Российской Федерации
Федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение
высшего образования
«ЮЖНЫЙ ФЕДЕРАЛЬНЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ»
Н.А. Беляева, Л.А. Недосека, И.И. Скнарина

Ростов-на-Дону
2016
Учебное пособие разработано преподавателями кафедры английского языка естественных факультетов Института филологии, журналистики и межкультурной коммуникации ЮФУ Беляевой Н.А., Недосека Л.А., Скнариной И.И.
Ответственный рецензент – канд филос. наук, доцент кафедры английского языка естественных факультетов Института филологии, журналистики и межкультурной коммуникации ЮФУ Белоусова М.М.
Печатается в соответствии с решением кафедры английского языка естественных факультетов ЮФУ, протокол № 2 от 29 сентября 2016 года.
Методическая записка
Данное учебное пособие предназначено для студентов 1 курса бакалавриата с низким уровнем владения английским языком (А1-А2 по международной шкале) естественно - научного направления подготовки. Целью учебного пособия является развитие навыков устной речи по темам академического обучения.
Развитие навыков устной речи осуществляется на основе упражнений, обучающих умению высказывать свое мнение, направленных на развитие коммуникативных навыков общения на основе предложенной тематики, а также навыков публичной речи – при подготовке мини-презентаций по предложенным темам на английском языке (см рубрику Project Work ).
Данное учебное пособие предлагает следующие темы: «My Personal Profile», «English and Me”, «Universities», «Information Age».
Учебное пособие состоит из 4 модулей. Каждый модуль включает в себя разделы (Units) с текстом, а также комплексом заданий, направленных на развитие навыков грамматики, чтения и говорения на английском языке. Учебные модули содержат следующие рубрики:
1. Having a talk – является неким введением в предложенную тему и представлен вопросами и упражнениями, которые способствует снятию лексических трудностей, а также повышению интереса студентов к изучаемому материалу ;
2. Reading – включает текст и задания на извлечение основной информации, понимание структуры и организации содержания текста;
3. Comprehension check – включает вопросы на проверку уровня понимания текста;
4. Vocabulary – акцентирует внимание студентов на ключевых словах и словосочетаниях по тематике модуля для последующего их использования в практике устной и письменной речи;
5. Grammar – формирует навыки употребления определенных грамматических явлений на английском языке и их перевода в предложенных ситуациях.
6. Video / Listening - содержит видео/аудио сюжеты и задания на формирование навыков аудирования и говорения на английском языке.
7. Writing – направлен на развитие определенных навыков письменной речи.
8. Speaking - включает задания на развитие навыков говорения на английском языке.
9. For my language portfolio – способствует формированию языкового портфеля студента, который предлагает упражнения на развитие навыков и говорении, и письма.
Каждый модуль завершается разделом Progress Test (тест рубежного контроля), который включает 3 задания и Evaluation form. Выполнение заданий рассчитывается в баллах по шкале; максимальное количество баллов - 15.
В учебном пособии содержится Грамматический справочник ( Grammar Reference ), в котором содержатся основные сведения по грамматике английского языка.
Учебное пособие разработано с использованием аутентичных материалов (адаптированных для уровня A 1-2), основными источниками которых является британские и американские издания, интернет, энциклопедии и словари. Новизна, информативность и соответствие информации профессиональным потребностям студентов были основными критериями отбора материалов для данного пособия.
Модули представляют собой самостоятельные разделы, что позволяет преподавателям и студентам соблюдать последовательность, в которой они представлены в пособии, или выбирать для изучения те модули, которые представляют особый интерес. Настоящее учебное пособие рекомендовано к использованию для аудиторной работы.
 MY PERSONAL
MY PERSONAL
PROFILE

Learning objectives:
ü To talk about yourself;
ü To revisit to BE, Present Simple and the word order of an English sentence;
ü To expand vocabulary on the topics “ Family”, “Hobbies” and “People”, “My home place”;
ü To practice dialogue speech on the topics;
ü To develop public speaking skills.
 Unit 1 Meeting people
Unit 1 Meeting people
| Having a talk |
Ex.1 Work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions:
1) What is your name?
2) What is your surname?
3) How old are you?
4) Where are you from?
5) What are you?
6) What are your hobbies and interests?
Ex.2 Read the questions and find the equivalents to some from Ex.1:
| A) What’s your job? B) What do you do? C) Where do you come from? D) What’s your first name? E) What do you do in free (spare) time? F) Who are you? G) What’s your last name? |
1) D ; 2)___; 3)___; 4)___; 5)___; 6)____.
| Grammar |
Study the picture to revisit to be and explain it in Russian:
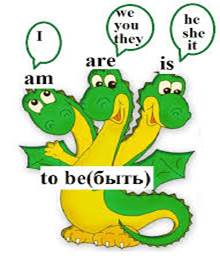
***Grammar Reference
Present Simple the verb ‘to be’
Ex.3 Read and complete the sentences with: am, is, are
1) My family is big.
2) We ___ friendly family.
3) My father ___ an engineer.
4) He ____ a tall man.
5) My parents____ nice people.
6) The University I study at___ big.
7) It ____ not far from my place.
8) The subjects ____ interesting.
9) I ___ fond of Sciences.
10) The University teachers____ competent.
Word Order
Ex.14 Put the words into the correct order:
1. help/my friends/I/with their homework
2. make/people/laugh/when they are sad/I
3. talk/to my friends/on the phone/I
4. do sports/I/at the weekends/not/do
5. play/I/a musical instrument/in the evening
6. do/the housework/I/for my parents
7. me/ than/my best friend/older/is
8. the cinema/I/go/do/to/not
9. to London /go/I/want/to
10. my favourite city/is/ Barcelona
Ex.15 Translate the sentences into English:
1. Я – студент(ка) первого курса .
2. Она - из Испании.
3. Университетская программа - интересная.
4. Мой друг по переписке сейчас находится в Ростове.
5. Моя мама - продавец.
6. Они – студенты дневного отделения.
7. Этот учебник английского языка старый.
8. Мои друзья очень общительны.
| Types of QUESTIONS |
| General (Yes/No –questions) |
| Word order: Verb Subject (Verb) Object Examples: Is Bob a student ? Does Bob study English? Are they nice people ? Do they go to the gym? |
| Special questions |
| Word order: Special word Verb Subject (Verb) Object Examples: Where is she from? Where does she study? Why are they here ? Why do you study English ? |
| Alternative question (Or-question) |
| Is she from England or Scotland? Does he study English or German? |
| Disjunctive question (Tag question) |
| She is from England, isn’t she? He studies English, doesn’t he? |
***Grammar Reference
Types of Questions
Ex.16 Which is correct: A) or B)?
| 1) A) How old is she? B) How old she is? | 5) A) They don’t take a bus to school. B) They take not a bus to school. |
| 2) A) I love rollerblading really. B) I really love rollerblading. | 6) A) Do you do sports? B) You do sports? |
| 3) A) He is fond of football very. B) He is very fond of football. | 7) A) She like to study very much. B) She likes to study very much. |
| 4) A) What nationality are you? B) What are you nationality? | 8) A) What do you do at the weekend? B) What you do at the weekend do? |
Ex.17 Read the sentences and write general and special questions:
1) She studies French. Does she study French? What does she study?
2) He is from Britain. ____________________________________.
3) My family likes traveling._______________________________.
4) My mother works as a manager in an office. ________________.
5) My friend is fond of chess._____________________________.
6) My group mates spend much time together. _________________.
7) We are old friends. _____________________________________.
8) I play the piano well._____________________________________.
9) She plays volleyball. _____________________________________.
10) They listen to jazz and pop music. _________________________.
Ex.18 Ask four different questions to every sentence:
1. She likes dancing. Does she like dancing? What does she like?
Does she like dancing or singing? She likes dancing, doesn’t she?
2. She is from Spain
3. They are University students.
4. They play basketball in their free time.
5. He is fond of music.
6. She studies Geography at the University.
7. We live in Rostov-on-Don.
8. He loves reading books.
9. His father is a manager.
10. My brother works at the hospital.

PROGRESS MONITORING
PROGRESS MONITORING
SAMPLE PROGRESS TEST 1
I. Choose the correct:
1. Water ... important to our body.
a) are
b) is
c) am
2. Their house … look like my house.
a) is not
b) does not
c) are not
3. …they from Spain?
a) Is
b) Are
c) Am
4. … Tom and Jane know how to speak French?
a) Are
b) Does
c) Do
5. … the pencils yellow?
a) Is
b) Are
c) Do
6. … she 18 years old?
a) Is
b) Does
c) Are
7. … the boy live in the city?
a) Do
b) Is
c) Does
8. … she have a family?
a) Is
b) Does
c) Do
9. Marta always … on Sundays because she has class on Mondays.
a) studies
b) study
c) studys
10. … you speak English?
a) Are
b) Does
c) Do
II. Put the words in order:
1. students often a computer University at use______________________
2. play computer teenagers a sometimes CDs on_______________________
3. never these people send days most letters___________________________
4. of English lot a learn students____________________________________
5. almost University students are at Russia all from_____________________
6. know does French she not_______________________________________
7. home he at now is?____________________________________________
8. at do you weekend what do?_____________________________________
9. he where study does?___________________________________________
10. lives the you who flat together in with?____________________________
III. Fill in the gaps with one word from the box:
|
Mark lives in a quiet 1) … area in Sydney. It is a 2) … city in Australia. Sydney is famous for its 3) … such as Sydney Opera House and Bondi Beach. In his 4) … time Mark likes surfing. He 5) … meeting 6) … and funny people. He studies at the university, it is difficult and 7) … . He studies hard and tries to be 8) … . He prefers to 9) … with 10) … and honest people.
EVALUATION FORM
Scores you can gain for:
| Exercise | 1 | 2 | 3 | Total |
| Maximum | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15 |
| Your scores |
Learning objectives
ü To talk about the reasons of learning English;
ü To develop listening skills on the topic;
ü To revisit the Present Simple and Present Continuous tenses;
ü To expand vocabulary on the topic.
Unit 1 Why learn English? 
| Having a talk |
Ex. 1 Work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions:
1) What languages do you speak?
2) Do your parents speak any foreign languages?
3) Why do people study foreign languages in your country?
4) What languages are popular in the world now?
5) Is it important for you to study English? Why?
| Vocabulary |
Ex. 2 Read and match the following words:
| 1 | Main | A | Важный |
| 2 | Useful | B | Международный |
| 3 | Important | C | Великий |
| 4 | International | D | Забавный |
| 5 | Funny | E | Полезный |
| 6 | Great | F | Главный, основной |
| Video |
Ex. 3 Watch the episode where University students in Cambridge speak about the reasons of learning English. Complete the sentences with one word and translate them into Russian:
1) English language is ____________ language in the world.
2) English is all over the world, it is___________ to learn more about other people.
3) It’ s_______ to go abroad and attend university there.
4) It’s __________ to watch movies and understand songs (lyrics).
5) English is ___________ when you want to find a job.
Present Simple
Work
Study .
Do
Work ?
Study?
Do
Not
Work .
Study.
Works
Studies .
Does
Does
Present Continuous
Ex. 20 Describe the picture using the Present Continuous tense:

Start with :
№ 1 The boy is ______________________________.
№ 2 The teacher______________________________.
№3________________________________________.
№4 ________________________________________.
№5 The boys are______________________________.
№ 6_________________________________________.
№7_________________________________________.
№8_________________________________________.
№ 9_________________________________________.
Dialogue 1
A: _____you______(use) the computer now?
B: No, the teacher______(wait) for me to discuss my home assignment. Why?
A: I_____ (make) a presentation for my English class at the moment.
B: What’s wrong with your computer?
A: It_____ (not, work) at the moment. I need my presentation tomorrow.
Dialogue 2
A: Hello, Ann speaking. How are you?
B: Hello, Ann! I’m fine. How are you?
A: I’m fine too. What _____you_____( do) ? ____I_____(disturb) you?
B: That’s O.K. I________(watch) a DVD film. And Why?
A: What about going to the cinema tonight? It’s Twilights.
B: When and where_____we ______ (meet)?
A: Let’s meet at 5 p.m. next to the Plaza cinema?
B: Fine. I’ll come. See you. Bye.
A: Bye.
Ex. 22 Read the text and answer the questions:
Dancing in Class
Mary is sitting in class, she is having Philosophy class. Her professor is standing in front of the room. He is talking. He is talking a lot. Mary is finding the class a bit boring. In Mary’s mind, she is doing something different. In her imagination, she is not sitting in class. She is dancing on a stage in front of hundreds of people/ she is wearing a beautiful costume. She is performing; she is spinning on one leg.
The stage lights are shining in her eyes. She is closing her eyes and concentrating on the music. She is having so much fun! Her heart is beating fast. The music is changing. She is changing her costumes. Now she is dancing again. She is leaping and flying through the air.
Soon, she is finishing her show. The audience is standing on their feet. They are clapping and shouting. “Bravo! Bravo!”. Mary is taking a bow. Mary is smiling for the cameras. “Bravo! Bravo!”. She is having so much fun!
“Mary?”
Mary’s classmates are staring at her.
“Mary?” her professor is saying, looking at her with concern. He is not teaching any more.
“Yes?” Mary is feeling a bit embarrassed. Her cheeks are getting red.
“Are you feeling okay? You are shouting “Bravo! Bravo!” in class.”
“Oh, yes, professor. Sorry. I am just enjoying the class so much. Bravo! Bravo!”
Questions:
1) Where is Mary? What class is she having?
2) What is the professor doing?
3) Does Mary like the class?
4) What is she doing in her imagination?
5) Why is she closing her eyes?
6) What is the audience doing at the end of the show?
7) How is Mary feeling when the professor starts talking to her?
| FOR MY LANGUAGE PORTFOLIO |
8) Why does she say she is shouting “Bravo!”?
PROGRESS MONITORING
Visual learner
Vocabulary
Ex. 4 Read and complete the sentences with a new word from the word on the right:
| 1) University students do a lot of_______which make their life more interesting. | ACTIVE |
| 2) She finds it difficult to remember ______when somebody explains her in the city. | DIRECT |
| 3) This company looks for responsible and _______ staff. | CREATE |
| 4) She is definitely a ______ learner, she takes a lot of notes during the lectures. | VISION |
| 5) Some teachers don’t know how to motivate kinaesthetic _______ . 6) I can __________read and understand simple texts in English. 7) My main_______ in learning English is grammar. 8) It’s easy for me to understand ________ instructions. 9) It helps me a lot, if I see the face of a ________. 10) Our University invites foreign________every year. | LEARN EASY PREFER WRITE SPEAK LECTURE |
Ex.5 Match the following words from the text:
| 1 | to take down | A | jokes |
| 2 | to understand | B | aloud |
| 3 | to tell | C | body language |
| 4 | to get | D | notes |
| 5 | to study | E | things |
| 6 | to picture | F | diagrams |
| 7 | to use | G | ideas |
| Speaking |
Ex. 6 Put a tick (۷) what you like doing in class and put a cross (x) what annoys you. Start with:
- I like+…. /I enjoy+… /I prefer+…
- I dislike+… /I hate+… /I can’t stand+…
| Reading texts in English | |
| Making up dialogues | |
| Listening to CDs | |
| Doing translation from Russian into English | |
| Writing letters or essays | |
| Speaking to the group mates in English | |
| Watching English movies | |
| Doing grammar exercises | |
| Making presentations | |
| Doing research in English |
| Reading |
Ex. 7 Read the short texts and say which student (Jack, Susan or Mark) is the most successful in your opinion:
Text A
Jack takes learning English very seriously. He is mainly keen on English grammar- he spends many hours at home studying grammar books and doing exercises. In class, he always has a lot of questions to the teacher- in fact, he knows so much about grammar that sometimes his teacher finds it hard to answer. Jack learns vocabulary. He enjoys working with his bilingual dictionary and looking up any new word. His pronunciation is quite good too. He quite enjoys his English classes but he thinks his teacher wastes too much time on group work. He doesn’t like speaking to other students. He doesn’t like to make mistakes.
Text B
Susan really enjoys her foreign classes, though she is very busy in her job. She likes her teacher and her group mates, she enjoys speaking English both with the teacher and with other students. She always tries to say as much as she can, even if the topic is not something that really interests her- it’ s still good practice. She tries to correct herself and use the new words. Susan is rather good at grammar. When she meets new grammar she tries to work out the rules herself. She sometimes gets the chance to practise English at work, when she meets English speaking colleagues.
Text C
Mark doesn’t really know why he is learning English, but maybe it’ll be useful some day. Anyway, his parents are paying a lot of money for his lessons. He attends most of these classes but he’s generally late. His teacher always explains new vocabulary and grammar in English, but Mark doesn’t usually listen very hard to the parts of the lesson- his friend John speaks much better English than he does, so he asks him to translate the teacher’s words. The teacher sometimes asks him questions. He usually answers in one word. The topics don’t interest him much.
Ex.8 Write J for Jack, S for Susan and M for Mark. Say who….
1) likes English classes very much. ______
2) answers the teacher’s questions in one word.______
3) enjoys learning grammar.______
4) learns vocabulary.______
5) doesn’t like group work._______
6) doesn’t know the reason of learning English.______
7) practices English apart from the work in class.______
8) doesn’t usually listen very hard._______
PROGRESS MONITORING
SAMPLE PROGRESS TEST 2
I. Choose the correct a) , b) or c):
1) My friend _____ Physics now, he can’t come to the party.
a) studies; b) study; c) is studying;
2) I study English____ make more friends.
a) for; b) to; c) because;
3) This teacher always ______ new vocabulary and grammar in English.
a) explains; b) is explaining; c) explain;
4) You can get many things if you speak English _____ .
a) good; b) well; c) best;
5) When learning I prefer _____ the teacher’s face a lot.
a) watch; b) is watching; c) watching;
6) I don’t like taking ______ notes when listening to the lecturer.
a) down; b) back; c) over;
7) She ________ know the reason of learning English.
a) isn’t; b) don’t; c) doesn’t;
8) We like to call English “the language ______ communication”.
a)for; b) with; c) of;
9) In class she ______ to speak English as much as she can.
a) is trying; b) tries; c) try;
10) We live in the information age, _______ we?
a) don’t ; b) aren’t; c) doesn’t’
II. Choose the right word:
1) English is the language of technology, it helps ____ technical knowledge.
a) take; b) gain; c) have;
2) Some people learn English to______ horizons.
a) expand; b) enhance; c) broaden;
3) She uses a lot of body ________ when she talks.
a) exercises; b) movements; c) language;
4) You should do the test to understand if you are a visual______.
a) learner; b) student; c) fellow;
5) English is all over the world, it is___________ to learn more about other people.
a) main; b) important; c) international;
6) The media gives you almost unlimited ______ to knowledge about your favorite subjects.
a) way; b) path; c) access;
7) The teacher asks us to______ Power Point presentations very carefully.
a) make; b) do; c) give;
8) Students of our department take an active _____ in University life.
a) half; b) piece; c) part;
9) My friend likes to _______ up dialogues with her group mates in class.
a) create; b) do; c) make;
10) My main_______ in learning English is listening.
a) liking; b) preference; c) funny;
III. Match the following halves to make a sentence:
| 1 | I need English | A | on English grammar. |
| 2 | She learns English to | B | to speak English as much as possible. |
| 3 | He is mainly keen | C | do research. |
| 4 | They prefer | D | for my job. |
| 5 | She tries | E | watching English movies. |
IV. Complete the sentences with a new word from the word on the right:
| 1) You are more _____, you don’t need an interpreter. | DEPEND |
| 2) My uncle learns English for______. | BUSY |
| 3) It’s funny to know other people from _____countries. | DIFFER |
| 4) You can get access to_____ if you speak good English. | KNOW |
| 5) English language is _________ language in the world. | NATION |
EVALUATION FORM
Scores you can gain for:
| Exercise | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Total |
| Maximum | 5 | 5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 15 |
| Your scores |
Learning objectives
ü To talk about universities (SFU, some British and American universities);
ü To discuss differences in the system of higher education in the countries;
ü To develop listening skills on the topic;
ü To revisit the Past Simple and comparisons;
ü To expand vocabulary on the topic.
 Unit 1 The University I study at
Unit 1 The University I study at
| Having a talk |
Ex 1. Work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions:
1) What University do you study at?
2) What is it like?
3) Do you like studying at the University? Why? Why not?
4) What facilities does the University have?
5) Do you live in a campus or rented apartment?
| Vocabulary |
Ex 2. Match the following words:
| 1 | Departments | A | Выпускники |
| 2 | A campus | B | Студенты - магистры |
| 3 | Halls of Residence | C | Кандидатская степень |
| 4 | Bachelor students | D | Исследование |
| 5 | Master students | E | Студ. городок |
| 6 | PhD degree | F | Студенты- бакалавры |
| 7 | Graduates | G | Общежитие |
| 8 | Research | H | Отделения, кафедры |
Ex. 3 Complete the sentences with the words from the table above changing its form if necessary:
1) There are many______ which make up different institutions of SFU.
2) The University______ is very big, modern and comfortable.
3) Students live in 8 _______.
4) ______ study for 4 years.
5) The course of study for ______ lasts 2 years.
6) University students are involved in academic activity and ______.
7) Southern Federal University is famous for its______, for example, A. Solzhenitsin, D. Dibrov, and others.
| Video |
Ex. 4 Watch the episode about Southern Federal University and put the headings (from A-G) in the order you watch the video:

|
 |  |


|
Ex 5. Watch the episode again and complete the sentences:
1) Southern Federal University is open to___________________.
2) It was founded in____________________________________.
3) The University unites 4 ___ , 11___________.
4) It includes _____ design bureaus, ____ small innovative enterprises.
5) The University offers________ programmes.
6) _________study at SFU.
7) The University is young,___________.
8) SFU is one ________.
| Reading |
Grammar
Crowded -the most crowded
Note :
The Past Simple Tense
Ex. 14 Look at the picture and work out the rule in your native language. How do we use the Past Simple Tense: 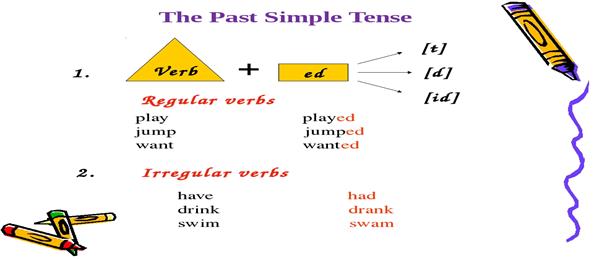
***Grammar Reference
Past Simple
PROGRESS MONITORING
Read and translate the following from UNIT 1:
| ü admission; ü alumni; ü undergraduates; ü entry; ü to do research; ü skilled; | ü campus; ü Master ; ü Bachelor; ü to graduate from; ü staff; ü prestigious. |
 Unit 2 American and British Universities
Unit 2 American and British Universities
| Having a talk |
Ex 1. Read and answer the questions:
1) What British or American Universities do you know?
2) What are they famous for?
3) How long is the course of study there?
4) Do American and British students have to pay for their education? How much?
5) How is the student’s progress evaluated?
| Video |
Ex. 2 Watch the episode about Oxford University and London School of Economics, take notes and say what these numbers refer to:
38; 20,000; 150; 700; 100; 70%;
Ex 3. A) Watch the episode about Oxford University again and complete the sentences:
1) Oxford University is one of ________________________________.
2) Carfax Tower has________________________________________.
3) Oxford University is located in_____________________________.
4) The University is made up of_______________________________.
5) Students do a lot of_______________________________________.
6) Oxford University is famous for_____________________________.
7) Students have to buy______________________________________.
B) Watch the episode about London School of Economics again and answer the questions:
1) Why does a Pakistan student live in the Halls of residence?
2) How far from the School is it located?
3) What facilities are there in the campus?
4) Where can students relax? What do they do?
5) What tips does a student from Hong Kong give?
| Speaking |
Past Continuous
PROGRESS MONITORING
Read and translate the following from UNIT 2:
| ü vocational; ü tuition fees; ü major/minor; ü intermission; ü flexible; ü expenses; | ü liberal arts; ü available; ü private; ü to evaluate; ü sophomore; ü term/semester. |
SAMPLE PROGRESS TEST 3
I. Choose the correct a) , b) or c):
1) My friend _____ Physics at school.
a) studied; b) study; c) was studying;
2) I ___ to be a pilot when I was young.
a) was wanting b) wanted c) was wanted
3) We were in a difficult situation. We ___ what to do.
a) didn’t know; b) were not knowing; c) not know;
4) He usually meets his sister on Fridays but he ___ her last Friday.
a) wasn’t visiting; b) didn’t visit; c) weren’t visiting;
5) What ___ at 6 p.m. yesterday?
a) did you do; b) were you doing; c) was you doing;
6) Where ___ when I met you yesterday?
a) were you going; b) did you going; c) did you went;
7) Which exams ___ at school?
a) did you took; b) were you taking; c) did you take
8) Greg ___ in a test when his teacher noticed it.
a) was cheating; b) cheated; c) was cheat;
9) In class she ______ to speak English as much as she could.
a) was trying; b) tried; c) try;
10) I ___ for the way out of the centre but couldn’t find it.
a) look; b) was looking; c) were looking.
II. Choose the right word:
1) English is the ______________language of technology, I have ever studied
a) difficult; b) more difficult; c) the most difficult;
2) Andrew is the _______________ student in our group.
a) most hard-working; b) hard-working; c) more hard-working;
3) There are ________ places in our city than this park.
a) most attractive; b) attractive; c) more attractive;
4) This test was ___________ I’ve ever had.
a) easier; b) the easiest; c) easy;
5) English is _______________ language in world communication.
a) important; b) the most important; c) more important;
6) The course in math is ___________ than in chemistry.
a) longer; b) the longest; c) as long as;
7) The academic year is __________into 2 semesters.
a) made; b) done; c) divided;
8) Students of our department __________an active part in University life last semester.
a) take; b) took; c) taking;
9) My friends____________ English movies with her group mates during the week of Academic Mobility.
a) watch; b) watching; c) watched;
10) It was the __________activity in everyday student life.
a) funniest; b) funnier; c) funny;
III. Match the following halves to make a sentence:
| 1 | Students enjoy | A | graduating from the university. |
| 2 | The students have | B | evaluated by means of tests and exams. |
| 3 | The progress is | C | all facilities are concentrated in one area. |
| 4 | My friend received a Master’s degree in Science after | D | doing extra curriculum activities. |
| 5 | It’s a campus university because | E | to submit their reports after taking a practical course. |
IV. Complete the sentences with a new word from the word on the right:
| 1) Almost each university in Russia offers loans and ____. | SCHOLAR |
| 2) The US first-year students are called______. | MEN |
| 3) American students have a 4- week-______ for the Christmas holidays. | MISSION |
| 4) Every university has its own traditions and______. | IDENTIFY |
| 5) There is enough _______ for British students to make a choice of subjects. | FLEXIBLE |
EVALUATION FORM
Scores you can gain for:
| Exercise | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Total |
| Maximum | 5 | 5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 15 |
| Your scores |
The Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect
Ex. 10 Read the sentences and use HAVE or HAS in the gaps:
1) The world ____ become faster nowadays.
2) People _____got an access to many information sources.
3) The Internet _______had a great impact on everybody’s life.
4) By now children______ become more dependable on the Internet.
5) Everything _____ been done by one click.
6) The Internet ______given rise to cyber thefts.
7) A lot of useful apps _____ appeared lately.
8) New hardware_____ been installed at my computer.
9) The Internet ______changed our lives in every manner.
Ex. 11 Write the 3d form of the following verbs:
| Begin begun Buy ____________ Become__________ Come____________ Change___________ Do _____________ Find _____________ Go _____________ Give _____________ Have_____________ | Hear_____________ Keep______________ Know_____________ Lose _____________ Learn _____________ Make _____________ Meet ______________ Put ________________ Speak ______________ Write ________________ |
Ex . 12 Complete the sentences with the right verb form;
1) He ______ just (send) me an e-mail.
2) My friends _______(be) to this library before.
3) They ______already (buy) new computer apps.
4) I ______ (do) this test several times.
5) I think I _______(meet) this IT specialist before.
6) ______you (download) this information yet?
7) She ______never (study) science.
8) My English _____(improve) since I started studying it at the University.
9) He ______(not, master) English, but he can communicate well.
10) We _______(have) many problems while working on this project.
PROGRESS MONITORING
Read and translate the following from UNIT 1:
| ü applications (apps); ü medium; ü access; ü addicted; ü sources; ü impact; | ü to contribute; ü victims; ü leakage; ü software; ü theft; ü legal. |
 Unit 2 Libraries
Unit 2 Libraries
| Having a talk |
Why go to the library?
Everyone knows that a library is a place in which reading materials, such as books, periodicals, and newspapers, and other materials such as musical and video recordings, are kept for use or lending. But how important are libraries in the modern society?
 The importance of a library in our society has come to question in the modern world because many people believe it is a thing of the past. Even with downloadable books and renovations, libraries are the first to be targeted for public use. For children, it is a place to go and learn to read and have fun in the programmes their library has to offer. Someone looking for a new job can learn skills to help them improve their resume while students can get some peace and quiet and quick access to information for their research.
The importance of a library in our society has come to question in the modern world because many people believe it is a thing of the past. Even with downloadable books and renovations, libraries are the first to be targeted for public use. For children, it is a place to go and learn to read and have fun in the programmes their library has to offer. Someone looking for a new job can learn skills to help them improve their resume while students can get some peace and quiet and quick access to information for their research.
More and more, the question of what the importance of a library in the society is in the modern world seems to come up from those who do not really know what their library has to offer. There are many reasons to go to the library. Two major reasons are to get information and to take advantage of the free programmes they offer.
Not only are there tons of books at your fingertips to check out or read right there, but there are also computers that are free to use as long as you have a library card (or student I.D. if it is a college or university library). Most libraries are also offering downloadable books and some even allow you to check out an e-reader if you do not have one.
Services provided by a library range from free programs to assistance in writing a resume for even dance classes. Libraries are supported by taxes from local and state governments that means that they are meant to serve the public. It may not be mandatory to use them, but they can come in handy for research, promoting cultural awareness, and education, amongst many other things.
 For me personally, it was a librarian who first taught me how to research for my first project in elementary school, and again in high school, and once more at the university. It was the library that I went to read my books while everyone was at recess or while I waited in between my classes during the latter part of my educational career.
For me personally, it was a librarian who first taught me how to research for my first project in elementary school, and again in high school, and once more at the university. It was the library that I went to read my books while everyone was at recess or while I waited in between my classes during the latter part of my educational career.
It is easy to overlook libraries and that stereotypical librarian with glasses and a tight bun at the back of their head shushing you every time you sneeze but there is a lot more to them than immediately meets the eye. Even without all they have to offer you, it is a place to go for knowledge and interaction with people who can help you find whatever you need.
| Comprehension check |
Ex. 4 Answer the following questions:
1) What is a library?
2) How important are libraries in the modern society?
3) What are the reasons to go to a library?
4) What do library services include?
5) What are libraries supported by?
6) How did the librarian help the author?
7) Do you think library is the place for interaction with people? Why?/Why not?
| Vocabulary |
Ex. 5 Match the words with their Russian equivalents:
| 1 renovation | A резюме |
| 2 to target | B игнорировать, пренебрегать |
| 3 а resume | C варьироваться |
| 4 at one’s fingertip | D обновление |
| 5 to allow | E перерыв |
| 6 to range | Fиметь что-нибудь под рукой |
| 7 to shush | G нацеливать |
| 8 recess | H позволять |
| 9 to overlook | I налог |
| 10 tax | J утихомирить |
Ex. 6 Complete the sentences with the words above:
1) There are tons of books at your ________ to read.
2) Free programmes at public libraries can help you to write a ______.
3) Libraries are the first to be _____ed for public use.
4) I used to go to the library at _______.
5) Most libraries ______ you to check out an e-reader.
6) Libraries are supported by _______s from local and state governments.
7) Library services_______ very much.
8) Librarians usually ______ those who make noise.
9) It is easy to_________libraries at the information age.
10) Most libraries need much_______.

Ex. 7 Watch the video about the Brantford public library and put the numbers opposite the headings in the order you watch them:
|
 Home work centre
Home work centre
|

 English conversation café
English conversation café
 Reference desk
Reference desk
 Programmes
Programmes
Neighborhood library

 Types of visitors
Types of visitors
 Wi-Fi and e-books
Wi-Fi and e-books
Public library
Ex. 8 Watch the video again and answer the questions:
1) How many people hold library cards for the Bradford public library?
2) Who can you ask reference questions?
3) What areas is the Brantford library located in?
4) What do the buildings house?
5) What are the visitors of the Brantford library?
6) How does the library help them?
7) What events can be organized by the library?
8) What programmes are offered at the library?
| Grammar |
Tense Review (The Present Tenses)
Before doing the exercises go to page 102-106 and read grammar rules if necessary. Try to use the verb forms correctly. Pay attention to the Present Perfect Continuous, its formation, use and modifiers.
Ex. 9 Complete the table:
| Present Simple | Present Continuous | Present Perfect | Present Perfect Continuous | |||
| We use the tense to talk about: | ||||||
| Action | something that happens again and again in the present. Something that is always true. | something that is happening at the moment of speaking . | past events with a connection to the present. | actions that started in the past and continued until recently or that continue into the future. | ||
| Modifies | Just, already, yet | |||||
| Formation |
| |||||
| negative | ||||||
| example | ||||||
PROGRESS MONITORING
Read and translate the following from UNIT 1:
| ü journal; ü periodical; ü article; ü to target; ü to overlook; ü handy; | ü to range; ü cultural awareness; ü downloadable; ü advantage; ü a reference desk; ü a recording. |
PROGRESS TEST 4
Task 1 Grammar. Choose a ,b, or c:
1) Shhh! We are in the library. The visitors______ here.
a)reading; b) read; c)are reading;
2) Diana isn’t hard-working. She often ______ University classes.
a)misses; b) miss; c) is missing;
3) We ______ do any tests last Monday.
a) doesn’t; b)don’t; c)didn’t;
4) When his colleague from Spain called, he _____ an important meeting.
a) has; b) is having; c) was having;
5) The Internet ______ the main source of information nowadays.
a) became; b) has become; c) becomes;
6) I______ English for 5 years.
a)am learning; b)learn; c) have been learning;
7) My friends ________ soon, I need to finish my homework.
a) are coming; b) come; c)came;
8) I am really lucky, I_______ some reliable information for my presentation.
a) found; b) find; c) have found;
9) Jane ______an article when her friends called and invited her to the party.
a) wrote; b) was writing; c) has written;
10) Students _______part in the scientific conference every April.
a) take; b) are taking; c) have taken;
Task 2. Vocabulary. Read and complete the sentences with a new word from the word on the right:
| 1) Most libraries also offer _______ books as well as printed ones. | DOWNLOAD |
| 2) Library visitors can ask any questions at the ______ desk. | REFER |
| 3) _____ on technology makes us being isolated from the rest of the world. | DEPEND |
| 4) Encyclopedias are______ of short, factual entries often written by different scientists. | COLLECT |
| 5) Technological advances have affected every sphere of our life making it_______ to organize work, leisure and even human relations without technology. | POSSIBLE |
Task 3. Reading. Read the text and put letters A (Encyclopedias), B (The Web), C (A database), D (Newspapers), and E (Books) opposite the type of information in the table:
Information can come from virtually anywhere — media, blogs, personal experiences, books, journal and magazine articles, expert opinions, encyclopedias, and web pages. Encyclopedias are collections of short, factual entries often written by different contributors who are knowledgeable about the topic. General encyclopedias provide concise overviews on a wide variety of topics. Subject encyclopedias contain in-depth entries focusing on one field of study. Books cover virtually any topic, fact or fiction. For research purposes, you will probably be looking for books that synthesize all the information on one topic to support a particular argument or thesis. The Web allows you to access most types of information on the Internet through a browser. One of the main features of the Web is the ability to quickly link to other related information. The Web contains information beyond plain text, including sounds, images, and video. The important thing to do when using information on the Internet is to know how to evaluate it! A database contains citations of articles in magazines, journals, and newspapers. They may also contain citations to podcasts, blogs, videos, and other media types. Some databases contain abstracts or brief summaries of the articles, while other databases contain complete, full-text articles. A newspaper is a collection of articles about current events usually published daily. Since there is at least one in every city, it is a great source for local information.
| Type of information | Source of information |
| 1) videos | |
| 2) overviews | |
| 3) articles | |
| 4) short, factual entries | |
| 5)images | |
| 6) brief summaries of the articles | |
| 7) citations to podcasts | |
| 8) articles about current events | |
| 9) fiction | |
| 10) citations of articles |
EVALUATION FORM
Scores you can gain for:
| Exercise | 1 | 2 | 3 | Total |
| Maximum | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15 |
| Your scores |
Grammar Reference
1. Present Simple the verb ‘to be’
Глагол to be означает "быть/находиться". Это начальная форма, инфинитив. Этот глагол изменяется по лицам и числам, и каждое лицо/число имеет свою форму:
To be
Краткие формы/сокращения
Краткие формы возникают
· при слиянии глагола (его части) с существительным (местоимением), которое обозначает субъекта (совершающего действие);
· при слиянии глаголов с отрицательной частицей not
| I + am = I'm | Am + Not не сливаются |
| He/She/It + Is = He's/She's/It's | Is + Not = Isn't |
| We/You/They + Are = We're/You're/They're | Are + Not = Aren't |
Утвердительная форма
| I am from London. = I'm from London. Я из Лондона. | We are from London = We're from London. Мы из Лондона. |
| You are from London = You're from London Ты/Вы из Лондона. | They are from London = They're from London. |
| He/She is from London. = He/She's from London. Он/Она из Лондона | |
| It is from London. = It's from London. Это из Лондона |
Отрицательная форма
| I am not from London. = I'm not from London. Я не из Лондона. | We are not from London = We aren't from London. Мы не из Лондона. |
| You are not from London = You aren't from London Ты/Вы не из Лондона. | They are not from London = They aren't from London. |
| He/She is not from London. = He/She isn't from London. Он/Она не из Лондона | |
| It is not from London. = It isn't from London. Это не из Лондона |
Word Order
Предложение - это сочетание слов, выражающее законченную мысль.
The sun rises in the east. Солнце всходит на востоке.
Члены предложения делятся на главные и второстепенные. Главные члены предложения - подлежащее и сказуемое. Второстепенные члены предложения - дополнение, определение, обстоятельство.
По составу предложения бывают простыми или сложными.
Структура английского простого повествовательного распространённого предложения следующая:
| подлежащее | сказуемое | дополнения обстоятельства |
Порядок слов в английском языке является основным средством различения членов предложения. Порядок слов английского повествовательного предложения - прямой, фиксированный: подлежащее, сказуемое, дополнение.
I study English every day. Я изучаю английский язык каждый день.
Types of Questions
Существуют три основных типа вопросов: общие вопросы, специальные вопросы и вопросы к подлежащему.
Общий вопрос - это вопрос ко всему предложению, и на него можно кратко ответить Yes / no (да / нет). Если вопрос задаётся к какому-либо члену предложения, кроме подлежащего, то это специальный вопрос. Кратким ответом на него будет любое слово из предложения, кроме подлежащего.
Если вопрос задаётся к подлежащему или его определению, то это так называемый "вопрос к подлежащему". Ответом на него будет либо само подлежащее, либо определение к подлежащему.
The passanger ship crosses the Atlantic Ocean.
What crosses the Atlantic Ocean? Что пересекает Атлантический океан ? - Корабль .
What ship crosses the Atlantic Ocean? Какой корабль пересекает Атлантический океан ? - Пассажирский .
Структурно эти типы вопросов различаются порядком слов в них.
Употребление
Обозначает постоянное повторяющееся, обычное действие, какой-либо факт или общеизвестную истину.
Образование
We live in St.Petersburg. The Earth rotates round its axis. I leave home at 8 every day.
Present Simple no форме совпадает с инфинитивом глагола (без частицы to) во всех лицах, кроме 3-го лица ед. ч., принимающего окончание -s (-es).
Утвердительная форма
Отрицательная форма
do not = don't
does not = doesn't
Present Continuous
Употребление
Настоящее продолженное время (Present Continuous) обозначает действие, происходящее в настоящий момент; действие, представляющее собой непрерывный процесс; будущее действие, если оно запланировано.
He is watching TV now.
The Earth is moving.
They are spending next winter in Spain.
Некоторые глаголы не употребляются в Continuous. Это глаголы обозначающие чувственное восприятие (to see, to hear), умственную деятельность (to know, to believe, to remember, to understand); желания, чувства (to want, to wish, to like, to love, to dislike, to hate).
Образование
Настоящее продолженное время (Present Continuous) образуется при помощи глагола to be в Present Indefinite и -ing формы смыслового глагола.
Утвердительная форма
Отрицательная форма
I am = I'm
He is = He's
We are = We're
is not = isn't
are not = aren't
Past Simple
Употребление
Обозначает действие, произошедшее в прошлом; последовательно произошедшие в прошлом действия; повторяющиеся действия в прошлом.
Образование
Past Indefinite правильных глаголов образуется прибавлением суффикса -ed к основе глагола. Форме Past Indefinite неправильных глаголов соответствует II форма глагола в соответствующих глагольных рядах, приводимых в специальных таблицах (см. таблицы неправильных глаголов).
We went to the cinema yesterday. He arrived in London last year.
She came up to the window and opened it.
Утвердительная форма
Отрицательная форма
Вопросительная форма
did not = didn't
Past Continuous
Употребление
Прошедшее продолженное время (Past Continuous) обозначает действие, происходившее в определённый момент в прошлом, который обозначен либо обстоятельством времени, либо другим действием в прошлом. При этом ни начало, ни конец длительного действия неизвестны. Подчёркивается сам процесс действия, его продолжительность.
| I was writing a letter to my friend | … at 5 o'clock yesterday. … from 5 to 6 on Sunday. … when my brother came. … while my mother was cooking dinner. |
Образование
Прошедшее продолженное время (Past Continuous) образуется при помощи глагола to be в Past Indefinite и -ing формы смыслового глагола.
Утвердительная форма
was not = wasn't
were not = weren't
Present Perfect
Употребление
1. Для выражения действия, завершившегося к моменту речи. Время действия не указывается, важен сам факт совершения действия к настоящему моменту или его результат.
She has read this book. Она прочитала эту книгу. (Действие завершено к моменту речи.)
В этом значении Present Perfect часто употребляется с наречиями just - только что, already - уже, yet - ещё, lately - недавно, of late - в последнее время, recently - недавно.
The mail has just come. Почта только что пришла.
He has seen many films lately. В последнее время он посмотрел много фильмов.
2. Для выражения действия, которое завершилось, но тот период, в котором оно происходило, ещё продолжается и может быть обозначен обстоятельствами времени today - сегодня, this week - на этой неделе, this month - в этом месяце, this century - в нашем веке и др.
I have written a letter this morning. Я написал письмо сегодня утром.
3. Для выражения действия, которое началось в прошлом и продолжается до настоящего времени.
I have known him all my life. Я знаю его всю жизнь.
I have known him for 2 years. Я знаю его 2 года.
He has not seen his parents since January. Он не видел своих родителей с января.
4. Present Perfect может употребляться с наречиями always - всегда, often - часто, seldom - редко, ever - когда-нибудь, never - никогда.
She has never been to London. Она никогда не была в Лондоне.
Have you ever been to Moscow? Вы когда-нибудь были в Москве?
Образование
Present Perfect образуется при помощи глагола to have в Present Indefinite и Participle II (Причастия II) смыслового глагола.
Утвердительная форма
Отрицательная форма
I have = I've
He has = He's
I have not = I haven't
He has not = He hasn't
Present Perfect Continuous
Употребление
Present Perfect Continuous употребляется для выражения длительного действия, которое началось в прошлом и еще совершается в настоящее время. При употреблении Present Perfect Continuous в данном значении всегда указан период, в течение которого совершается действие. Для обозначения времени используются обстоятельства for (в течение) и since (с тех пор, как; с):
I've been working for the same company for twelve years. - Я работаю в одной и той же компании 12 лет .
Образование
Present Perfect Continuous образуется при помощи глагола to have в Present Indefinite + been и Participle I (Причастия I) смыслового глагола.
Утвердительная форма
Отрицательная форма
Российской Федерации
Федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение
высшего образования
«ЮЖНЫЙ ФЕДЕРАЛЬНЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ»
Н.А. Беляева, Л.А. Недосека, И.И. Скнарина

Ростов-на-Дону
2016
Учебное пособие разработано преподавателями кафедры английского языка естественных факультетов Института филологии, журналистики и межкультурной коммуникации ЮФУ Беляевой Н.А., Недосека Л.А., Скнариной И.И.
Ответственный рецензент – канд филос. наук, доцент кафедры английского языка естественных факультетов Института филологии, журналистики и межкультурной коммуникации ЮФУ Белоусова М.М.
Печатается в соответствии с решением кафедры английского языка естественных факультетов ЮФУ, протокол № 2 от 29 сентября 2016 года.
Методическая записка
Данное учебное пособие предназначено для студентов 1 курса бакалавриата с низким уровнем владения английским языком (А1-А2 по международной шкале) естественно - научного направления подготовки. Целью учебного пособия является развитие навыков устной речи по темам академического обучения.
Развитие навыков устной речи осуществляется на основе упражнений, обучающих умению высказывать свое мнение, направленных на развитие коммуникативных навыков общения на основе предложенной тематики, а также навыков публичной речи – при подготовке мини-презентаций по предложенным темам на английском языке (см рубрику Project Work ).
Данное учебное пособие предлагает следующие темы: «My Personal Profile», «English and Me”, «Universities», «Information Age».
Учебное пособие состоит из 4 модулей. Каждый модуль включает в себя разделы (Units) с текстом, а также комплексом заданий, направленных на развитие навыков грамматики, чтения и говорения на английском языке. Учебные модули содержат следующие рубрики:
1. Having a talk – является неким введением в предложенную тему и представлен вопросами и упражнениями, которые способствует снятию лексических трудностей, а также повышению интереса студентов к изучаемому материалу ;
2. Reading – включает текст и задания на извлечение основной информации, понимание структуры и организации содержания текста;
3. Comprehension check – включает вопросы на проверку уровня понимания текста;
4. Vocabulary – акцентирует внимание студентов на ключевых словах и словосочетаниях по тематике модуля для последующего их использования в практике устной и письменной речи;
5. Grammar – формирует навыки употребления определенных грамматических явлений на английском языке и их перевода в предложенных ситуациях.
6. Video / Listening - содержит видео/аудио сюжеты и задания на формирование навыков аудирования и говорения на английском языке.
7. Writing – направлен на развитие определенных навыков письменной речи.
8. Speaking - включает задания на развитие навыков говорения на английском языке.
9. For my language portfolio – способствует формированию языкового портфеля студента, который предлагает упражнения на развитие навыков и говорении, и письма.
Каждый модуль завершается разделом Progress Test (тест рубежного контроля), который включает 3 задания и Evaluation form. Выполнение заданий рассчитывается в баллах по шкале; максимальное количество баллов - 15.
В учебном пособии содержится Грамматический справочник ( Grammar Reference ), в котором содержатся основные сведения по грамматике английского языка.
Учебное пособие разработано с использованием аутентичных материалов (адаптированных для уровня A 1-2), основными источниками которых является британские и американские издания, интернет, энциклопедии и словари. Новизна, информативность и соответствие информации профессиональным потребностям студентов были основными критериями отбора материалов для данного пособия.
Модули представляют собой самостоятельные разделы, что позволяет преподавателям и студентам соблюдать последовательность, в которой они представлены в пособии, или выбирать для изучения те модули, которые представляют особый интерес. Настоящее учебное пособие рекомендовано к использованию для аудиторной работы.
 MY PERSONAL
MY PERSONAL
PROFILE

Learning objectives:
ü To talk about yourself;
ü To revisit to BE, Present Simple and the word order of an English sentence;
ü To expand vocabulary on the topics “ Family”, “Hobbies” and “People”, “My home place”;
ü To practice dialogue speech on the topics;
ü To develop public speaking skills.
 Unit 1 Meeting people
Unit 1 Meeting people
| Having a talk |
Ex.1 Work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions:
1) What is your name?
2) What is your surname?
3) How old are you?
4) Where are you from?
5) What are you?
6) What are your hobbies and interests?
Ex.2 Read the questions and find the equivalents to some from Ex.1:
| A) What’s your job? B) What do you do? C) Where do you come from? D) What’s your first name? E) What do you do in free (spare) time? F) Who are you? G) What’s your last name? |
1) D ; 2)___; 3)___; 4)___; 5)___; 6)____.
| Grammar |
Study the picture to revisit to be and explain it in Russian:

***Grammar Reference
Present Simple the verb ‘to be’
Ex.3 Read and complete the sentences with: am, is, are
1) My family is big.
2) We ___ friendly family.
3) My father ___ an engineer.
4) He ____ a tall man.
5) My parents____ nice people.
6) The University I study at___ big.
7) It ____ not far from my place.
8) The subjects ____ interesting.
9) I ___ fond of Sciences.
10) The University teachers____ competent.
Ex.4 Make the above sentences negative. Then write questions according to the model.
Model: 1) My family is big. My family isn’t big. Is your family big?
2)We are friendly family. ______________. _____________?
Ex.5 Read and complete the dialogue with one word:
| Student A: | Student B: |
| - Hello! What’ s your_____? | |
| - Hello! I ___ Mary. What’s your name? | |
| - My name is Alex. Nice ___ meet you. | |
| - Nice to_____ you too. What’s your ___ name? | |
| - Brown. And what’s your____? | |
| - Ivanova. Where are you ____? | |
| - I’m from Great Britain, London. And _____ are you from? | |
| - I’m from Russia. Rostov-on-Don. What ____ you? | |
| - I’m a student. I study Science. Are you a______ too? | |
| - | - Yes, I am. I_____ Liberal arts. |
| - Thanks ____ the talk. It was nice meeting you. | - |
| - | - Thank you ____ much too. See you. |
| - See you. Bye! - | - Bye! |
Дата: 2019-07-24, просмотров: 671.