The Copenhagen climate conference COP15 resulted in a document called the Copenhagen Accord. It was hammered out by a small group of countries - including the world's two biggest greenhouse gas polluters, China and the US. The conference as a whole did not adopt the accord, but voted to "take note" of it.
Was the summit a success?
This depends on your point of view. On the positive side, the Copenhagen Accord, for the first time, unites the US, China and other major developing countries in an effort to curb global greenhouse gas emissions. The Kyoto Protocol did not achieve this - it imposed no obligations on developing countries to restrain the growth of their emissions, and the US never acceded to it. The accord also says developed countries will aim to mobilise $100bn per year by 2020, to address the needs of developing countries.
On the other hand, the summit did not result in a legally binding deal or any commitment to reach one in future. The accord calls on countries to state what they will do to curb greenhouse gas emissions, but these will not be legally binding commitments. Furthermore, there is no global target for emissions reductions by 2050 and the accord is vague as to how its goals - such as the $100bn of funds annually for developing countries - will be achieved.
What are the key points of the Copenhagen Accord?
• A commitment "to reduce global emissions so as to hold the increase in global temperature below 2C" and to achieve "the peaking of global and national emissions as soon as possible"
• Developed countries must make commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and developing countries must report their plans to curb greenhouse gas emissions to the UN by 31 January 2010
• New and additional resources "approaching $30bn" will be channelled to poorer nations over the period 2010-12, with an annual sum of $100bn envisaged by 2020
• A Copenhagen Green Climate Fund will be established under the UN convention on climate change, to direct some of this money to climate-related projects in developing countries
• Projects to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries will be subject to international monitoring if they are internationally funded
• Programmes to provide developing countries with financial incentives to preserve forests - REDD and REDD-plus - will be established immediately
• Implementation of the accord will be reviewed in 2015 and an assessment will be made of whether the goal of keeping global temperature rise within 2C needs to be strengthened to 1.5C
Which countries backed the accord?
The essential points of the deal were brokered by US President Barack Obama with representatives of China, India, Brazil and South Africa. Mr Obama also consulted with the leaders of France, Germany and the UK. Most countries at the conference gave it their support, but some countries were resolutely opposed, including Venezuela, Bolivia, Ecuador and Cuba.
Why did the Copenhagen summit take place at all?
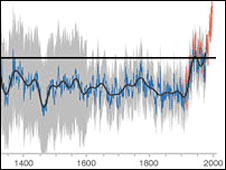
The majority of the world's governments believe that climate change poses a threat to human society and to the natural world.

| 
 A brief history of climate change
A brief history of climate change
| Successive scientific reports, notably those from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), have come to ever firmer conclusions about humankind's influence on the modern-day climate, and about the impacts of rising temperatures.
In 2007, at the UN climate talks held in Bali, governments agreed to start work on a new global agreement.
The Copenhagen talks marked the end of that two-year period. |