 JOKES ABOUT LAWYERS
A. A gang of robbers broke into a lawyer's club by mistake. The old legal lions gave them a fight for their life and their money. The gang was very happy to escape.
«It isn't so bad», one crook noted. «We got $25 between us.»
The boss screamed: «I warned you to stay clear of lawyers... we had $100 when we broke in!»
B. An engineer, a physicist, and a lawyer were being interviewed for a position as chief executive officer of a large corporation. The engineer was interviewed first, and was asked a long list of questions, ending with «How much is two plus two?» The engineer excused himself, and made a series of measurements and calculations before returning to the board room and announcing, «Four.»
The physicist was next interviewed, and was asked the same questions. Before answering the last question, he excused himself, made for the library, and did a great deal of research. After a consultation with the United States Bureau of Standards and many calculations, he also announced «Four.»
The lawyer was interviewed last, and was asked the same questions. At the end of his interview, before answering the last question, he drew all the shades in the room, looked outside the door to see if anyone was there, checked the telephone for listening devices, and asked «How much do you want it to be?» JOKES ABOUT LAWYERS
A. A gang of robbers broke into a lawyer's club by mistake. The old legal lions gave them a fight for their life and their money. The gang was very happy to escape.
«It isn't so bad», one crook noted. «We got $25 between us.»
The boss screamed: «I warned you to stay clear of lawyers... we had $100 when we broke in!»
B. An engineer, a physicist, and a lawyer were being interviewed for a position as chief executive officer of a large corporation. The engineer was interviewed first, and was asked a long list of questions, ending with «How much is two plus two?» The engineer excused himself, and made a series of measurements and calculations before returning to the board room and announcing, «Four.»
The physicist was next interviewed, and was asked the same questions. Before answering the last question, he excused himself, made for the library, and did a great deal of research. After a consultation with the United States Bureau of Standards and many calculations, he also announced «Four.»
The lawyer was interviewed last, and was asked the same questions. At the end of his interview, before answering the last question, he drew all the shades in the room, looked outside the door to see if anyone was there, checked the telephone for listening devices, and asked «How much do you want it to be?»
|
Task 33. Read the text below and make a list of the courts mentioned there.
THE HIERARCHY OF THE COURTS
In the English legal system some courts are bound to follow the decisions of judges in the higher courts. The following text provides an outline of the hierarchy of the courts and the ways in which judges are bound by the decisions of other courts and the ways in which judges are bound by the decisions of other judges.
The House of Lords is the highest appeal court in the English legal system. Its decisions are binding upon all other courts. Until 1966 the House of Lords was also bound by its own previous decisions. In that year the Lord Chancellor, Lord Gardiner, issued a Practice Statement which stated that «while treating former decisions of this House as normally binding» their Lordships would «depart from a previous decision when it appears right to do so».
The Court of Appeal is below the House of Lords in the hierarchy. It is bound by the decisions of the House of Lords and its decisions are binding on lower courts. It is also bound to follow its own previous decisions except when a previous decision of the Court of Appeal conflicts with a decision of the House of Lords, there are two conflicting Court of Appeal decisions when it must choose which one to follow, and a previous decision was given per incuriam (through lack of care — generally when some relevant law was not taken into consideration). These exceptions to the rule that the Court of Appeal must abide by its own previous decisions are called the rules in Young v. Bristol Aeroplane Company (1944), the case in which the rules were laid down.
 The court below the Court of Appeal is the High Court of Justice. It is bound to follow the decisions of the House of Lords and the Court of Appeal. Judges of the High Court will normally follow the decisions of fellow High Court judges but they are not absolutely bound to do so.
The court below the Court of Appeal is the High Court of Justice. It is bound to follow the decisions of the House of Lords and the Court of Appeal. Judges of the High Court will normally follow the decisions of fellow High Court judges but they are not absolutely bound to do so.
The court of first instance for criminal cases, the Crown Court is bound by the House of Lords and the Court of Appeal; the lowest courts in the hierarchy, the county court and the magistrates' courts are bound by the high Court, the Court of Appeal and the House of Lords. No court is bound by the decisions of these lower courts.
Since 1972 when Britain joined the European Community, the position of the European Court of Justice must also be considered. It is a court of referral in relation to EC law and not a court of appeal, although its decisions on the interpretation of EC law are binding on British courts.
Task 34. Study the table and tell about the structure of the court system in the UK.
THE COURT STRUCTURE OF HER MAJESTY'S
COURTS SERVICE (HMCS)
Her Majesty's Courts Service carries out the administrative and support for the Court of Appeal, the High Court, the Crown Court, the magistrates' courts, the county courts and the Probate Service.
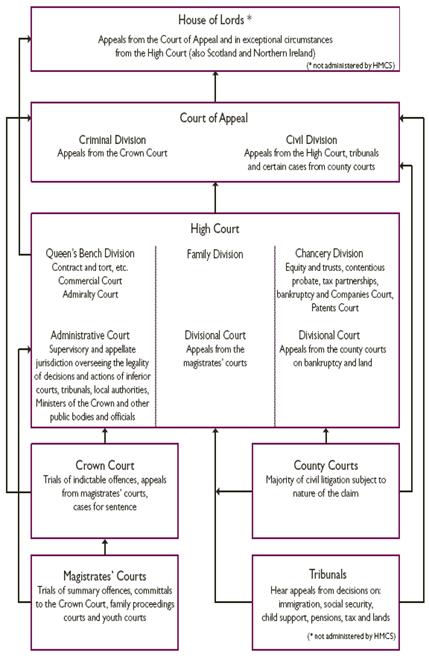
Источник. http://www. hmcourts-service.gov.uk/aboutus/structure/index.htm
 Unit 2
Unit 2
U.S. COURTS
Дата: 2019-02-02, просмотров: 428. |