After its 200th birthday the United States of America still holds the leading position in the western world. A country that inspired many appelations - "Land of Opportunity," "Melting Pot," "God's Country," is still referred to us as a land of superlatives -"the richest," "the greatest," "the most."
What makes the USA the leader of the western world is its economic, political and military dominance over other countries.
The United States lies in the central part of the North American Continent between the two oceans: the Atlantic Ocean to the East and the Pacific Ocean to the West. Friendly Canada to the north and friendly Mexico to the south are the only countries bordering it.
The USA consists of three separate parts. They are the Hawaiian Islands, situated in the central part of the North American continent of the Pacific Ocean, Alaska separated by the Canadian territory and the rest major part of the USA. The states differ very much in size, population and economic development.
There are many big cities and towns in the USA: New York, San Francisco, Washington, Chicago, Los Angeles are the biggest of them.
The United States of America is a parlamentary republic. The government is divided into three branches: legislative (the US Congress), executive (the President and his Administration) and judicial (the US Supreme Court).
There are two main political parties in the USA: the Democratic (symbolized by a "donkey") and the Republican (its symbol is an "elephant"). The US President is both head of state and government. He is elected for a four-year term. Presidential elections are held every leap year on first Tuesday after first Monday in November. The President is assisted by Secretaries who are the heads of the executive departments. The Supreme Court consists of Chief Justice and eight Associate Justices who are appointed for life. It is supposed to decide whether a law of the Congress or an executive order of the President is constitutional or not.
The form of US government is based on the Constitution of September 17, 1787, adopted after the War of Independence. In December 1791, the Congress adopted ten amendments to the Constitution, known as the Bill of Rights. The latter enumerated what the government controlled by the oligarchy was not going to be allowed to do, which was, of couse, an important democratic gain for people.
The Congress of the United States is composed of two houses, the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate represents the states and the House represents the population according to its distribution among the states. All states have electoral requirements of the same nature. First of all they are residence requirements.
Through its power over the purse, the US Congress can control much that relates to foreign policy, also it is a governmental body that determines taxation.
Each of the fifty states of the USA has a constitution patterned after the federal Constitution, with its divisions of power: legislative, executive, and judicial.
The Presidency means not only a man: means an institution - the "executive branch" of the government.
Unit 12
Grammar: 1. Герундий.
2. Герундиальные обороты.
I. Language Practice
1. Practise the fluent reading and correct intonation:
— `Can you re`duce your `prices at `least by ø 3 per `cent?
— ø Well, I don’t `think we ö can, the `world ø `prices have `recently `gone ö `up, you ö know. ø Besides, we’ve `made some ø modifi`cations and improved the ö design.
— That’s ö `true, We’ve ö `seen that, but we’d `like you to reduce the ø `prices be`cause we are `going to `place a `very `big ö`order.
— Will a `two per `cent dis`count off the `price be ø acceptable?
— That’s `just what we were `going to ö ask you about.
— ö Settled.
2. Listen to the speaker; read and memorize the following words and phrases:
1. money supply - денежная масса
2. advice - сîâåò, консультация
3. lender - кредитор
4. to rediscount - переучитывать
5. discount rate - учетная ставка
6. to withdraw - изымать
7. currency - деньги, валюта
8. account - счет
9. deposit - вклад
10. for collection - на инкассо (денежный сбор)
11. to transfer - перевод, перечисление
12. the Treasury - казначейство
13. to issue - выпускать
14. to redeem - погашать
15. securities - ценные бумаги, акции
Text. The Federal Reserve System
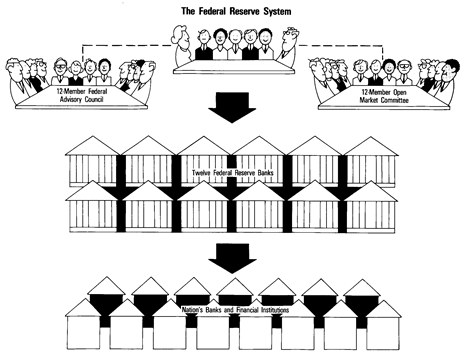
The Federal Reserve System, or the Fed as it is often called, was created by an act of Congress in 1913. The Fed, the nation’s central bank, is made up of a Board of Governors, 12 district banks, and two committees: the Open Market Committee and the Federal Advisory Council.
Board of Governors. The Board of Governors establishes policies for the system. It consists of seven persons appointed by the President for 14-year terms.
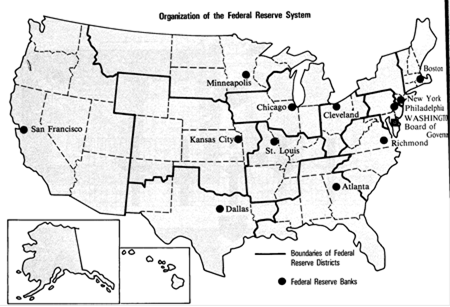
Twelve District Banks. The Federal Reserve System is built around 12 geographic districts. District Federal Reserve banks supervise banking in each of these areas.
Open Market Committee. The Open Market Committee is made up of the seven members of the Board of Governors and presidents of five of the district banks. Its primary responsibility is to regulate the nation’s money supply.
Federal Advisory Council. The Federal Advisory Council does just that: it offers advice on the nation’s financial problems. It is comprised of 12 prominent commercial bankers, one selected from each district.
As the nation’s central bank, the Federal Reserve System has four separate and distinct roles that profoundly affect the economy:
· Provides banking services for financial institutions;
· Serves as federal government’s bank;
· Supervises member banks;
· Manages the nation’s supply of money and credit.
Provides banking services for financial institutions. The Fed provides the kinds of services for banks that banks provide for public. The Federal Reserve Banks hold the reserves of the member banks, i.e. the commercial banks which are members of the Federal Reserve System. The FR Banks supply the member banks with currency if necessary and act to them as lenders by rediscounting bills. The Board determines the reserve requirements of the commercial banks. The Board too really determines discount rates. The Board discount rate corresponds in nature to the English Bank rate, though the Federal Reserve Banks do not always have the same discount rate.
Hold deposit accounts. Banks keep their reserves and other funds on deposit in a kind of checking account at their district bank.
Make loans. Financial institutions, like most businesses must borrow from time to time. When this happens they can go to the Fed for a loan.
Transfer funds. The Federal Reserve System’s wire services and computers enable local banks to transfer funds from one to the other almost instantaneously.
Banker to the Federal Government. The Federal Reserve banks function as the federal government’s banker. They maintain the Treasury Department’s «checking account» and issue and redeem government bonds and other securities.
Supervises and regulates the nation’s banking system. The Federal Reserve System, along with a number of other agencies, is charged with establishing the rules of behaviour for the banking system in general, and its individual institutions in particular. The purpose of these rules is to ensure the safety and soundness of the agencies that handle our funds.
Managers the supply of money and credit. One of the principal responsibilities of the Fed is to see what the nation needs. In addition to the Controller of the Currency and the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation), the Federal Reserve supervises nationally chartered and state-chartered banks and state banking agencies.
All national banks must be members of the Federal Reserve System. Incorporated state banks including commercial banks, mutual savings banks, trust companies, and industrial banks may also join the System.
Incorporated banks are those which have a charter from the state to act as an individual. Mutual savings banks are savings banks owned by their depositors. Industrial banks make loans for the purchase or manufacture of industrial products.
II. Exercises on the Text:
3. Give Russian equivalents to:
the nation’s central bank; Board of Governors; the Open Market Committee; the Federal Advisory Council; for 14-year terms; supervise banking; is made up of the seven members; the nation’s money supply; it offers advice; prominent commercial bankers; profoundly affect; to act as lenders; corresponding in nature; banks draw currency; the checks are credited to the deposits’ accounts; are presented for collection; from time to time; wire services; almost instantaneously; government bond and other securities; establishing the rules of behavior; in general; in particular; the safety and soundness; the amount of money and credit in circulation; nationally charted; state-charted; incorporated state banks; mutual savings banks; trust companies.
4. Answer the following questions:
1. What is the Fed? 2. When was the Fed created? 3. What is the structure of the Fed? 4. What are the main functions of the Board of Governors? 5. How many Reserve Districts are there in the U.S.A? 6. What is the primary responsibility of the Open Market Committee? 7. Does the Federal Advisory Council offer advice on the nation’s financial problems? 8. What are the main roles of the Fed? 9. How does the FR Banks work with the member banks? 10. What are presented to the district banks for collection? 11. What are the ways at transferring funds? 12. What does the FR Banks issue and redeem? 13. How does the Fed supervise and regulate the Nation’s Banking System? 14. What financial institutions may be members of the Fed?
5. Sum up what the text says about:
the structure of the Fed;
what the Fed does;
incorporated state banks;
mutual savings banks;
industrial banks;
6. Translate into Russian paying attention to other bank services:
Other Bank Services
Trusts. A trust arrangement exists when a bank provides safekeeping and management of funds for individuals, estates or institutions such as pension funds. The bank's job is to administer the money entrusted to it wisely and for the benefit of the owner. The bank receives a fee for managing these funds.
Currency Exchange Banks can buy or sell foreign currencies for their own benefit or for their clients. Importers, exporters and travelers are major users of these services. Even domestic travelers may purchase travelers' checks issued by banks.
Safekeeping. Many banks rent safety deposit boxes in their vaults to persons seeking a safe and secure place for their valuables.
Credit Cards. Some banks derive significant revenues from operating bankcard programs. There is usually an annual fee to use the credit card, and the consumer pays interest on the unpaid balance. Merchants pay a fee to the bank as well.
Brokerage. In very recent times (and still on a highly limited basis) some banks have entered the brokerage business. As brokers they buy and sell stocks and bonds for their clients.
Insurance. In a number of states certain banks can sell their customers life insurance policies.
Letters of Credit. Banks may aid commerce by writing letters of credit. In these documents, the bank guarantees one party (such as a seller) that payment will be made if certain conditions are met (such as the delivery of merchandise). Letters of credit are common when goods are bought or sold abroad. There is a fee for providing this letter of credit.
Investments. Banks are permitted to buy U.S. government bonds for their own accounts. Banks may make money in trading such bonds and from the interest paid by the government to the holders of such securities.
Underwriting. When companies (or even units of government) raise money by issuing shares of stocks or by the sale of bonds, they use the services of certain financial specialists. Some very large banks provide such assistance, as do major brokerage companies.
Consulting. A growing business for banks is to give advice to other businesses. Especially significant in recent years is the assistance provided to firms involved in corporate mergers and takeovers.
III. Grammar Exercises
Forms of the Gerund.
| Active | Passive | |
| Indefinite | asking (V-ing) спрашивать | being asked (being + V3) быть спрашиваемым |
| Perfect | having asked (having + V3) уже спросить | having been asked (having been + V3) уже быть спрошенным |
Дата: 2019-07-31, просмотров: 380.