint disease, a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints.
Epidemiology: 27 million people in the United States; 735,000 hospitalizations for OA in the USA; 8 million people in the United Kingdom.
Causes and risk factors: mechanical stress, loss of strength in muscles and supporting joints, impairment of peripheral nerves, congenital disorders of joints, pathogenic factors, diabetes, overweight, obesity, injury to joints, aging, etc. Genetic factors: up to 60% of OA cases.
Symptoms, signs, clinical manifestations, clinical features: acute pain, sharp aches, loss of ability, stiffness, tenderness, a burning sensation in the muscles and tendons, a crackling noise, muscle spasms, regional muscular atrophy, etc.
Commonly affected joints: the hands, feet, spine, and fingers.
Evaluation: history: a personal medical history, a family history, a medication history, an occupational history, a social history, a surgical history, etc.
Physical examination: observation, palpation, persussion, and auscultation.
Instrumental evaluation: X-ray.
Treatment: weight loss, physical therapy, exercises, analgesics, acetaminophen / paracetamol, vitamin A, C, and E, omega-3 fatty acids, joint replacement, etc.
MEDICAL HUMOR
Boneheads – orthopaedics. Overpriced carpenter - orthopaedic doctor
Dr. Chicken Bones - medical slang for Chiroprators that take a little different approach to treating their clients. Some times they practice without a license and only deal in cash or trade.
Does it hurt when you go to that Dr. Chicken Bones?
Sometimes...but afterwards it does make my back feel better
MUSCLES
Phonetic exercise: muscles [‘mʌslz], muscular [‘mʌskjulə], contractile [kən’træktail], tissue [‘tisju:], skeletal [‘skelitəl], smooth [smu:ð], cardiac [‘ka:diæk], involuntary [in’vɔləntəri], striated [strai’eitid], average [‘ævəridʒ], conscious [‘kɔnʃəs], control [kən’troul]
Make a report on muscles according to the plan below:
Definition: contractile tissue of animals and humans.
Groups of muscles: head muscles, neck muscles, intraocular muscles, ear muscles, nose muscles, mouth muscles, tongue muscles, vertebral muscles, back muscles, chest muscles, abdominal muscles, pelvic muscles, muscles of upper extremities, muscles of lower extremities, shoulder muscles, hand muscles, thigh muscles, leg muscles, etc.
Function: to produce force and cause motion.
Types of muscles: first(ly), skeletal muscles, second(ly), smooth muscles, and third(ly) cardiac muscles;
Skeletal muscles: "voluntary muscle", anchored by tendons to bones, striated muscles; 639 skeletal muscles.
Function: to effect skeletal movements.
Smooth muscles: "involuntary” muscles, are not under conscious control.
Location: within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels, etc.
Cardiac muscle: an "involuntary muscle", a striated muscle.
Location: only in the heart.
Common diseases: cerebrovascular accident (stroke), Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, etc.
POLYMYOSITIS
Phonetic exercise: chronic [‘kr  nik], inflammatory [in’flæmətəri], myopathy [mai’
nik], inflammatory [in’flæmətəri], myopathy [mai’  pəθi], early [‘ə:li], fatigue [fə‘ti:g], autoimmune [,
pəθi], early [‘ə:li], fatigue [fə‘ti:g], autoimmune [,  təui’mju:n], kinase [’kineis], electromyography [,ilektro‘maiogrəfi], biopsy [‘baiəpsi], characterized [‘kærəktəraizd], evaluation [i,vælju’ei∫n], epidemiology [‘epi,di:mi’
təui’mju:n], kinase [’kineis], electromyography [,ilektro‘maiogrəfi], biopsy [‘baiəpsi], characterized [‘kærəktəraizd], evaluation [i,vælju’ei∫n], epidemiology [‘epi,di:mi’  ləd3i]
ləd3i]
Make a report on polymyositis according to the plan below:
Definition: a type of chronic inflammatory myopathy, 'many muscle’ inflammation.
Symptoms, signs, clinical manifestations, clinical features: bilateral proximal muscle weakness often noted in the upper legs, early fatigue while walking, progressive weakness, etc.
Risk groups: The disease strikes females with greater frequency than males.
Causes: unknown; possible causes: autoimmune factors, genetics, and perhaps viruses.
Evaluation:
History: a personal medical history, a family history, a medication history, an occupational history, an environmental history, a surgical history, etc.
Physical examination: observation and palpation.
Instrumental evaluation: creatine kinase, electromyography, and muscle biopsy, etc.
Treatment: high-dose steroids, specialized exercise therapy, etc.
Myasthenia gravis
Phonetic exercise: myasthenia [,maiæs’θi:niə], evaluation [i,vælju’ei∫n], fatigue [fə‘ti:g], facial [‘fei∫əl], control [kən’troul], limb [lim], swallowing [‘sw  ləuiŋ], noticeabl [‘nəutisəbl], upward [‘Λpwəd], spirometry [,spaiə‘r
ləuiŋ], noticeabl [‘nəutisəbl], upward [‘Λpwəd], spirometry [,spaiə‘r  mitri]
mitri]
Make a report on myasthenia gravis according to the plan below:
Definition: an autoimmune neuromuscular disease leading to fluctuating muscle weakness and fatiguability.
Affected organs: eye muscles, eyelid muscles, facial muscles, muscles that control breathing, neck muscles, limb muscles, etc.
Symptoms, signs, clinical manifestations, clinical features: fatiguability, the most noticeable symptoms: weakness of the eye muscles, difficulty in swallowing, slurred, drooping of one or both eyelids; other symptoms: double vision, unstable or waddling gait, weakness in arms, hands, fingers, legs, and neck, a change in facial expression, etc.
Evaluation:
Physical examination:
· looking upward and sidewards for 30 seconds: ptosis and diplopia.
· looking at the feet while lying on the back for 60 seconds
· keeping the arms stretched forward for 60 seconds
· 10 deep knee bends
· walking 30 steps on both the toes and the heels
· 5 situps, lying down and sitting up completely
Instrumental evaluation: blood tests, X-ray, CT, MRI, pulmonary function tests, spirometry, muscle biopsy, etc.
Treatment: medications: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and immunosuppressive drugs; plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG), surgery: thymectomy, etc.
MEDICAL HUMOR
So this man was helping his best friend move to a new house. He groaned as he helped a large couch. “Look,” his friend said helpfully, “at least you are developing your muscles.”
“Yeah,” replied the friend, wryly, “either that or a hernia.”
THE HEART
Phonetic exercise: heart [ha:t], pear [pεə], muscular [‘m  skjulə], pump [p
skjulə], pump [p  mp], organ [‘
mp], organ [‘  :gən], blood [bl
:gən], blood [bl  d], vessels [‘veslz], repeated [ri’pi:tid], rhythmic [‘riðmik], contractions [kən’træk∫nz], thorax [‘θ
d], vessels [‘veslz], repeated [ri’pi:tid], rhythmic [‘riðmik], contractions [kən’træk∫nz], thorax [‘θ  :r
:r  ks], surrounded [s
ks], surrounded [s  ’raundid], breastbone [‘brestboun], cardiac [‘k
’raundid], breastbone [‘brestboun], cardiac [‘k 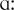 diæk], involuntary muscles [in’v
diæk], involuntary muscles [in’v  ləntəri ‘mΛslz], pericardium [,peri’k
ləntəri ‘mΛslz], pericardium [,peri’k 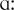 diəm], endocardium [,endə’k
diəm], endocardium [,endə’k 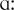 diəm], myocardium [,maiə’k
diəm], myocardium [,maiə’k 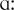 diəm], chamber [‘t∫eimbə], chambers [‘t∫eimbəz], upper atria [‘Λpə ‘eitriə], lower ventricles [‘ləuə ‘ventriklz], mitral valve [‘maitrəl ‘vælv], tricuspid valve [trai’kΛspid ‘vælv], semilunar valve [,semi’lu:nə ‘vælv], aorta [ei’
diəm], chamber [‘t∫eimbə], chambers [‘t∫eimbəz], upper atria [‘Λpə ‘eitriə], lower ventricles [‘ləuə ‘ventriklz], mitral valve [‘maitrəl ‘vælv], tricuspid valve [trai’kΛspid ‘vælv], semilunar valve [,semi’lu:nə ‘vælv], aorta [ei’  :tə], pulmonary artery [‘pΛlmənəri ‘a:təri], females [‘fi:meilz], males [meilz], beats per minute [‘bi:ts ‘p
:tə], pulmonary artery [‘pΛlmənəri ‘a:təri], females [‘fi:meilz], males [meilz], beats per minute [‘bi:ts ‘p  :‘minit], bradycardia [,brædi’k
:‘minit], bradycardia [,brædi’k  diə], tachycardia [,tæki’ka:diə], circulation [,s
diə], tachycardia [,tæki’ka:diə], circulation [,s  :kju’lei∫n], oxygenated blood [‘
:kju’lei∫n], oxygenated blood [‘  ksid3ineitid ‘bl
ksid3ineitid ‘bl  d], deoxygenated blood [di:’
d], deoxygenated blood [di:’  ksid3ineitid ‘bl
ksid3ineitid ‘bl  d], endocarditis [,endoka:’daitis], pericarditis [,perika:’daitis], myocarditis [,maiəka:’daitis], myocardial infarction [,maiə’ka:diəl in’fa:k∫n]; congestive heart failure [kən’d3estiv ‘ha:t ‘feiljə], angina pectoris [æn’d3ainə ‘pektəris], atrial fibrillation [‘eitriəl ,faibri’lei∫n]
d], endocarditis [,endoka:’daitis], pericarditis [,perika:’daitis], myocarditis [,maiəka:’daitis], myocardial infarction [,maiə’ka:diəl in’fa:k∫n]; congestive heart failure [kən’d3estiv ‘ha:t ‘feiljə], angina pectoris [æn’d3ainə ‘pektəris], atrial fibrillation [‘eitriəl ,faibri’lei∫n]
Make a report on the heart according to the plan below:
Definition: a pear shaped, muscular organ.
Function: to pump blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions.
Location: to the left of the middle of the thorax; surrounded by the lungs, protected by the thorax: the breastbone and ribs.
Structure: cardiac muscle: striped and involuntary;
the pericardium, the endocardium, the myocardium;
four chambers: the two upper atria and the two lower ventricles;
four valves: the mitral valve, the tricuspid valve, the semi-lunar valve of the aorta, and the semi-lunar valve of the pulmonary artery.
Size and/or weight or volume: about three fourths the size of a clenched fist;
250 g in females and 350 g in males; the abnormal heart: up to 1,000 g
Physiology: the normal heart beat: 70 bpm in males and 75 bpm in females;
bradycardia: if less than 60 bpm; tachycardia: if greater than 100 bpm.
120 times (beats) per minute in childhood;
Two types of circulation: the systemic circulation and the pulmonary circulation.
Deoxygenated blood: from the right atrium to the right ventricle, from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Oxygenated blood: from the lungs to the left atrium, from the left atrium to the left ventricle, from the left ventricle to all tissues.
The most common diseases: endocarditis, pericarditis, myocarditis, myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation, congenital heart defects, acquired heart defects, valvular heart disease, etc.
Myocardial infarction
Phonetic exercise: heart [h  t], attack [ə’tæk], pericarditis [,perik
t], attack [ə’tæk], pericarditis [,perik  ’daitis], myocarditis [,maiək
’daitis], myocarditis [,maiək  ’daitis], myocardial infarction [,maiə’k
’daitis], myocardial infarction [,maiə’k  diəl in’f
diəl in’f  k∫n]; congestive heart failure [kən’d3estiv ‘h
k∫n]; congestive heart failure [kən’d3estiv ‘h  t ‘feiljə], angina pectoris [æn’d3ainə ‘pektəris], atrial fibrillation [‘eitriəl ,faibri’lei∫n], interruption [,intə’rΛp∫n], supply [sə‘plai], cholesterol [kə‘lestr
t ‘feiljə], angina pectoris [æn’d3ainə ‘pektəris], atrial fibrillation [‘eitriəl ,faibri’lei∫n], interruption [,intə’rΛp∫n], supply [sə‘plai], cholesterol [kə‘lestr  l], pressure [‘pre∫ə], ischaemic [is’ki:mik], ischemia [is’ki:miə], obesity [əu’bi:səti], evaluation [i,vælju’ei∫n], cessation [ses’ei∫n], saturated [‘sæt∫əreitid], statin [‘stætin], characterized [‘kærəktəraizd], epidemiology [‘epi,di:mi’
l], pressure [‘pre∫ə], ischaemic [is’ki:mik], ischemia [is’ki:miə], obesity [əu’bi:səti], evaluation [i,vælju’ei∫n], cessation [ses’ei∫n], saturated [‘sæt∫əreitid], statin [‘stætin], characterized [‘kærəktəraizd], epidemiology [‘epi,di:mi’  ləd3i]
ləd3i]
Make a report on myocardial infarction according to the plan below:
Definition: a heart attack, the interruption of blood supply to part of the heart, causing heart cells to die.
Epidemiology: 12.6 percent of worldwide deaths from ischemic heart disease.
Risk factors: diabetes, tobacco smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, family history of ischaemic heart disease (IHD), obesity, age, stresses, alcohol, etc. Males are more at risk than females.
Symptoms: sudden chest pain, pain typically radiating to the left arm or left side of the neck, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, palpitations, sweating, and anxiety; silent infarction: 10-25%.
Evaluation: History: a personal medical history, a family history, a medication history, an occupational history, etc.
Physical examination: observation, palpation, percussion, and auscultation
Instrumental evaluation: electrocardiography, coronary angiography
Treatment: oxygen, aspirin, and nitroglycerin, bypass surgery.
Prevention: strict blood pressure management, lifestyle changes: smoking cessation, regular exercise, a sensible diet for patients with heart disease, polyunsaturated fats instead of saturated fats and limitation of alcohol intake, antiplatelet drug therapy such as aspirin and/or clopidogrel, beta blocker therapy, statin therapy, ACE inhibitors, omega-3 fatty acids.
HYPERTENSION
Phonetic exercise: blood [blΛd], pressure [‘pre∫ə], chronic [‘kr  nik], heart failure [‘h
nik], heart failure [‘h 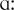 t ‘feiljə], stroke [str
t ‘feiljə], stroke [str  uk], transient [‘trænziənt], ischemic [is’ki:mik], hypertension [,haipə’ten∫n], hypertensive [,haipə’tensive], primary [‘praiməri], secondary [‘sekəndəri], renal failure [‘ri:nl ‘feiljə], attack [ə’tæk], cardiomyopathy [,k
uk], transient [‘trænziənt], ischemic [is’ki:mik], hypertension [,haipə’ten∫n], hypertensive [,haipə’tensive], primary [‘praiməri], secondary [‘sekəndəri], renal failure [‘ri:nl ‘feiljə], attack [ə’tæk], cardiomyopathy [,k  di
di  mai’
mai’  pəθi], previous [‘pri:viəs], measurement [‘me3əmənt], environmental [in,vaiərən’məntl]
pəθi], previous [‘pri:viəs], measurement [‘me3əmənt], environmental [in,vaiərən’məntl]
Make a report on high blood pressure according to the plan below:
Definition: a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated.
Epidemiology: nearly one billion people or ~ (approximately) 26% of the adult population have hypertension worldwide.
Classification: primary hypertension (95%), secondary hypertension (5%).
Causes of primary hypertension: no medical causes
Causes and risk factors of secondary hypertension: conditions that affect the kidneys, arteries, heart, or endocrine system; a body mass index greater than 25 salt (sodium) sensitivity, alcohol intake, vitamin D deficiency, aging, some inherited genetic mutations, a family history of hypertension, an elevation of renin, a hormone secreted by the kidney, etc.
Дата: 2018-09-13, просмотров: 489.