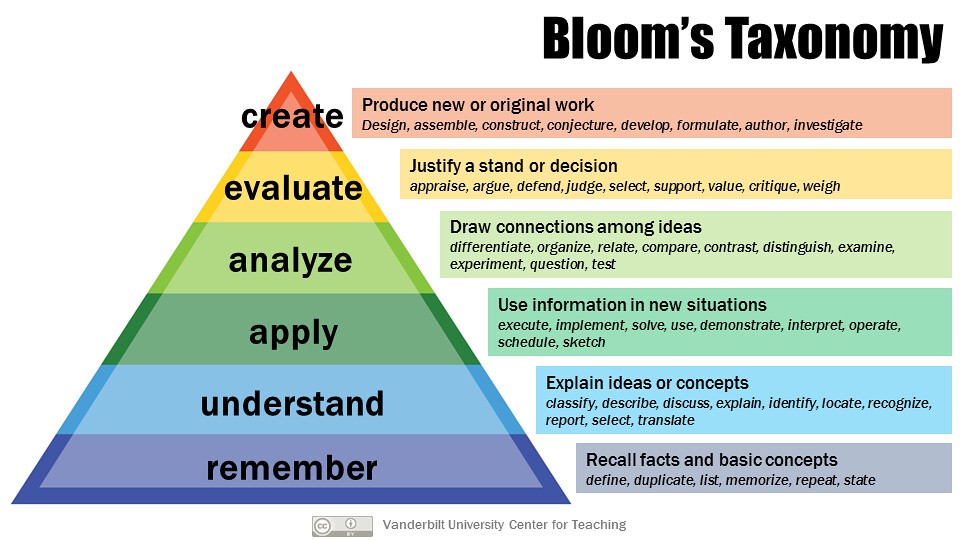
Here are the authors’ brief explanations of these main categories in from the appendix of Taxonomy of Educational Objectives :
- Knowledge “involves the recall of specifics and universals, the recall of methods and processes, or the recall of a pattern, structure, or setting.”
- Comprehension “refers to a type of understanding or apprehension such that the individual knows what is being communicated and can make use of the material or idea being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implications.”
- Application refers to the “use of abstractions in particular and concrete situations.”
- Analysis represents the “breakdown of a communication into its constituent elements or parts such that the relative hierarchy of ideas is made clear and/or the relations between ideas expressed are made explicit.”
- Synthesis involves the “putting together of elements and parts so as to form a whole.”
- Evaluation engenders “judgments about the value of material and methods for given purposes.”
Explain the influence of social constructivism on teaching at HEI’s (the Zone of Proximal Development, the role of peers, collaborative learning).
Constructivism can be seen as a major theory of learning, and in a broader sense as a philosophy of education, used as a general title to classify several theories. There is then a need to define what we mean by constructivism, in order to adequately found our work in education, and more specifically in the field of education technology.
The concept, zone of proximal development was developed by Soviet psychologist and social constructivist Lev Vygotsky (1896 – 1934).
The zone of proximal development (ZPD) has been defined as: "the distance between the actual developmental level as determined by independent problem solving and the level of potential development as determined through problem-solving under adult guidance, or in collaboration with more capable peers" (Vygotsky, 1978, p. 86).
Vygotsky believed that when a student is in the zone of proximal development for a particular task, providing the appropriate assistance will give the student enough of a "boost" to achieve the task.
To assist a person to move throught the zone of proximal development, educators are encouraged to focus on three important components which aid the learning process:
- The presence of someone with knowledge and skills beyond that of the learner (a more knowledgeable other).
- Social interactions with a skillful tutor that allow the learner to observe and practice their skills.
- Scaffolding, or supportive activities provided by the educator, or more competent peer, to support the student as he or she is led through the ZPD.
More Knowledgeable Other
The more knowledgeable other (MKO) is somewhat self-explanatory; it refers to someone who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept.
Although the implication is that the MKO is a teacher or an older adult, this is not necessarily the case. Many times, a child's peers or an adult's children may be the individuals with more knowledge or experience.
Social Interaction
According to Vygotsky (1978), much important learning by the child occurs through social interaction with a skillful tutor. The tutor may model behaviors and/or provide verbal instructions for the child. Vygotsky refers to this as cooperative or collaborative dialogue.
The child seeks to understand the actions or instructions provided by the tutor (often the parent or teacher) then internalizes the information, using it to guide or regulate their own performance.
Дата: 2019-05-29, просмотров: 335.