When she died at the age of 122, Jeanne Calment was the oldest person on record. This amazing woman, from Arles in France, had not exactly lived what might be described as ‘a healthy lifestyle’. Family and friends reported that she (1) _________fond of cheese, wine and chocolate. She had also smoked cigarettes until she was 117. We asked several experts how a person, especially a cigarette-smoker, (2) _________live so long. They offered more than one answer. ‘The average life expectancy (3) _________. now about 80 for women and 75 for men,’ observed Dr Elizabeth Jones, director of the Centre for Studies on Ageing. She says that there (4) _________been a steady rise in the maximum age of death throughout Europe during the past century and a major reason for this is improved medical care. Another researcher, Dr Michael Glass, says, ‘There (5_________no theoretical reasons why we (6) _________have a life span of 200 years.’ Better medical care (7) _________ be the only factor, according to Dr Glass. He explained that genetic engineering (8) _________soon allow us to repair or replace damaged cells, the real cause of ageing. He believes that we (9). _________ able to stop the ageing process. Other researchers have noted that attitude is also an important factor in longer life. Dr John Park is the author of ‘Living Beyond 100’. ‘Those who (10) _________to a ripe old age,’ he says, ‘are those who (11) _________ cope with stress and other difficulties in life.’ He wrote in his best-selling book that people who (12) _________past 100 (13) _________almost always optimistic and (14) _________a great attitude to life.
Task 15. Find for these words correct preposition. Make up sentences in reported speech using these words.
| 1. graduate | 5. spent |
| 2. give | 6. responsible |
| 3. born out | 7. threat |
| 4. drop | 8. affected |
Task 16. Make reported requests or orders. Start each sentence with 'she asked me' or 'she told me'. It's the same day, so you don't need to change the time expressions.
1. "Please help me to understand this law concerning health care"
2. "Don't smoke!"
3. “Could you please explain these terms?”
4. "Could you bring the book tonight?"
5. "Do you best to save your health."
Task 17. Complete the asterisked gaps in the chart below. Use dictionary if necessary.
| NOUN | ADJECTIVE | VERB |
| relief | relieved | * |
| affectation | affected | * |
| moderate | * | moderate |
| expectation | expected | * |
| * | equal | |
| * | perpetuate | |
| need | * | |
| * | educational |
Task 18. Change the interview above to reported speech. Pay attention to tense, pronoun, and adverb agreement.
REPORTER: Congratulations on winning the marathon. How long have you been preparing for this race?
RUNNER: Thank you. About five years, running twelve miles, three times a week.
REPORTER: Why do you like to run?
RUNNER: I haven't always been a runner. I started running when my doctor told me I was over-weight and needed to improve my over all health. At first, it was hard to go a few miles, but now, I'm in better shape and I love it. I can't wait to get out in the morning and run.
REPORTER: What is your favorite part of a marathon?
RUNNER: You might expect me to answer "crossing the finish line", but actually it's when I get to the 20-mile point of the race. I think I can't go on, and then I do! That's my most challenging moment. It's "mind over matter"
REPORTER:Are you planning to run more marathon in the near future?
RUNNER: Yes, I am looking forward to running one in Seattle next month.
REPORTER: Can you give me some advice about getting in shape?
RUNNER: Well, I guess I would tell you to keep moving. Eat healthy food and keep moving.
REPORTER: Wonderful! Thank you for talking to us today and please thank your coach as well. Get some rest!
RUNNER: Thank you. I'm honored to be here on your show.
1. The reporter asked ________
a) how long is it he prepare for race
b) he prepare how long for the race
c) how long did he prepare for the race
d) how long he had been preparing for the race
2. The runner replied that __________ .
a) I have been running for about five years
b) I was running for about five years
c) he had been running for about five years
d) he is running for about five years
3. Next, the reporter asked him _________.
a) why he likes to run
b) why does he like to run
c) why do you like to run
d) why he liked to run.
4. The athlete said _________I needed to improve my overall health.
a) that he needs to improve his overall health.
b) he needed to improve his over-all health.
c) that I have needed to improve my overall health.
d) I needed to improve my overall health.
5. He added that ___________ to get out in the morning and run.
a) I can't wait
b) I couldn't wait
c) he can't wait
d) he couldn't wait
6. Next, the reporter asked him _________.
a) what is your favourite part of a marathon
b) what his favourite part of the marathon was
c) what is his favourite part of the marathon
d) what is it his favourite part of the marathon
7. The marathoner replied ______________ to the 20-mile point in the marathon race.
a) that it is when he gets
b) that it is when I get
c) that it is when he got
d) when he gets
8. He added __________.
a) what is his most challenging moment
b) that was it his most challenging moment
c) that it was his most challenging moment
d) is it his most challenging moment.
9. The reporter inquired __________ more marathons in the near future.
a) whether he was going to run
b) that you are going to run
c) whether are you going to run
d) you going to run
10. The athlete answered ______________.
a) that he was looking forward to running one in Seattle in the coming month
b) that he is looking forward to running one in Seattle next month
c) that he looks forward to running one in Seattle next month
d) if he was looking forward to running one in Seattle next month
11.The reporter asked ______________ about getting back in shape.
a) could he give him some advice
b) whether you could give me some advice
c) that he could give him some advice
d) whether he could give him some advice
12. The athlete advised ________________ .
a) that he eat healthy food and kept moving
b) that he eats healthy food and keeps moving
c) that he is eating healthy food and keeping moving
d) that healthy food he should eat and moving he should keep.
13. The reporter thanked him and ________ his coach as well
a) told him thank
b) told him that he thank
c) told to him to thank
d) told him to thank
14. The reported suggested ___________ some rest.
a) that he get
b) that he got
c) that he will get
d) that he get
15. The athlete responded ____________.
a) I am honored to be here on your show
b) that he is honored to be here on your show.
c) that he was honored to be here on his show.
d) that he was honored to be there on his show
Task 19. Rearrange these words to form sentences, and translate them into Ukrainian.
1. is /well-being / both / as / the / of / illness / as / health / absence / a / state / and/ of / physical / defined / and / emotional /
2. determine / social / factors / and / of / education / largely / income / what / kind/ health / two / we / have /
3. a / in / social / change / also / alcohol / the / harm / done / by / and / automobile / behavior / would / accidents/
4. other / for / national / health-care / improving / emphasize / suggestions / care the / benefits / of / health / a / system /
5. of / the / social / health / emphasize / social / preventing / by / changing / advocates / disease / behavior / movement /
v TRANSLATION
Task 21. Translate the following paragraph into Ukrainian, pay attention to the sentence construction.

Task 22. Choose the best option to translate the sentences.
1. Longer life expectancy is related to a healthy life style.
A. Довше очікування життя пов’язано зі здоровим способом життя.
В. Тривалість життя пов’язана зі здоровим способом життя.
С. Тривалість життя відноситься до здорового способу життя.
2. Mental illness appears to be rather widespread.
A.Виявляеться, психічні хвороби достатньо поширені.
В. Психічні хвороби виникають досить часто.
С. Психічні хвороби виявляеться достатньо поширено.
3. The social model looks for the causes of illness in the social structure.
A. Соціальна модель шукає причини хвороб у соціальній структурі.
В. Соціальна модель схожа на причини хвороб соціальних структур.
C. Соціальна структура шукає причини хвороб у соціальних моделях.
4. Два соціальні фактори – освіта та прибуток – визначають те, яке в нас здоров’я.
А. Two social factors – income and education – largely determine what kind of health we have.
В. Two social factors – income and education – largely determine what kind of health have we.
С. Income and education are two social factors which largely determine what kind of health we have.
5. Чи задоволені ви медичним обслуговуванням у вашій країні?
А. Are you satisfied with medical care in your country?
В. Do you satisfied with medical care in your country?
С. Have you satisfied with medical care in your country?
6. Ціни на медичні послуги в Україні дуже високі.
A. The prices for medical service very high in Ukraine.
B. The prices for medical service are very high in Ukraine.
C.The price tags for medical services are hight.
v WRITING
Task 23. Think about the health care in your country. Do you think this sphere needs some changes? Write five sentences. Then find out about your partner.
 Task 24. Read paragraph about mental illness and analyze it.
Task 24. Read paragraph about mental illness and analyze it.
1. Underline the topic sentence. Is it the first or second sentence?
___________________________
2. Is the first sentence indented?
___________________________
3. How many supporting sentences are there? Which are they?
___________________________
4. Circle the concluding sentence or clause.
__________________________
Task 25. Write a small summary of the text Society and Health for about 10 sentences.
Begin with: 
CHECK YOUR WORK
Have you
used any expressions from the text in your summary?
written 10 sentences?
checked your spelling?
checked punctuation and grammar?

UNIT 10
THE HIDDEN CURRICULUM
v SPEAKING
Task 1. Discuss these questions with a partner.
Ø How would you most like to be remembered in higher school?
Ø Is it popular today to be a brilliant student? Why?
Ø How do you understand a term "student subculture"?
v STUDY SKILLS
Task 2. There are a lot of rhetorical techniques, which can help you to be successful during your presentations in class. The main ones are listed below. Complete them using the words in the box.
| questions language words threes points sounds opposites |
THE SEVEN RULES OF RHETORIC
1. Repeat _______________
I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream.
2. Repeat _______________
We are the people ... who persuaded others to buy British, not by begging them to do so, but because it was best.
3. Use contrasts and __________________
Ask not what your country can do for you – ask what you can do for your country.
4. Group key points in _________________
We must therefore act together as a united people, for national reconciliation, for nation building, for the birth of a new world.
5. Ask rhetorical _____________________
What are our chances of success? It depends on what kind of people we are.
6. Accumulate supporting _________________
We are the people who, amongst other things, invented the computer, the refrigerator, the electric motor, the stethoscope, rayon, the steam turbine, stainless steel, the tank ...
7. Use metaphorical __________________
To lead our country out of the valley of darkness.
v READING
Task 3. Read the text about the important consequences of American education. Write down three interesting things you remember. Compare your notes with other students.
THE STUDENT SUBCULTURE
The primary aim of education remains the transmission of culture. Most parents want the schools to teach their children the skills and knowledge they need to get ahead. But cultural transmission involves more than lessons in geography and long division; it also involves instruction in values and attitudes. Students learn these lessons from all aspects of the school situation, not just from their textbooks. In schools, as in other social organizations, people learn special ways of coping with the situation in which they find themselves. This hidden curriculum, unofficially taught and unconsciously absorbed, is one very important consequence of American education that its founders never intended.
As we have already seen, socialization is best accomplished in primary groups. In schools the most influential primary group for students is their fellow students, or peer group. Young people teach each other how the school system works and how to deal with the demands of the formal curriculum. They also pass on much information to each other directly: information about sex, about drugs, and about the latest fads in clothes and music. More important, students learn the attitudes and values of their peer group.
In any group some kinds of behaviour are considered admirable and will be rewarded with praise and social esteem. To find out what kinds of behaviour adolescents admire most, James Coleman investigated the status systems of ten high schools in the Midwest. All the boys were asked, "How would you most like to be remembered in school: as a brilliant student, as a leader in extra-curricular activities, or as most popular?" Although Coleman had expected to find that high schools in different neighborhoods would have different status systems, he discovered that the similarities were much more striking than the minor differences. Nearly every boy replied that he would rather be a star athlete than be considered popular or brilliant. In every school the "leading crowd," or highest status group, had twice as many athletes and many more popular boys than it had brilliant students.
Similarly, the girls, who were generally better students than the boys in every school, did not want to be considered "brilliant students." They had good reason not to want a reputation for brains: the girls named "best students" in each school had fewer friends and were even less likely than the best male students to be members of the leading crowd. In all the schools students admired academic achievement less than other attributes, especially being a star athlete for boys and being "good looking" for girls. To Coleman these results suggested that the values of the adolescent subculture were a deterrent to academic success. The lesson: Don't be too smart!
Another interesting finding was that students who are seen by their schoolmates as "intellectuals" – and who come to think of themselves in that way – were not necessarily the most intelligent. More important than their intellectual ability was their willingness to work hard at a relatively unrewarded activity. Coleman found a basic sociological reason for the students' low opinion of high grades. Unlike the outstanding athlete, whose victories bring glory to the school in interscholastic competitions, the outstanding students' successes are purely personal triumphs usually won at the expense of their classmates. From the sociological perspective it is not surprising that academic accomplishments are undervalued and that star students are often ridiculed as "grinds."
V VOCABULARY
Task 4. Chose the best headline A-E for each paragraph 1-5 (All the headlines will be used).
| A | Results of investigation | Paragraph 1 |
| B | Point of view about grades | Paragraph 2 |
| C | Ulterior lessons | Paragraph 3 |
| D | Who teaches? | Paragraph 4 |
| E | To be clever or to be sports | Paragraph 5 |
Task 5. Match the column A with column B.
| A | В | ||
| long division | A | впливовий; | |
| a consequence | B | мода; | |
| Influential | C | чудовий; | |
| a fad | D | натовп; компанія; | |
| an \ to esteem | E | невинагороджений; | |
| Admirable | F | стримуючий фактор; | |
| a crowd | G | ботан; зубрило; | |
| a deterrent | H | арифметика; математика; | |
| Unrewarded | I | результат; | |
| a grind | J | повага; високо оцінювати; |
Task 6. Fill in the correct words from the previous exercise into the gaps below (not all words are needed).
1. These aspects of schooling are unintended _________ of establishing an educational institution where children of the same age spend most of their waking hours together in an organizational setting.
2. By setting up a situation in which Peggy "wins" and Boris "loses", the higher school is shaping their image of themselves as a "_________." or a "loser".
3. In hundreds of formal and informal ways teachers unwittingly _________students by their own standards of behaviour.
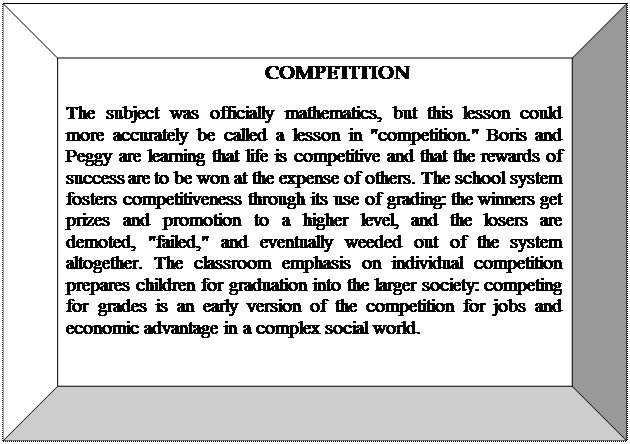
4. The subject was officially _________, but this lesson could more accurately be called a lesson in "competition".
5. Punctuality, obedience, politeness, and other aspects of "_________" behaviour are not so much worthwhile ends in themselves as they are the necessary means to a desirable diploma.
Task 7.Match the words from column A with the words from column B to make six common collocations.
| A | B |
| 1. unconsciously | A. group |
| 2. peer | B. crowd |
| 3. formal | C. subculture |
| 4. leading | D. accomplishments |
| 5. adolescent | E. absorbed |
| 6. academic | F. curriculum |
Task 8. Are the following statements about the text true (T) or false (F)?
| 1. | The primary aim of education is to teach students to be obedient. | T / F |
| 2. | The symbolic lessons of the hidden curriculum are more effective than any textbook. | T / F |
| 3. | Peer group is the most important primary group for students in any educational institutions. | T / F |
| 4. | James Coleman studied the status systems of ten universities in the Midwest. | T / F |
| 5. | Coleman found a basic sociological reason for the students' high opinion of low grades. | T / F |
Task 9. Now look again at the text and find words in the paragraphs 1-5, which mean the same as:
a) delivery (1) _______________________
b) invisible (1) _______________________
c) requirements (2) _______________________
d) vogue (2) _______________________
e) youth (3) _______________________
f) likeness (3) _______________________
g) image (4) _______________________
h) characteristics (4) _______________________
i) readiness (5) _______________________
j) prominent (5) _______________________
Task 10. Rearrange the letters to form a word used in the unit, then match the word to its definition.
| nogitocan | a a set of shared ideas, or the customs, beliefs, and knowledge that characterize a society's way of life; | ||
| ucadntieo | btime occupied by freely chosen activities that are enjoyable or self-fulfilling in themselves; | ||
| teuurcl | c adjective usually used to characterize groups of equals in age, sex, occupational level, and the like; | ||
| ummitaisnernstl | d any social position that has socially defined rights and obligations; | ||
| lreieus | e LeBon's theory that the actions of one person in a crowd tend to be imitated by the next, and so on; | ||
| erpe | f distinctive cultural ideas that people share because they are members of a certain group; | ||
| atusts | g the deliberate, formal transfer of knowledge, skills, and values from one person or group to another; | ||
| ulebrscutu | hrational, goal-oriented behaviour. |
Task 11. Check how do you know the collocations.
| 1. collective behaviour | A. the function of education to pass on accumulated knowledge and thus protect cultural standards |
| 2. conspicuous leisure | B. standards of behaviour gradually established by people in groups |
| 3.cultural transmission | C. unintended consequences of social actions |
| 4. hidden curriculum | D. social groups whose members have disparate, rather than common, goals and value the extrinsic political, economic, or other benefits of the relationship rather than the relationship itself |
| 5. emergent norms | E. the relatively unorganized and spontaneous behaviour of people in crowds and masses |
| 6. latent functions | F. in education, the transmission of cultural values and attitudes such as punctuality and obedience through the school situation, in contrast to the manifest, or formal, curriculum |
| 7. secondary groups | G. Veblen's term for obvious, nonproductive consumption of time |
Task 12. Put the underlined word from task 11 into the appropriate sentences.
1. These _____________ organizational lessons are so much a part of the underlying assumptions of schooling that we tend to forget how pervasive and important they are.
2. They also learn the organizational ropes – the ___________ of a bureaucratic world.
3. To meet the requirements of organizational efficiency, the higher school day is divided into class periods, lunch hours, and _____________time.
4. Goal-oriented _______________is one of the guiding principles of bureaucracy.
5. Students learn to accept the norms of their peer ___________________.
6. Much social behaviour has unintended consequences, or ___________ functions, as well as intended consequences, or manifest functions.
7. It is believed that __________ ideas and social structures influence each other.
v GRAMMAR
|

Task 13. There seem to be no limits to what the Ivy League Universities will do to enjoy more popularity. Five of the following are facts and three are hoaxes. Find out which facts are and which hoaxes are? Mark them F or H. Check your answers in the end of this unit.
a Dartmouth College can justifiably be considered the cradle of business education furthermore it was the first that gave their graduates MBA.
b Harvard University is negotiating with the city of New York to replace Statue of Liberty with a similar-sized statute of John Harvard for 18 weeks.
c In 2007 Princeton University joined the scandal Google project that promised to digitize a million books (from Princeton repository), but only those the copyright for which has expired.
d On February 2014 Yale University invited Nina Davaluri (Miss America 2014) shared her goal of spreading cross-cultural understanding and combating ignorance before their students and teachers.
e Columbia University celebratedits 250 year anniversaryby painting an entire street in the UK bright pink – houses, cars, trees, even dogs.
f The authorities of Brown University have included the sex-change surgery in the insurance program for students.
g In 2012 The Pennsylvania State University agreed to pay victims of sexual abuse (defendant is football coach Gerald Sandusky) $ 60 million.
h Scientists from the University of Cornwall are proposing to decorate the twin Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur with the emblem of this University.
Task 14. We can make –ing/-ed adjectives and adverbs from verbs e.g.
 bore bored / boring. How many –ing/-ed adjectives can you find in the paragraph 5 in the text you have read? What are the verbs?
bore bored / boring. How many –ing/-ed adjectives can you find in the paragraph 5 in the text you have read? What are the verbs?
Complete these questions with the correct adjectives. Then ask and answer the questions with a partner.
1. What is the most __________thing you have ever done at University? (excite)
2. Is there anything that you are_________by? (fascinate)
3. What is the most__________thing that has happened to you at University? (embarrass)
4. When did you last feel__________ at University? (surprise)
5. What is the most___________thing you have known at class? (amaze)
Task 15. Rewrite the sentences, beginning with the words in bold.
1. Mastering the subject is certainly most important.
Example: Certainly most important is mastering the subject.
2. The most teachers come from middle-class backgrounds.
3. The university day meets the requirements of organizational efficiency.
4. Students are required to do in higher school many of the things.
5. Time at university is precise and arbitrary.
6. The democratic idea of equality thus came to be defined as equality of achievement.
Task 16. Rephrase the following sentences in as many ways as possible, as in the example.
1. Students in a competitive university system soon learn to work for higher grades.
Example:
…It is studentswho soon learn to work for higher grades in a competitive university system. (emphasis on the subject = students)
… It is a competitive university system where students soon learn to work for higher grades. (emphasis on the adverbial phrase = in a competitive university system)
…It is higher grades for which students soon learn to work in a competitive university system. (emphasis on the object = higher grades)
2. James S. Coleman published his book in 1960.
3. The girls were generally better students than the boys in this higher school.
4. To Coleman these results suggested that the values of the adolescent subculture were a deterrent to academic success.
5. Teachers also teach students values and attitudes that are not in the school's formal curriculum.
6. One of the first things a student learns in higher school is to be on time.
Task 17. Delete the extra word in these sentences. Then translate them into Ukrainian.
1. Selection is a traditional function of education, by which do candidates are selected for various occupational roles.
2. Only when did I talked to him in person was the matter settled.
3. It was Coleman who he told me about hidden curriculum.
4. Marion likes students who conform to her own ethnic and so does like her sister.
5. Only by you entering the college will you be able to find a good job.
Task 18. Complete the asterisked gaps in the chart below with words from the paragraphs indicated. Then fill in the other gaps.
| PARAGRAPH | NOUN | ADJECTIVE | VERB |
| § 1 | Involved | * | |
| § 2 | * | inform | |
| § 3 | popularity | * | |
| Expected | * | ||
| § 4 | * | achieve | |
| § 5 | basicity | * |
Task 19. Study the table then agree or disagree with the following statements.
| WE USE INVERSION TO EXPRESS AGREEMENT OR DISAGREEMENT IN FOLLOWING CASES | |
| SO | to agree with the affirmative statements |
| NOR NEITHER | to agree with the negative statements |
1. "I did not estimate that students".
"Nor ___________We have problems with grades".
2. “I can appreciate the potentialities in this field".
“So ____________________ it's easy".
3. “We are not going to that seminar".
"Neither ______________. We can't afford it".
4. “I will cope with those difficulties at University".
“So_________________. I will go there tomorrow”.
5. “I've got some good news!”
“So _____________. I've received the highest grades”.
Task 20. Find at least three examples of Emphasis in the text you have read.
v TRANSLATION
Task 21. Translate the following paragraph about obedience into Ukrainian.

Task 22. Choose the best option to translate the sentences.
1. Learning to line up quietly, for example, does not help the first grader learn to read, but it does make running the classroom easier for the teacher.
A. Наприклад, вміння стояти струнко, не допомагає першокласникам навчитися читати, однак саме це допомагає викладачеві працювати з класом.
В. Наприклад, вміння стояти струнко, не допомагає першому в колоні навчитися читати, однак саме це допомагає викладачеві працювати з класом.
С. Наприклад, вміння поводитися тихо, не допомагає першокласникам навчитися читати, однак саме це допомагає викладачеві працювати з класом.
2. It is exactly this composition that will do for our purpose.
A. Це саме цей склад підійде для нашої мети.
В. Саме цей склад підійде для нашої мети.
С. Саме цю композицію ми замовляли.
3. It is precisely this opinion that makes a person defend this approach.
A. Саме така точка зору змушує особу захищати цей метод.
В. Це саме така точка зору змушує персону захищати цей метод.
C. Це саме така точка зору, що змушує персону захищати цей метод.
4. Цей критерій, хоча й є зручним, повинен використовуватися обережно.
А. The figure of merit, useful criterion as it is, must be used with reserve.
В. The figure of merit, useful criterion as it is, must be used with reservation.
С. This figure useful criterion as it is, must be used with reserve.
5. Нам не вдалося розрахувати змінну величину, ми також не знаємо як оцінити характеристики цієї системи.
A. We did failed to estimate the variables, nor did we know how to evaluate the performance of system.
B. We failed to estimate the variables, nor did we know how to evaluate the performance of system.
C. We did not fail to estimate the variables, nor did we know how to evaluate the performance of system.
6. Саме про цю проблему вони говорили і писали.
A. It was that problem that they spoke and wrote about.
B. It was of this problem which they spoke of and wrote by.
C. It was of this problem that they spoke and wrote about.
v WRITING
Task 23. Think about the influence of hidden curriculum on adolescents. Does it exist in your class? Write five sentences. Then find out about your partner.
Task 24. Read the paragraph about the competition in class and analyze it.
1. Underline the topic sentence. Is it the first or second sentence?
___________________________
2. Is the first sentence indented?
___________________________
3. How many supporting sentences are there? Which are they?
___________________________
4. Circle the concluding sentence or clause.
Task 25. Write a small summary of the text Capitalism and Socialism for about 10 sentences.
 Begin with:
Begin with:
CHECK YOUR WORK
Have you
used any interesting expressions from the text in your summary?
written 10 sentences?
checked your spelling?
checked punctuation and grammar?
UNIT 11
FAMILY
v SPEAKING
Task 1. Read these three quotations. Which one would be more relevant to you? Why? Introduce balanced arguments discussing points in favour of the family as well as against the family.
Ø If the family were a fruit, it would be an orange, a circle of sections, held together but separable – each segment distinct. (Letty Cottin Pogrebin)
Ø Our most basic instinct is not for survival but for family. Most of us would give our own life for the survival of a family member, yet we lead our daily life too often as if we take our family for granted. (Paul Pearshall)
Ø Family life is a bit like a runny peach pie — not perfect but who's complaining? (Robert Brault)
v STUDY SKILLS
Task 2. Do the following questionnaire to find out whether you are ambitious or not. Then turn to page 184 to read the analysis of your answers.
HOW AMBITIOUS ARE YOU?
1. In ten years do you hope to:
a) be married with a family?
b) have an interesting but not very well-paid job?
c) have a well-paid job that isn't very interesting?
2. In twenty years' time do you hope to:
a) have enough money to pay your bills?
b) have quite a lot of money?
c) have a lot of money?
3.Here is a list often jobs. Which would you like to do? Put 1 next to your favourite, 2 next to your next favourite, etc.
| Nurse accountant teacher politician policeman/woman | builder journalist artist engineer actor/actress/popstar |
4. Is improving your standard of living important for you?
5. Do you think people who have money should help people who don't have money?
6.How old do you want to be when you have children?
| a) 18 - 22 b) 23 - 26 | c) 27 – 30 d) over 30 |
7. When you are playing a game, do you always want to win?
8. Can you tell a white lie?
9. Do you think that rich people are happier and more interesting than other ones?
10. Do you work hard because you want to be successful?
11. If you have a job to do, do you do it immediately, or do you wait until the last moment?
12. Would you like to have more money than your parents?
13. Do you agree with the philosophy "Every man for himself"?
14. Do you like hard work?
15. Which of the following is most important to you: love, happiness, money, health?
v READING
Task 3. Read the text about the main concepts of marriage and family. Write down some interesting things you remember. Compare your notes with other students.
Дата: 2016-10-02, просмотров: 400.