1) Sinus sagittalis superior- passes sagittaly along superior margin of falx cerebri. It contains anastomoses with emisssaria parietalis et emissaria foraminis coeci.
2) Sinus sagittalis inferior- located along inferior margin of falx cerebri. It is connected with v. magna cerebri Galeni that forms sinus rectus, running into sinus sagittalis superior.
3) Sinus occipitalis- from foramen magnum and merges with sinus sagittalis superior and sinus rectus, forming expansion of venous flow (confluens sinum)
4) Sinus transversus- located on the sulcus transversus of occipital bone and transforms into S-shaped sinus.
5) Sinus sigmoideus (S-shaped) - located on the sulcus sigmoideus of processus mastoideus up to foramen jugularis on the base of skull. It goes through v emissaria mastoidea- forms anastomosis with occipital vein.
6) Sinus cavernosus- It is the system of venous sinuses that surrounds sella turcica with hypophysis. It forms anastomosis with orbital veins and deep veins of facial region. Blood from sinus cavernosus moves away through paired sinus petrosus superior et inferior- located on the similarly named sulcus (sulcus petrosus superior et inferior) in pyramid of temporal bone, to sinus sigmoideus.
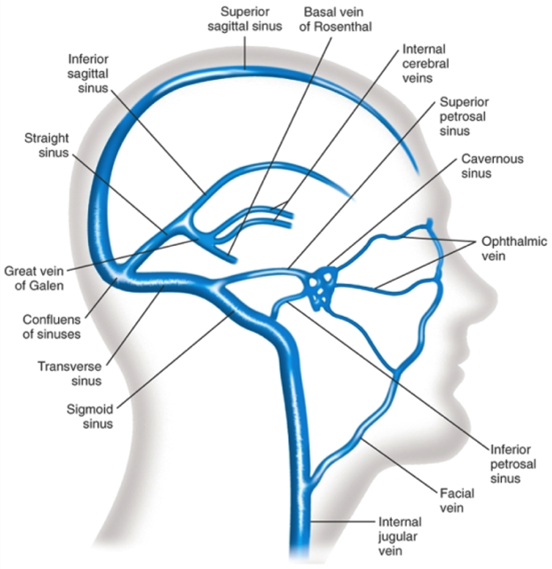
Fig 46. Venous sinuses of dura mater encephali.
BLOOD SUPPLY TO BRAIN
Paired arteries: aa. carotis interna et aa. vertebralis supply blood to brain. The two vertebral arteries join at the base of skull to form a. basilaris. Two aa. cerebri posterioris branch out from a. basilaris, while from a. carotis interna- a. cerebri media, a. cerebri anterior and a. communicans anterior. Hence forms circulus anteriosus cerebri (Wilisii) which lies in the subarachnoid space at the base of the brain and surrounds sella turcica and chiasm of optical nerves.
Cronlein’s scheme, further added by S.S. Brjusova is recommended for the projection of sulcus, gyrus of brain and vessels on the surface of calvarium. Following lines are applied on the skin of the head:
1) lower horizontal- follows through the lower margin of orbit.
2) upper horizontal- goes parallel to first one through superior margin of orbit.
3) median line- follows suture sagittalis.
4) anterior- vertical- passes through the mid of zygomatic arch.
5) medial-vertical- passes through the middle of processus condylaris of mandibula
6) posterior-vertical- through base of processus mastoideus.
7) line connecting the crossway of 2nd and 4th lines with 6th line.
8) line representing the bisector angle, formed by the 7th line and the 2nd line.
9) Brjusov’s line- passes parallel to 2nd line through the crossing point of 6th and 8th line.
Central (Roland’s) sulcus corresponds to the scheme of 7th line, occupying from second and third verticals. Anterior central gyrus of brain lies in front of this line while posterior central gyrus of brain lies behind it. Projection of Sylvian’s sulcus corresponds to the scheme of 8th line.
The main trunk of a. meningea media is projected on the crossing point of first vertical and upper margin of zygomatic arch. Anterior branch passes through the crossing point of first vertical with 2nd line, posterior branch- through the crossing point of posterior vertical with the same 2nd line.
Location of internal carotid artery along the sinus cavernosus is projected on the anterio-inferior quadrangual scheme (Bergman quadrangle). Otogenic abscesses are also located here.
A. cerebralis anterior corresponds to horizontal Brjusov’s line. The place of division of a. cerebralis medialis corresponds to the crossing point of 2nd and 4th line. A. cerebralis posterior is projected above medial horizontal line in its posterior part.
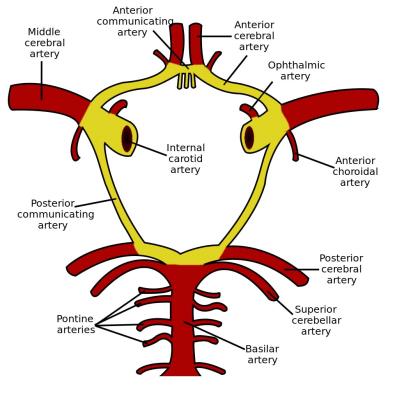
Fig 47. Blood brain to supply.
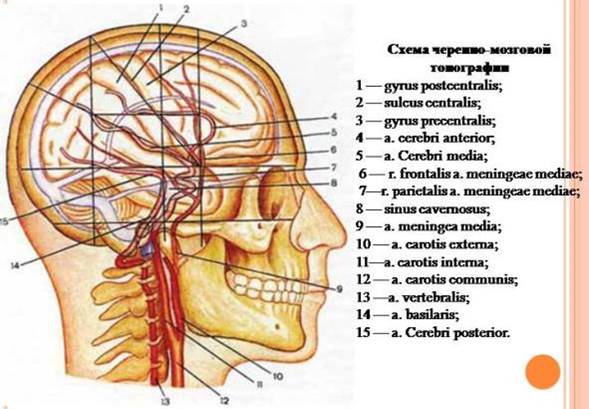
Fig 48. Krenlein scheme.
ТЕМА 10.
Дата: 2019-03-05, просмотров: 1695.